Chapter: 9th Social Science : Geography : Atmosphere
Structure of the Atmosphere
Structure of the Atmosphere
The atmosphere is thick near the earth surface and
thins out until it eventually merges with space. The five atmospheric layers
are: Troposphere, stratosphere, Mesosphere, Thermosphere and Exosphere.
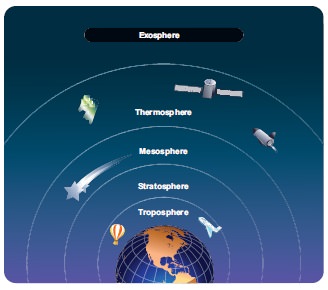
Troposphere:
The lowest layer of the atmosphere is the
troposphere. The Greek word ‘tropos’ means ‘turn’ or change. The layer extends
up to 8 kms at the poles and up to 18 kms at the Equator. The temperature
decreases with increasing height. Almost all weather phenomenon take place in
this layer. Hence it is called weather making layer. The upper limit of the
troposphere is called as tropopause.
1. Stratosphere
Stratosphere lies above the troposphere. It extends
to a height of about 50km above earth surface. Since this layer is a
concentration of ozone molecules, it is also referred as ozonosphere. The temperature
increases with increase in height in this layer. Large jet planes normally fly
here. The upper limit of the stratosphere is called as stratopause.
2. Mesosphere
Mesosphere extends between 50km and 80km. The
temperature increases with increasing height. Radio waves transmitted from
earth are reflected back to earth from this layer. Most of the meteors nearing
the earth, get burned here. The upper most limit of the mesosphere is the
mesopause.
3. Thermosphere
Thermosphere exists above the mesosphere. It
extends to about 600 km. The composition of gases in the lower thermosphere is
more or less uniform, hence it is called “Homosphere”. The upper portion of the
thermosphere has uneven composition of gases and hence it is referred as
“Heterosphere”. Here the temperature increases with increasing height.
Ionosphere is a layer of the thermosphere that contains Ions and free
electrons.

4. Exosphere
The uppermost layer of the atmosphere is called exosphere. This layer is extremely rarefied with gases and gradually merges with the outer space. This zone is characterized by aurora Australis and aurora borealis.

5. Weather and Climate
Weather and climate are the terms that are related
to the atmospheric conditions. Weather denotes the way the atmosphere behaves
every day and climate reveals the average of weather conditions over relatively
long periods of time. The difference between the two may be clearly understood
with the following table.

