Chapter: Computer Networks : Physical Layer
Datagram Networks
Datagram Networks:
In data
communications, we need to send messages from one end system to another. If the
message is going to pass through a packet-switched network, it needs to be
divided into packets of fixed or variable size. The size of the packet is
determined by the network and the governing protocol.
In a packet-switched network, there is no resource
reservation; resources are allocated on demand.
In a
datagram network, each packet is treated independently of all others. Even if a
packet is part of a multipacket transmission, the network treats it as though
it existed alone. Packets in this approach are referred to as datagrams. Datagram
switching is normally done at the network layer. Figure 1.48 shows how the
datagram approach is used to deliver four packets from station A to station X.
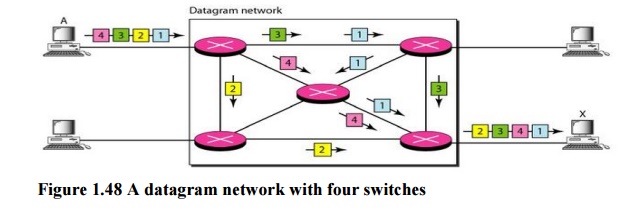
1. Routing table:
In this
type of network, each switch (or packet switch) has a routing table which is
based on the destination address. The routing tables are dynamic and are
updated periodically. The destination addresses and the corresponding
forwarding output ports are recorded in the tables. This is different from the
table of a circuit switched network in which each entry is created when the
setup phase is completed and deleted when the teardown phase is over. Figure
8.8 shows the routing table for a switch.
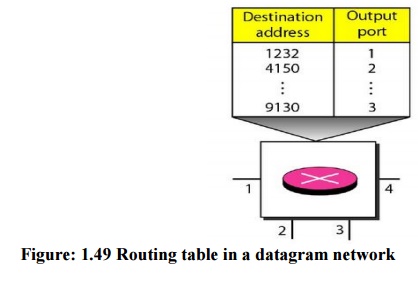
A switch in a datagram network uses a routing table
that is based on the destination address.
Destination
Address
Every
packet in a datagram network carries a header that contains, among other
information, the destination address of the packet. When the switch receives
the packet, this destination address is examined; the routing table is
consulted to find the corresponding port through which the packet should be
forwarded.
The destination address in the header of a packet
in a datagram network remains the same during the entire journey of the packet.
Datagram Networks in the Internet:
The
Internet has chosen the datagram approach to switching at the network layer. It
uses the universal addresses defined in the network layer to route packets from
the source to the destination.
Related Topics