Chapter: 11th 12th standard bio Biotany Plant Tree higher secondary school
Plant Cell Plastids - chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leucoplasts
Plastids
Plastids are the largest cytoplasmic organelles bounded by double membrane. These are found in most of the plant cells and in some photosynthetic protists. These are absent in prokaryotes and in animal cells. Plastids are of three types namely chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leucoplasts.
Chromoplasts
Chromoplasts are coloured plastids other than green. They are found in coloured parts of plants such as petals of the flower, pericarp of the fruits etc.
Leucoplasts
Leucoplasts are the colourless plastids. These colourless plastids are involved in the storage of carbothydrates, fats and oils and proteins. The plastids which store carbohydrates are called amyloplasts. The plastids storing fats and oils are called elaioplasts. The plastids storing protein are called proteinoplasts.
Chloroplast
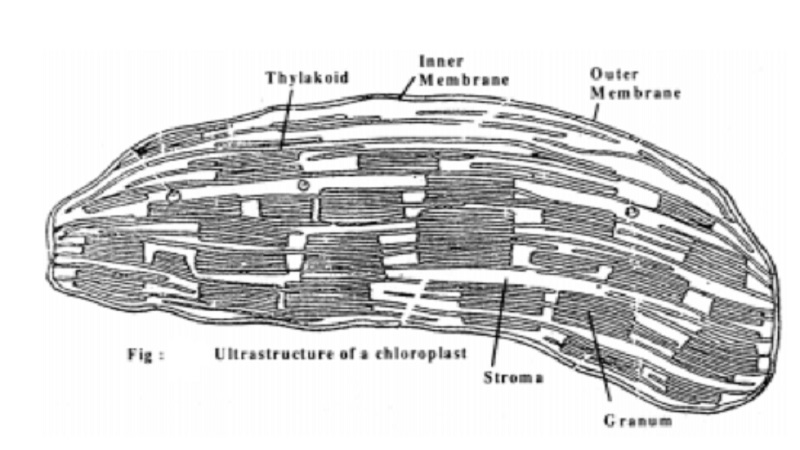
Chloroplasts can be as long as 10Am and are typically 0.5 - 2.0 Am thick, but they vary in size and shape in different cells, especially among the algae. Like mitochondrion, the chloroplast is surrounded by an outer and inner membrane. In addition to this, chloroplasts contain an internal system of extensive inter connected membrane-limited sacs called thylakoids which are flattened to form disks. These are often grouped in stakes of 20-50 thylakoids to from what are called grana and embedded in a matrix calledstroma.
Stroma, a semi fluid, colourless, colloidal complex contains DNA, RNA, ribiosomes and several enzymes. The DNA of chloroplast is circular. The ribosomes are of 70s type. The matrix of higher plant's chloroplasts may contain starch as storage product. Thylakoids may occur attached to the inner membrane of the chloroplast envelop.
About 40-100 grana may occur in a chloroplast. Many membranous tubules called stroma lamellae (intergranal thylakoids) interconnect thylakoids of different grana. Thylakoid membrane contains photosynthetic pigments.
The thylakoid membrane contains green pigments (Chlorophylls) and other pigments and enzymes that absorb light and generate ATP during photosynthesis. Part of this ATP is used by enzymes located in stroma to the convert CO2 into three carbon (3C) intermediates which are then exported to the cytosol and converted to sugars.
The molecular mechanism by which ATP is formed is very similar in mitochondria and chloroplasts. Chloroplasts and mitochondria have other features also in common. Both migrate often from place to place within cells and both contain their own DNA which code for some of the key organellar proteins. These proteins are synthesized in the ribosomes within the organelle. However, most of the proteins in each of these organelles are encoded in the nuclear DNA and are synthesized in the cytosol. These proteins are then incorporated into the organelles.
Related Topics