Chapter: Computer Networks : Physical Layer
Important Short Questions and Answers:Computer Networks - Physical Layer
1. What is mean by data communication?
Data
communication is the exchange of data (in the form of 1s and 0s) between two
devices via some form of transmission medium (such as a wire cable).
2. What are the three criteria necessary for an
effective and efficient network?
The most
important criteria are performance, reliability and security.
Performance of the network depends on number
of users, type of transmission medium, and thecapabilities of the connected h/w
and the efficiency of the s/w.
Reliability is measured by frequency of
failure, the time it takes a link to recover from thefailure and the network’s
robustness in a catastrophe.
Security issues include protecting data
from unauthorized access and viruses.
3. What are the three fundamental characteristics
determine the effectiveness of the data communication system?
The
effectiveness of the data communication system depends on three fundamental
characteristics:
Delivery:
The system must deliver data to the correct destination.
Accuracy:
The system must deliver data accurately.
Timeliness:
The system must deliver data in a timely manner.
4. What are the advantages of distributed
processing?
An
advantage of distributed processing includes security/encapsulation, distributed
databases, faster problem solving, security through redundancy and
collaborative processing.
5. Why are protocols needed?
In
networks, communication occurs between the entities in different systems. Two
entities cannot just send bit streams to each other and expect to be
understood. For communication, the entities must agree on a protocol. A
protocol is a set of rules that govern data communication.
6. Why are standards needed?
Co-ordination
across the nodes of a network is necessary for an efficient communication. If
there are no standards, difficulties arise. A standard provides a model or
basis for development to which everyone has agreed.
7. For n devices in a network, what is the number
of cable links required for a mesh and ring topology?
Mesh
topology – n (n-1)/2.
Ring
topology – n
8. What is the difference between a passive and an
active hub?
An active
hub contains a repeater that regenerates the received bit patterns before
sending them out. A passive hub provides a simple physical connection between
the attached devices.
9. Distinguish between peer-to-peer relationship
and a primary-secondary relationship. Peer-to-peer relationship:
All the
devices share the link equally.
Primary-secondary relationship:
One
device controls traffic and the others must transmit through it
10. Assume 6 devices are arranged in a mesh
topology. How many cables are needed? How many ports are needed for each
device?
Number of
cables=n (n-1)/2=6(6-1)/2=15
Number of
ports per device=n-1=6-1=5
11. Group the OSI layers by function.
The seven
layers of the OSI model belonging to three subgroups. Physical, data link and
network layers are the network support layers; they deal with the physical
aspects of moving data from one device to another. Session, presentation and
application layers are the user support layers; they allow interoperability
among unrelated software systems. The transport layer ensures end-to-end
reliable data transmission.
12. What are header and trailers and how do they
get added and removed?
Each
layer in the sending machine adds its own information to the message it
receives from the layer just above it and passes the whole package to the layer
just below it. This information is added in the form of headers or trailers.
Headers are added to the message at the layers 6,5,4,3, and 2. A trailer is
added at layer2. At the receiving machine, the headers or trailers attached to
the data unit at the corresponding sending layers are removed, and actions
appropriate to that layer are taken.
13. Discuss the mode for propagating light along
optical channels.
There are
two modes for propagating light along optical channels, multimode and single mode.
Multimode: Multiple beams from a light
source move through the core in different paths.
Single mode: Fiber with extremely small
diameter that limits beams to a few angles, resulting inan almost horizontal
beam.
14. How are the guided media differing from
unguided transmission media? Guided transmission media
1. Guided
indicate, medium is contained have any within physical boundary
2. Transmission
takes place through wire.
Unguided transmission media
1. Unguided
medium does not Physical boundary
2. It is
a wireless transmission.
15. What are the disadvantages of optical fiber as
a transmission medium?
The
disadvantages of optical fiber are
·Very
expensive.
·Installation
and maintenance is difficult.
·Fragility.
16. What are the criteria used to evaluate
transmission medium?
The
criteria used to evaluate transmission medium are
·Throughput
·Propagation
speed
·Propagation
time
·Wavelength
17. Give the relationship between propagation speed
and propagation time?
Propagation
time = distance / propagation speed
The time
required for a signal or a bit to travel from one point to another is called Propagation time. Propagation speed is
the distance, a signal or a bit travel through a mediumin one second.
