Chapter: Computer Networks : Physical Layer
Cable TV Networks
CABLE TV NETWORKS:
The cable
TV network started as a video service provider, but it has moved to the
business of Internet access.
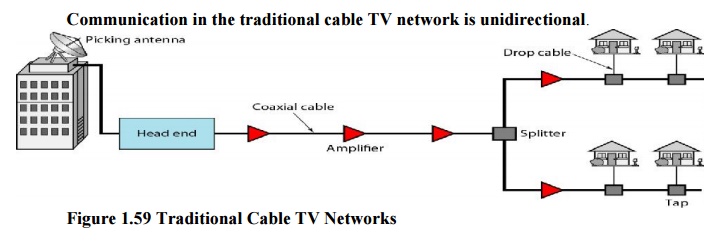
1. Traditional Cable Networks
Cable TV
started to distribute broadcast video signals to locations with poor or no
reception. It was called community antenna TV (CATV) because an antenna at the
top of a tall hill or building received the signals from the TV stations and
distributed them, via coaxial cables, to the community.
The cable
TV office, called the head end, receives video signals from broadcasting
stations and feeds the signals into coaxial cables. The signals became weaker
and weaker with distance, so amplifiers were installed through the network to
renew the signals. There could be up to 35 amplifiers between the head end and
the subscriber premises. At the other end, splitters split the cable, and taps
and drop cables make the connections to the subscriber premises.
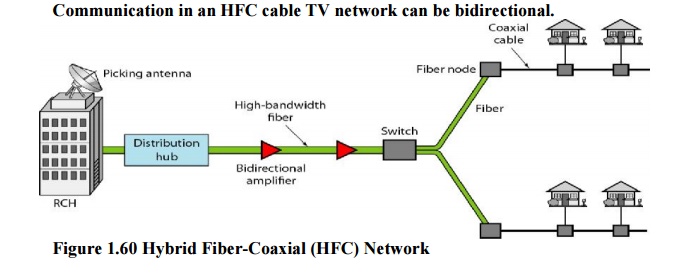
2. Hybrid Fiber-Coaxial (HFC)
Network
The
second generation of cable networks is called a hybrid fiber-coaxial (HFC)
network. The network uses a combination of fiber-optic and coaxial cable. The
transmission medium from the cable TV office to a box, called the fiber node,
is optical fiber; from the fiber node through the neighborhood and into the
house is still coaxial cable.
Related Topics