Chapter: 9th Social Science : Geography : Atmosphere
Winds - Elements of Weather and Climate
Winds
The horizontal movement of air along the surface of
the earth is called the ŌĆ£Wind' while the vertical movement of air is a called
an ŌĆ£Air CurrentŌĆØ. The winds always blow from a high pressure area to a low
pressure area. Wind is mostly named after the direction from which it blows.
For example, the wind blowing from the east is known as the easterly wind.
An ŌĆ£anemometerŌĆØ records wind speed while a ŌĆ£wind
vaneŌĆØ measures the direction of the wind. The unit of measurement is kilometre
per hour or knots


Types of Winds
Winds are generally classified into the following
four major types:
ŌŚÅ
Planetary winds
ŌŚÅ
Periodic winds
ŌŚÅ
Variable wind
ŌŚÅ
Local wind
i. Planetary winds:
The winds which constantly blow in the same
direction throughout the year are called the Planetary winds. They are also
called as permanent winds or the prevailing winds. These winds include Trade
winds, Westerlies and Polar Easterlies
Trade Winds
Trade winds blow from the subtropical high pressure belt to the Equatorial low pressure belt in both the hemispheres. They blow with great regularity, force and in a constant direction throughout the year. These winds were very helpful to traders who depended on the winds while sailing in the seas. And so, they are named as Trade winds. As they travel over vast oceans, they collect more moisture and bring heavy rainfall to the East Coast of the continents of the tropics. As they move westwards, they become dry and do not give rainfall
Westerlies
Westerlies are the permanent winds that blow from
the tropical high pressure belt to the sub polar low pressure belt in both the
hemispheres. They blow from South West to North East in the northern hemisphere
and North West to South East in the southern hemisphere. The velocity of
westerlies become so vigorous and fast to be called Roaring Forties at 400, Furious
Fifties at 500 and Screaming Sixties at 600 latitudes.
Polar Easterlies:
Polar easterlies are cold and dry polar winds that
blow from the polar high pressure belt to the sub polar low pressure belt.
These are weak winds blowing from North East direction in the Northern
Hemisphere and South East direction in the Southern Hemisphere.
ii. Periodic winds
The periodic winds are the seasonal winds that
change their direction periodically.
These winds are caused by the differential heating
of land and ocean.
Winds which reverse their direction with the change
of seasons are called monsoons. Tropical Monsoon winds of Indian subcontinent
is a best example.

