Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 9 : Tissue and Tissue System
Anatomy and Primary Structure of a Dicot Leaf-sunflower Leaf
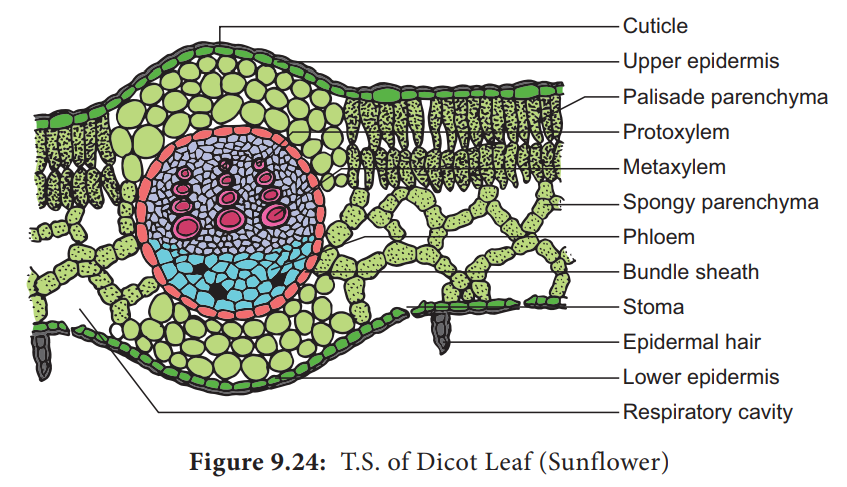
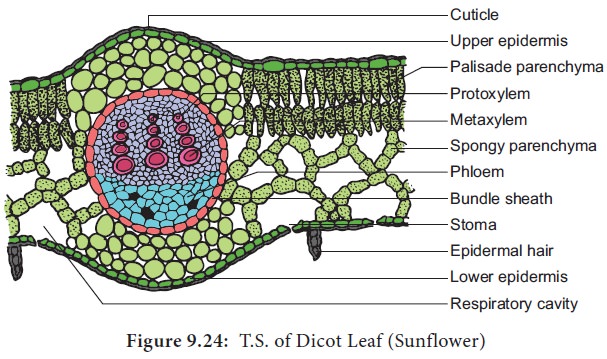
Anatomy of a Dicot Leaf-sunflower
Leaf
Internal
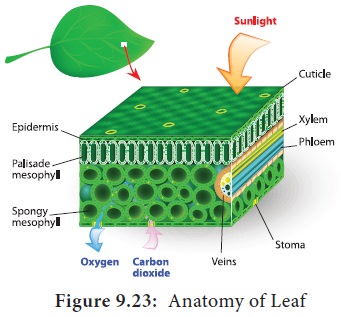
structure of dictoyledonous leaves reveal epidermis, Mesophyll and vascular
tissues.
Epidermis
This leaf
is generally dorsiventral. It has
upper and lower epidermis. The epidermis is usually made up of a single layer
of cells that are closely packed. The cuticle on the upper epidermis is thicker
than that of lower epidermis. The minute openings found on the epidermis are
called stomata. Stomata are more in
number on the lower epidermis than on the upper epidermis. A stomata is
surrounded by a pair of bean shaped
cells called guard cells.
![]()
![]()
Each
stoma internally opens into an air chamber. These guard cells contain
chloroplasts, whereas other epidermal cells do not contain chloroplasts. The
main function of the epidermis is to give protection to the inner tissue called
mesosphyll. The cuticle helps to
check transpiration. Stomata are
used for transpiration and gas exchange.
Mesophyll
The
entire tissue between the upper and lower epidermis is called the mesophyll (GK meso = in the middle, phyllome = leaf). There are
two regions in the mesophyll. They
are palisade parenchyma and spongy parenchyma. Palisade parenchyma cells are seen beneath the
upper epidermis. It consists of vertically elongated cylindrical cells in one
or more layers. These cells are compactly arranged and are generally without
intercellular spaces. Palisade parenchyma cells contain more chloroplasts than
the spongy parenchyma cells. The function of palisade parenchyma is photosynthesis. Spongy parenchyma lies
below the palisade parenchyma. Spongy cells are irregularly shaped. These cells
are very loosely arranged with numerous airspaces. As compared to palisade
cells, the spongy cells contain lesser number of chloroplasts. Spongy cells
facilitate the exchange of gases
with the help of air spaces. The air space that is found next to the stomata is
called respiratory cavity or substomatal
cavity.
Vascular Tissues
Vascular
tissues are present in the veins of leaf. Vascular bundles are conjoint, Collateral and closed. Xylem
is present towards the upper
epidermis, while the phloem towards the lower epidermis. Vascular bundles are
surrounded by a compact layer of parenchymatous cells called bundle sheath or border parenchyma.
Xylem
consists of metaxylem and protoxylem elements. Protoxylem is present towards
the upper epidermis,while the phloem consists of sieve tubes, companion cells
and phloem parenchyma. Phloem fibres are absent. Xylem consists of vessels and
xylem parenchyma. Tracheids and xylem fibres are absent.
Related Topics