Chapter: Computer Networks : Physical Layer
Dial-up Modems
Dial-up Modems:
Traditional
telephone lines can carry frequencies between 300 and 3300 Hz, giving them a
bandwidth of 3000 Hz. All this range is used for transmitting voice, where a
great deal of interference and distortion can be accepted without loss of
intelligibility.
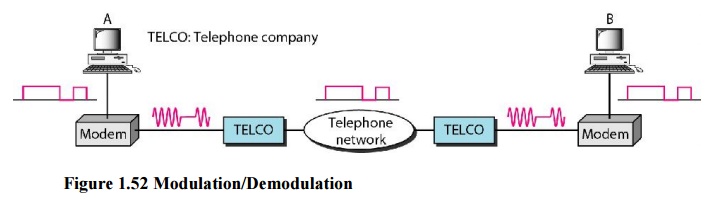
The term
modem is a composite word that refers to the two functional entities that make
up the device: a signal modulator and a signal demodulator. A modulator creates
a band pass analog signal from binary data. A demodulator recovers the binary
data from the modulated signal.
Modem stands for
modulator/demodulator.
Modem
Standards
The most
popular modems available are based on the V-series standards by the ITU-T.
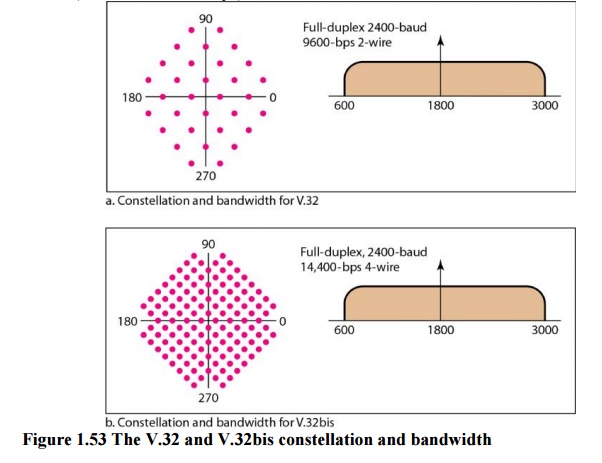
a. V.32 and V.32bis
The V.32
modem uses a combined modulation and encoding technique called trelliscoded
modulation. Trellis is essentially QAM plus a redundant bit. The data stream is
divided into 4-bit sections.
The V.32
calls for 32-QAM with a baud rate of 2400. Because only 4 bits of each pentabit
represent data, the resulting data rate is 4 x 2400 = 9600 bps. The
constellation diagram and bandwidth are shown in Figure 1.53
The
V.32bis modem was the first of the ITU-T standards to support 14,400-bps
transmission. The V.32bis uses 128-QAM transmission (7 bits/baud with I bit for
error control) at a rate of 2400 baud (2400 x 6 = 14,400 bps).
b. V.34bis
The
V.34bis modem provides a bit rate of 28,800 with a 960-point constellation and
a bit rate of 33,600 bps with a 1664-point constellation.
c.V.90
Traditional
modems have a data rate limitation of 33.6 kbps, as determined by the Shannon
capacity. However, V.90 modems with a bit rate of 56,000 bps are available;
these are called 56K modems. These modems may be used only if one party is
using digital signaling.
d.V.92
The
standard above V90 is called ~92. These
modems can adjust their speed, and if the noise allows, they can upload data at
the rate of 48 kbps. The downloading rate is still 56 kbps. The modem has
additional features. For example, the modem can interrupt the Internet
connection when there is an incoming call if the line has call-waiting service.
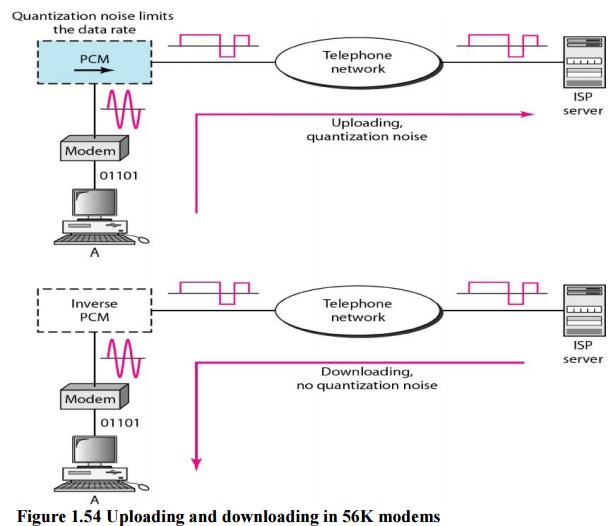
Figure 1.54 Uploading and downloading in 56K modems
Related Topics