Chapter: Microprocessor and Microcontroller
8085 Pin Description
8085 PIN DESCRIPTION
Properties:
·
It is a 8-bit microprocessor
·
Manufactured with N-MOS technology
·
40 pin IC package
·
It has 16-bit address bus and thus has 216
= 64 KB addressing capability.
·
Operate with 3 MHz single-phase clock
·
+5 V single power supply
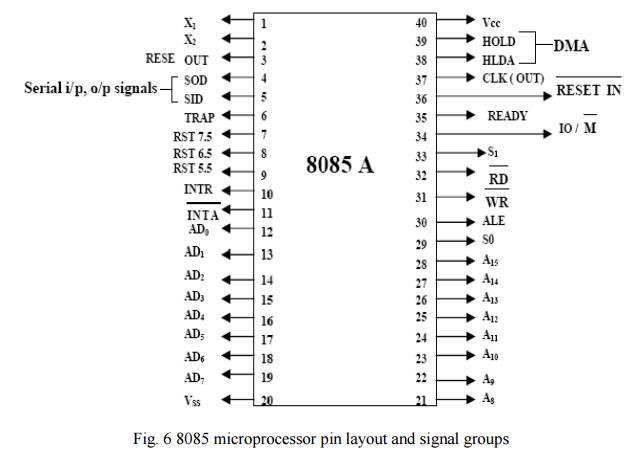
The logic
pin layout and signal groups of the 8085nmicroprocessor are shown in Fig. 6.
All the signals are classified into six groups:
·
Address bus
·
Data bus
·
Control & status signals
·
Power supply and frequency signals
·
Externally initiated signals
·
Serial I/O signals
Address
and Data Buses:
·
A8 – A15 (output, 3-state): Most significant eight
bits of memory addresses and the eight bits of the I/O addresses. These lines
enter into tri-state high impedance state during HOLD and HALT modes.
AD0 – AD7
(input/output, 3-state): Lower significant bits of memory addresses and the
eight bits of the I/O addresses during first clock cycle. Behaves as data bus
during third and fourth clock cycle. These lines enter into tri-state high
impedance state during HOLD and HALT modes.
Control
& Status Signals:

·
Power Supply & Clock Frequency:
·
Vcc: +5 V power supply
·
Vss: Ground reference
·
X1, X2: A crystal having frequency of 6 MHz is
connected at these two pins
·
CLK: Clock output
![]()
Externally
Initiated and Interrupt Signals:
· Bar(RESET IN) : When the signal
on this pin is low, the PC is set to 0, the buses are tri stated and the
processor is reset.
·
RESET OUT: This signal indicates that the processor is being reset. The
signal can be used to reset other devices.
·
READY: When this signal is low, the processor waits
for an integral number of clock cycles until it goes high.
·
HOLD: This signal indicates that a peripheral like
DMA (direct memory access) controller is requesting the use of address and data
bus.
·
HLDA: This signal acknowledges the HOLD request.
·
INTR: Interrupt request is a general-purpose
interrupt.
·
Bar(INTA) : This is used to acknowledge an
interrupt.
·
RST 7.5, RST 6.5, RST 5,5 – restart interrupt:
These are vectored interrupts and have highest priority than INTR interrupt.
·
TRAP: This is a non-maskable interrupt and has the
highest priority.
Serial
I/O Signals:
·
SID: Serial input signal. Bit on this line is
loaded to D7 bit of register A using RIM instruction.
·
SOD: Serial output signal. Output SOD is set or
reset by using SIM instruction.
Related Topics