18. Explain cross talk and what is needed to reduce
it?
Effect of
one wire on another is called as cross talk. One wire will be the sending
antenna and the other wire will be the receiving antenna. We can use the
shielded twisted pair cable or coaxial cable for transmission, which contains
metal foil to reduce cross talk.
19. Compare datagram networks and virtual
circuit networks.
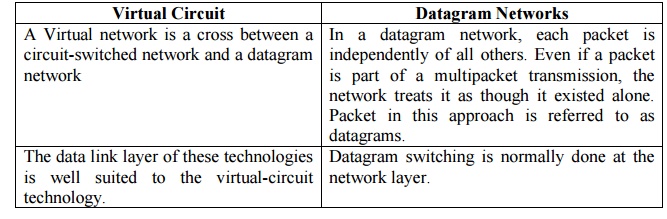
20. What is TCP/IP?
TCP/IP is
a hierarchical protocol made up of interactive modules, each of which provides
a specific functionality: however, the modules are not necessarily
interdependent.
21. State the role of DSL.
DSL
Technology supports high speed digital communication over the existing local
loops.
22. What is the role of DSL Modem?
DSL
Technology is one of the most promising for supporting high-speed digital
communication over the existing local loops.
23. What are the features provided by layering?
Two nice
features are:
o
It decomposes the problem of building a network
into more manageable components.
o
It provides a more modular design.
Glossary:
ADSL Lite: A splitterless ADSL. This technology allows an ASDL Lite modem
to be pluggeddirectly into a telephone jack and connected to the computer. The
splitting is done at the telephone company.
Bandwidth: The difference between the highest and the lowest frequencies of a
compositesignal. It also measures the information-carrying capacity of a line
or a network.
Bayone-Neill-Concelman (BNC) connector: A common coaxial cable connector.
Bit Stuffing: In a bit-oriented protocol, the process of adding an extra bit in
the data section of aframe to prevent a sequence of bits from looking likes a
flag.
Bit-Oriented Protocol: A protocol in which the data frame is interpreted as a sequence of
bits.Cable Modem: A technology in which the TV cable provides Internet access.
Cable Modem Transmission System (CMTS): A device installed inside the distribution hubthat receives data
from the Internet and passes them to the combiner.
Cable TV Network: A system using coaxial or fiber optic cable that brings multiple
channels of
video
programs into homes.
Circuit Switching’s: switching technology that establishes an electrical connection
betweenstations using a dedicated path.
Cladding: Glass or plastic surrounding the core of an optical fiber; the
optical density of thecladding must be less than that of the core.
Coaxial Cable: A transmission medium consisting of a conducting core,
insulating material, anda second conducting sheath.
Community Antenna TV (CATV): A cable network service that broadcasts video signals tolocations
with poor or no reception.
Constellation Diagram: A graphical representation of the phase and amplitude of
different bitcombinations in digital-to-analog modulation.
Datagram Network: A packet-switched network in which packets are independent from
eachother.
Digital Subscriber Line Access
Multiplexer (DSLAM): A telephone company site device
thatfunctions like an ADSL modem.
Error Control: The handling of errors in data transmission.
Flow Control: A technique to control the rate of flow of frames (packets or
messages).
Guided Media: Transmission media with a physical boundary.
Hop-To-Hop Delivery: Transmission of frames from one node to the next.
Internet service provider (ISP): Usually, a company that provides Internet services.
Jitter: A phenomenon in
real-time traffic caused by gaps between consecutive packets at thereceiver.
Local Area Network (LAN) A network connecting devices inside a single building or insidebuildings
close to each other.
Node-To-Node Delivery: Transfer of a data unit from one node to the next.
Optical Fiber: A thin thread of glass or other transparent material to carry
light beams.
Packet Switching: Data transmission using a packet-switched network.
Peer-To-Peer Process: A process on a sending and a receiving machine that communicates
at agiven layer.
Physical Layer: The first layer of the Internet model, responsible for the
mechanical andelectrical specifications of the medium.
Switch: A device connecting multiple communication lines together.
Topology: The structure of a network including physical arrangement of
devices.
Wide Area Network (WAN): A network that uses a technology that can span a largegeographical
distance.
Related Topics