Banking - NABARD and its role in Agricultural credit | 12th Economics : Chapter 6 : Banking
Chapter: 12th Economics : Chapter 6 : Banking
NABARD and its role in Agricultural credit
NABARD and its role in Agricultural credit
Since its inception, RBI has shown keen interest in agricultural
credit and maintained a separate department for this purpose. RBI extended
short-term seasonal credit as well as medium-term and long-term credit to
agriculture through State level co-operative banks and Land Development banks.
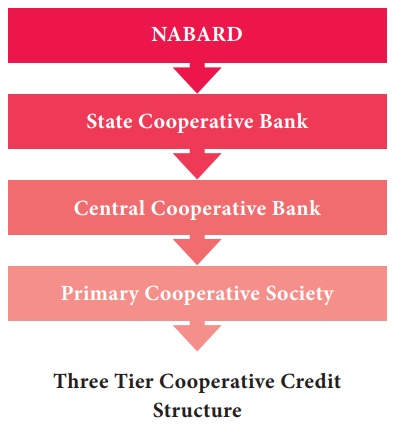
At the same time, RBI has also set up the Agricultural Refinance
Development Corporation (ARDC) to provide refinance support to the banks to
promote programmes of agricultural development, particularly those requiring
term credit. With the widening of the role of bank credit from “agricultural
development” to “rural development” the Government proposed to have a more
broad-based organization at the apex level to extend support and give guidance
to credit institutions in matters relating to the formulation and
implementation of rural development programmes.

A National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD),
was therefore, set up in July 1982 by an Act of parliament to take over the
functions of ARDC and the refinancing functions of RBI in relation to
co-operative banks and RRBs. NABARD is linked organically with the RBI by the
latter contributing half of its share capital the other half being contributed
by the Government of India(GOI). GOI nominates three of its Central Board
Directors on the board of NABARD.A Deputy Governor of RBI is appointed as
Chairman of NABARD.
Functions of NABARD
NABARD has inherited its apex role from RBI i.e, it is performing
all the functions performed by RBI with regard to agricultural credit.
(i) NABARD acts as a refinancing institution for all kinds of
production and investment credit to agriculture, small-scale industries,
cottage and village industries, handicrafts and rural crafts and real artisans
and other allied economic activities with a view to promoting integrated rural
development.
(ii) It provides short-term, medium-term and long-term credits to
state co-operative Banks (SCBs), RRBs, LDBs and other financial institutions
approved by RBI.
(iii) NABARD gives long-term loans (upto 20 Years) to State
Government to enable them to subscribe to the share capital of co-operative
credit societies.
(iv) NABARD gives long-term loans to any institution approved by
the Central Government or contribute to the share capital or invests in
securities of any institution concerned with agriculture and rural development.
(v) NABARD has the responsibility of co-ordinating the
activities of Central and State
Governments, the Planning Commission (now NITI Aayog) and other all India
and State level institutions entrusted with the development of small scale
industries, village and cottage industries, rural crafts, industries in the
tiny and decentralized sectors, etc.
(vi) It has the responsibility to inspect RRBs and co-operative
banks, other than primary co-operative societies.
(vii) It maintains a Research and Development Fund to promote
research in agriculture and rural development
Related Topics