Chapter: Computer Networks : Physical Layer
Data Communications
Data Communications:
Data communications are the
exchange of data between two devices via some form oftransmission medium such
as a wire cable.
1. Characteristics:
The
effectiveness of a data communications system depends on four fundamental
characteristics:
a. Delivery:
The
system must deliver data to the correct destination. Data must be received by
the
intended
device or user and only by that device or user.
b. Accuracy:
The
system must deliver data accurately.
c. Timeliness:
The
system must deliver data in a timely manner. In the case of video and audio,
timely delivery means delivering the data as they are produced. In the same
order, that they are produced, and without significant delay. This kind of
delivery is called real-time transmission.
d. Jitter:
Jitter
refers to the variation in the packet arrival time. It is the uneven delay in
the delivery of audio or video packet.
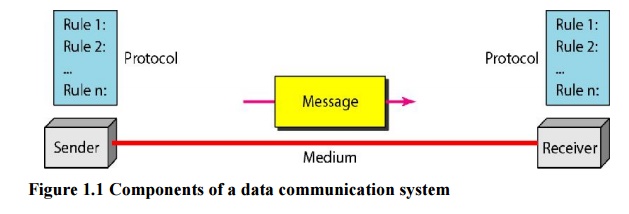
2. Components:
A data
communication system has five components.
a. Message:
The
message is the information to be communicated. Popular forms of information
include text, numbers, pictures audio and video.
b. Sender:
The
sender is the device that sends the data message. It can be a computer,
workstation, telephone handset, video camera, and so on.
c. Receiver:
The
receiver is the device that receives the message. It can be a computer,
workstation, telephone handset, television and so on.
d. Transmission medium:
The
transmission medium is the physical path by which a message travels from sender
to receiver. Ex. Twisted pair wire, coaxial cable, fiber optic cable and radio
waves.
e. Protocol:
A protocol
is the set
of rules that governs data
communications. It represents
an agreement between the communicating devices.
3. Data Representation:
Information
today comes in different forms such as text, numbers, images, audio, and Video.
a. Text:
Text is
represented as a bit pattern, a sequence of bits (Os or 1s). Different sets of
bit patterns have been designed to represent text symbols. Each set is called a
code, and the process of representing symbols is called coding.
b. Numbers:
Numbers
are also represented by bit patterns. The number is directly converted to a binary
number to simplify mathematical operations.
c. Images:
Images
are also represented by bit patterns. An image is composed of a matrix of
pixels (picture elements), where each pixel is a small dot. The size of the
pixel depends on the resolution.
d. Audio:
Audio
refers to the recording or broadcasting of sound or music. It is continuous,
not discrete.
e. Video:
Video
refers to the recording or broadcasting of a picture or movie. Video can either
be produced as a continuous entity (e.g., by a TV camera), or it can be a
combination of images, each a discrete entity, arranged to convey the idea of
motion.
4. Data Flow:
Communication
between two devices can be simplex, half-duplex, or full-duplex.
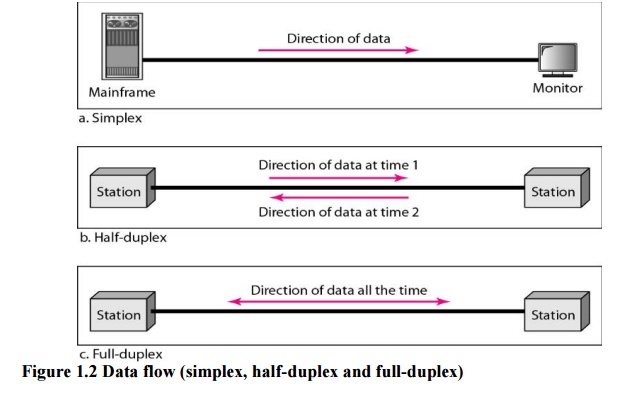
a. Simplex:
In
simplex mode, the communication is unidirectional, as on a one-way street. Only
one of the two devices on a link can transmit; the other can only receive (see
Figure 1.2a). Keyboards and traditional monitors are examples of simplex devices.
b. Half-Duplex:
In
half-duplex mode, each station can both transmit and receive, but not at the
same time. When one device is sending, the other can only receive, and vice
versa (see Figure 1.2b). Walkie-talkies and CB (citizens band) radios are both
half-duplex systems.
c. Full-Duplex:
In
full-duplex mode (also called duplex), both stations can transmit and receive
simultaneously (see Figure 1.2c). One common example of full-duplex
communication is the telephone network.
Related Topics