Chapter: Computer Networks : Physical Layer
Unguided media
Unguided media:
Unguided
media transport electromagnetic waves without using a physical conductor. This
type of communication is often referred to as wireless communication. Figure
1.39 shows the part of the electromagnetic spectrum, ranging from 3 kHz to 900
THz, used for wireless communication.

Unguided
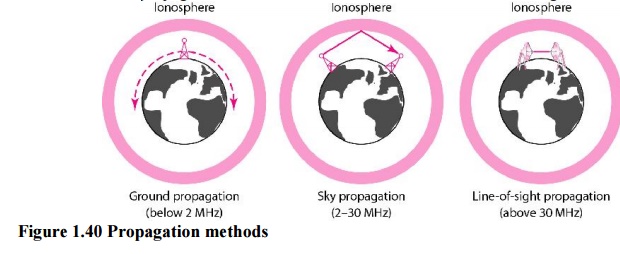
signals can travel from the source to destination in several ways: ground
propagation, sky propagation, and line-of-sight propagation, as shown in Figure
1.40
We can
divide wireless transmission into three broad groups: radio waves, microwaves,
and infrared waves.
1. Radio Waves:
Electromagnetic
waves ranging in frequencies between 3 kHz and 1 GHz are normally called radio
waves; waves ranging in frequencies between 1 and 300 GHz are called
microwaves. Radio waves, for the most part, are omnidirectional. When an
antenna transmits radio waves, they are propagated in all directions. Radio
waves, particularly those waves that propagate in the sky mode, can travel long
distances. This makes radio waves a good candidate for long-distance
broadcasting such as AM radio.
Radio waves are used for multicast communications,
such as radio and television, and paging systems.
Omnidirectional
Antenna
Radio
waves use omnidirectional antennas that send out signals in all directions.

Applications
The
omnidirectional characteristics of radio waves make them useful for
multicasting, in which there is one sender but many receivers. AM and FM radio,
television, maritime radio, cordless phones, and paging are examples of
multicasting.
2. Microwaves
Electromagnetic waves
having frequencies between
I and 300
GHz are called Microwaves. Microwaves are
unidirectional. When an antenna transmits microwave waves, they can be narrowly
focused. This means that the sending and receiving antennas need to be aligned.
The unidirectional property has an obvious advantage. A pair of antennas can be
aligned without interfering with another pair of aligned antennas
Microwaves are used for unicast communication such
as cellular telephones, satellite networks, and wireless LANs.
Unidirectional
Antenna
Microwaves
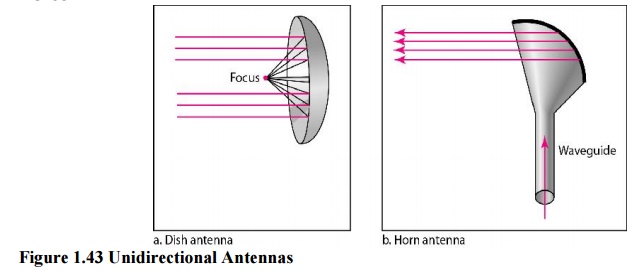
need unidirectional antennas that send out signals in one direction. Two types
of antennas are used for microwave communications: the parabolic dish and the
hom.
A
parabolic dish antenna is based on the geometry of a parabola: Every line
parallel to the line of symmetry (line of sight) reflects off the curve at
angles such that all the lines intersect in a common point called the focus.
The parabolic dish works as a funnel, catching a wide range of waves and
directing them to a common point. In this way, more of the signal is recovered
than would be possible with a single-point receiver.
Applications
Microwaves,
due to their unidirectional properties, are very useful when unicast
(one-to-one) communication is needed between the sender and the receiver. They
are used in cellular phones, satellite networks and wireless LANs.
3. Infrared:
Infrared
waves, with frequencies from 300 GHz to 400 THz (wavelengths from 1 mm to 770
nm), can be used for short-range communication. Infrared waves, having high
frequencies, cannot penetrate walls. This advantageous characteristic prevents
interference between one system and another; a short-range communication system
in one room cannot be affected by another system in the next room.
Infrared signals can be used for short-range
communication in a closed area using line-of-sight propagation.
Applications
The
infrared band, almost 400 THz, has an excellent potential for data
transmission. Such a wide bandwidth can be used to transmit digital data with a
very high data rate. The Infrared Data Association (IrDA), an association for
sponsoring the use of infrared waves, has established standards for using these
signals for communication between devices such as keyboards, mice, PCs, and
printers. For example, some manufacturers provide a special port called the
IrDA port that allows a wireless keyboard to communicate with a PC.
Related Topics