Chapter: 11th Botany : Chapter 9 : Tissue and Tissue System
Anatomy and Primary Structure of Dicot stem - sunflower stem
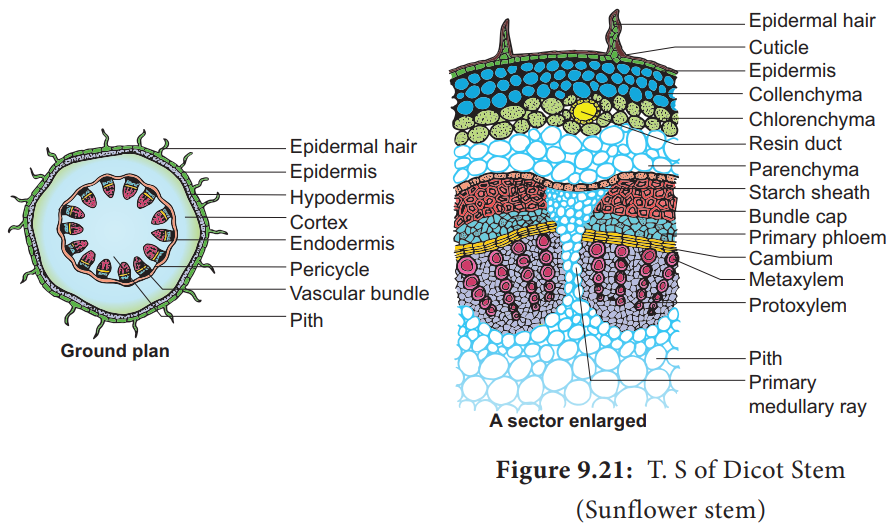
The
transverse section of the dicot stem [sunflower] shows the following plan of
arrangement of tissues from the periphery to the centre.
Epidermis
It is
protective in function and forms the outermost layer of the stem. It is a
single layer of parenchymatous rectangular cells. The cells are compactly
arranged without intercellular spaces. The outer walls of epidermal cells have
a layer called cuticle. The cuticle checks the transpiration. The cuticle is
made up of waxy substance known as cutin. Stomata may be present here and
there. Epidermal cells are living. Chloroplasts are usually absent. A large
number of multicellular hairs occur on the epidermis.
Cortex
Cortex
lies below the epidermis. The cortex is differentiated into three zones. Below
the epidermis, there are few layers of collenchyma cells. This zone is called hypodermis. It gives mechanical
strength of the Stem. These cells
are living and thickened at the corners.
Inner to
the hypodermis, a few layers of collenchyma cells are present. This zone is
called hypodermis. It gives mechanical strength to the stem. These cells are
living and thickened at the corners. Inner to the hypodermis, a few layers of
chlorenchyma cells are present with conspicuous intercellular spaces. This
region performs photosynthesis. Some resin ducts also occur here. The third
zone is made up of parenchyma cells. These cells store food materials. The
innermost layer of the cortex is called endodermis.
The cells of this layer are barrel shaped and arrange compactly without
intercellular spaces. Since starch grains are abundant in these cells, this
layer is also known a starch sheath.
This layer is morphologically homologous to the endodermis found in the root.
In most of the dicot stems, endodermis with casparian strips is not developed.
Stele
The
central part of the stem inner to the endodermis is known as stele. It consists of pericyle,
vascular bundles and pith. In dicot stem, vascular bundles are arranged in a
ring around the pith. This type of stele is called eustele.
Pericycle
Pericycle
is the layers of cells that occur between the endodermis and vascular bundles.
In the stem of sunflower (Helianthus),a
few layers of sclerenchyma cell
occur in patches outside the phloem in each vascular bundle. This patch of
sclerenchyma cell is called Bundle cap
or Hardbast. The bundle caps and the parenchyma cells between them
constitute the pericycle in the stem of sunflower.
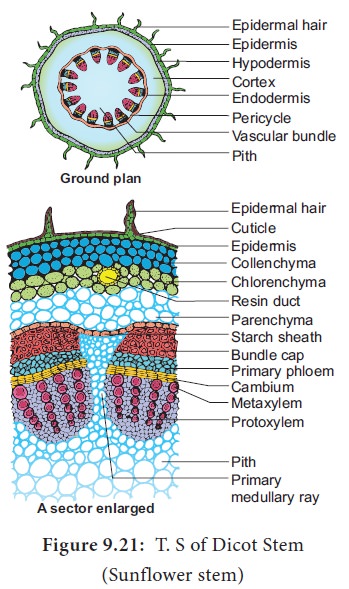
Vascular Bundles
The
vascular bundles consist of xylem, phloem and cambium. Xylem and phloem in the
stem occur together and form the vascular bundles. These vascular bundles are Wedge shaped. They are arranged in the
form of a ring. Each vascular bundle is conjoint,
collateral, open and endarch.
Phloem
Primary
phloem lies towards the periphery. It consists of protophloem and metaphloem. Phloem
consists of sieve tubes, companion
cells and phloem parenchyma. Phloem fibres are absent in the primary phloem.
Phloem conducts organic food materials from the leaves to other parts of the
plant body.
Cambium
Cambium
consists of brick shaped and thin
walled meristematic cells. It is one to four layers in thickness. These cells
are capable of forming new cells during secondary
growth.
Xylem
Xylem
consists of xylem fibres, xylem parrenchyma vessels and tracheids. Vessels are
thick walled and arranged in a few rows.
Xylem
conducts water and minerals from the root to the other parts of the plant body.
Pith
The large
central portion of the stem is called pith.
It is composed of parenchyma cells with intercellular spaces. The pith is also
known as medulla. The pith extends
between the vascular bundles. These extensions of the pith between the vascular
bundles are called primary pith rays or primary medullary rays. Function of the
pith is storage of food.
Related Topics