iii. Variable winds
The disturbance and the changes in the local
weather cause variations in the prevailing winds. These winds are known as the
variable winds. Variable winds usually end up with the development of cyclones,
anticyclones and storms.
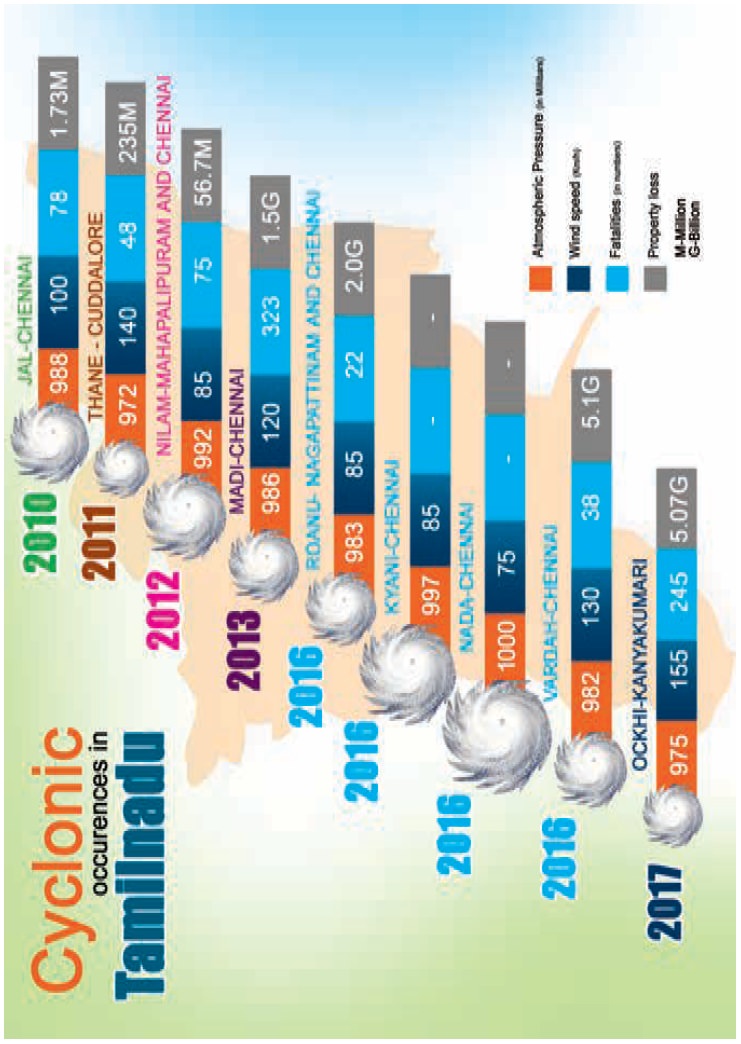
Cyclones
The term cyclone is a Greek word meaning ŌĆ£coil of a
snake". Cyclones are centres of low pressure where, winds from the
surrounding high pressure area converge towards the centre in a spiral form.
Due to the rotation of the earth, the cyclonic winds in the northern hemisphere
move in anti clock wise direction, where as they move in clockwise direction in
the southern hemisphere.
Cyclones can be classified into
a. Tropical cyclones
b. Temperate cyclones
c. Extra tropical cyclones
a. Tropical cyclones:
Tropical cyclones develop in the Inter tropical
convergence zone [ITCZ]. They are formed due to the differential heating of
land and sea.
Tropical cyclones are known as ŌĆścyclonesŌĆÖ in Indian ocean, ŌĆśtyphoonsŌĆÖ in the western pacific ocean,
ŌĆśhurricanesŌĆÖ in the Atlantic and
eastern Pacific ocean, ŌĆśbaguiosŌĆÖ in
Phillipines and ŌĆś willy willyŌĆÖ in
Australia. Tropical cyclones often cause heavy loss of life and property on the
coasts and become weak after reaching the landmasses.



b. Temperate cyclones:
Temperate cyclones are formed along a front where
hot and cold air masses meet in mid-latitudes between 35┬░ and 65┬░N and S.
Temperate cyclones do not become weak like the tropical cyclones on reaching
the land. Temperate cyclone commonly occurs over the North Atlantic Ocean,
North West Europe, Mediterranean basin. Mediterranean basinŌĆÖs temperate
cyclones extend up to Russia and India in winter. In India it is as called
western disturbances.

c. Extra tropical cyclones:
Extra tropical cyclones occur in the latitudes
between 30┬░ and 60┬░ in both the hemispheres. They are also called as mid-latitude cyclones . They collect
energy from temperature differences
which are found in higher latitudes. Extra tropical cyclones produce mild
showers to heavy gales, thunderstorms, blizzards, and tornadoes.
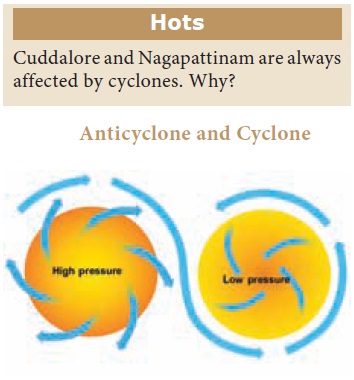
Anticyclones:
Anticyclones are the opposite of cyclones. Here an
area of high pressure region is found in the centre surrounded by low pressure
on all sides. The wind from the high pressure region move outwards to the low
pressure regions in a spiral form. Anticyclones are often accompanied by cold
and heat waves.
Local Winds:
Local winds are the winds that blow only in a
particular locality for a short period of time, The effect of these local winds
are experienced only in that particular area.
They are mostly seasonal and have local names
like....
┬Ę
Foehn (Alps-Europe)
┬Ę
Sirocco (North coast of Africa)
┬Ę
Chinook (Rockies-North America)
┬Ę
Loo (Thar Desert- India)
┬Ę
Mistral (Mediterranean sea in France)
┬Ę
Bora (Mediterranean sea in Italy)
Related Topics