Chapter: Computer Networks : Physical Layer
Virtual-Circuit Networks
Virtual-Circuit Networks:
A virtual-circuit
network is a cross between a circuit-switched network and a datagram network.
It has
some characteristics of both.
1.
As in a circuit-switched network, there are setup
and teardown phases in addition to the data transfer phase.
2.
Resources can be allocated during the setup phase,
as in a circuit-switched network, or on demand, as in a datagram network.
3.
As in a datagram network, data are packetized and
each packet carries an address in the header. However, the address in the
header has local jurisdiction not end-to-end jurisdiction. The reader may ask
how the intermediate switches know where to send the packet if there is no
final destination address carried by a packet.
4.
As in a circuit-switched network, all packets
follow the same path established during the connection.
5.
A virtual-circuit network is normally implemented
in the data link layer, while a circuit-Switched network is implemented in the
physical layer and a datagram network in the network layer.
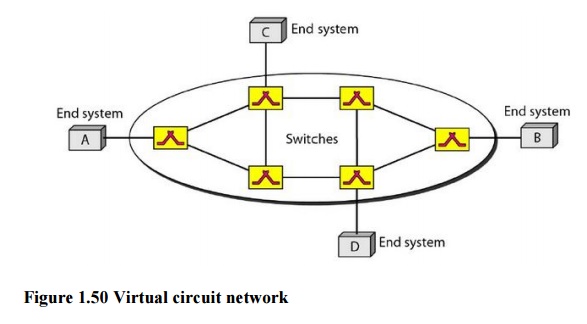
Figure
1.50 is an example of a virtual-circuit network. The network has switches that
allow traffic from sources to destinations. A source
or destination can be a computer, packet switch, bridge, or any other device
that connects other networks.
1. Addressing
In a
virtual-circuit network, two types of addressing are involved: global and local
(virtual-circuit identifier).
Global
Addressing
A source
or a destination needs to have a global address-an address that can be unique
in the scope of the network or internationally if the network is part of an
international network.
Virtual-Circuit
Identifier
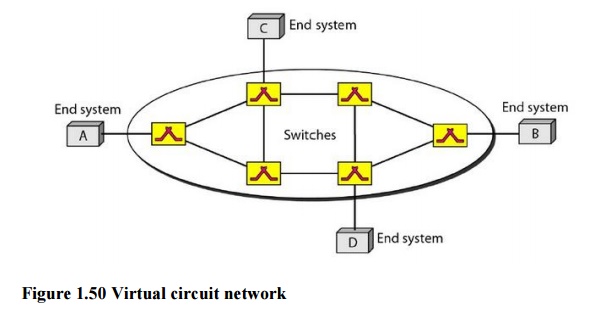
The
identifier that is actually used for data transfer is called the
virtual-circuit identifier (VCl). A VCl, unlike a global address, is a small
number that has only switch scope; it is used by a frame between two switches.
When a frame arrives at a switch, it has a VCI; when it leaves, it has a
different VCl.
2. Circuit-Switched Technology in
WANs
Virtual-circuit
networks are used in switched WANs such as Frame Relay and ATM networks. The
data link layer of these technologies is well suited to the virtual-circuit
technology.
Switching at the data link layer in a switched WAN
is normally implemented by using virtual-circuit techniques.
Related Topics