Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Pharmacologic Management of Parkinsonism & Other Movement Disorders
Acetylcholine-Blocking Drugs
ACETYLCHOLINE-BLOCKING DRUGS
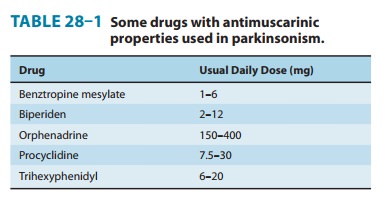
A number of centrally
acting antimuscarinic preparations are available that differ in their potency
and in their efficacy in differ-ent patients. Some of these drugs were
discussed. These agents may improve the tremor and rigidity of parkin-sonism
but have little effect on bradykinesia. Some of the more commonly used drugs
are listed in Table 28–1
Clinical Use
Treatment is started
with a low dose of one of the drugs in this category, the dosage gradually
being increased until benefit occurs or until adverse effects limit further
increments. If patients do not respond to one drug, a trial with another member
of the drug class is warranted and may be successful.
Adverse Effects
Antimuscarinic drugs
have a number of undesirable central ner-vous system and peripheral
effects and are poorly tolerated by the
elderly. Dyskinesias occur in rare cases. Acute sup-purative parotitis sometimes
occurs as a complication of dryness of the mouth.
If medication is to be
withdrawn, this should be accomplished gradually rather than abruptly to
prevent acute exacerbation of parkinsonism. For contraindications to the use of
antimuscarinic drugs.
Related Topics