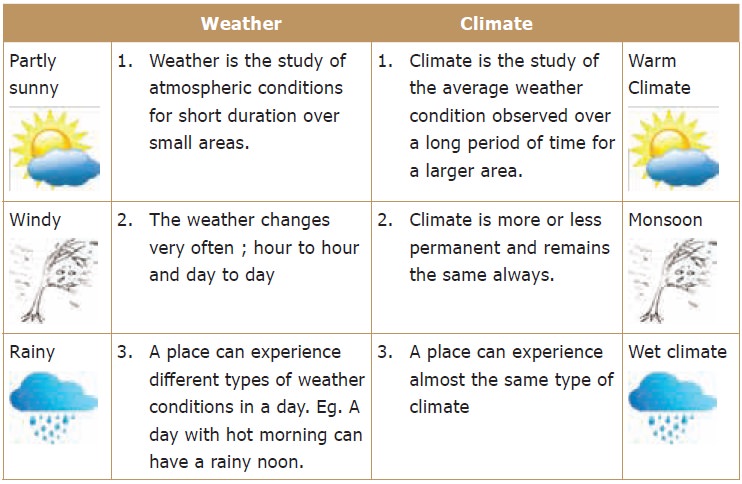
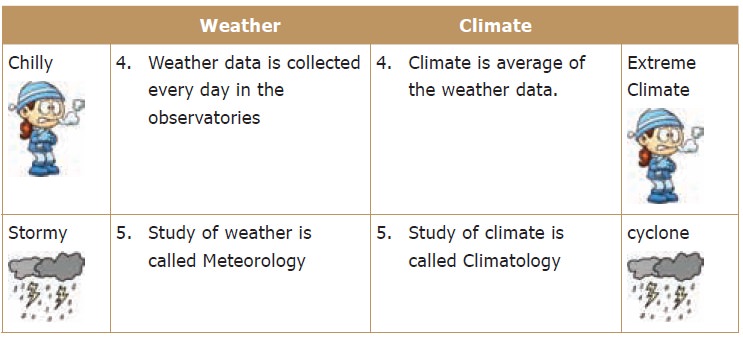
2. There are many factors that influence weather and climate.
·
Distance from the equator
·
Altitude
·
Nearness to the sea
·
Nature of the prevailing winds
·
Mountain barrier
·
Cloud cover
·
Ocean currents
·
Natural vegetation
Distance from the Equator
The sun’s rays fall vertically on the equator. The
rays are inclined on the regions away from the equator and near the poles due
to the spherical shape of the earth. The vertical rays heat up the earth more
than the inclined rays. Thus, the places near the equator are warmer than the
places which are far away from the equator.
Altitude:
Altitude refers to the height above sea level. The
temperature decreases at the rate of 1° C for every 165 mt of height.
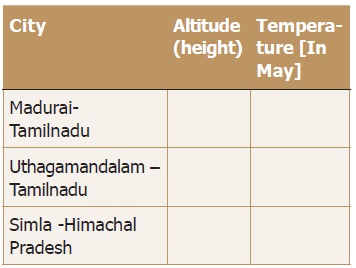
This is called Normal
lapse rate. So, places at the higher altitude have a lower temperature.
Nearness to the sea:
The climate of a place, varies according to its
nearness to the sea. Places near the coast experience equable climate due to
the influence of the winds from the sea. Places located in the land, far from
the sea, does not experience the moderating influence of the sea, such places
experience a continental type of climate.
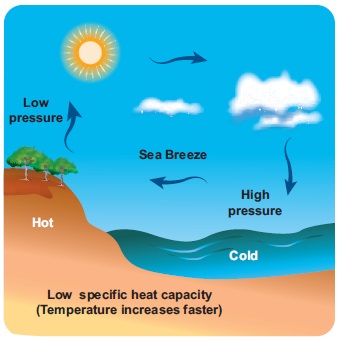
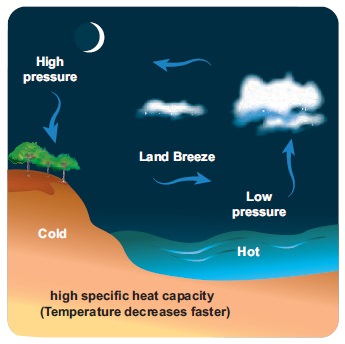

Nature of the Prevailing Winds
The winds change the climate of a place based on,
from where they blow. When wind blows from a warm region, it makes the place
warm and cold, when blows from a colder region. The on-shore winds cause
rainfall making the place cool whereas the off-shore winds bring dry weather.
Mountains barriers
The location of the mountains influence the climate of a place. The mountain chains act as natural barrier for the wind. Sometimes they prevent the entry of cold winds into the country or the escape of monsoon winds, thus having a great influence over the climate.
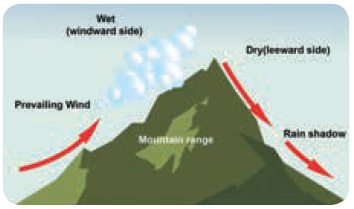
Cloud Cover
Clouds reflect a large amount of radiation from the
sun. This prevents the entry of heat to the earth’s surface. So, in areas
generally of cloudless sky like the deserts, temperature is very high. On the
other hand under cloudy sky, the temperature is low.
Ocean currents
The warm ocean currents raise the temperature of
the nearby coastal areas, while the cold current lower the temperature of aw
place.
Natural vegetation
The trees release water vapour into the air and
makes it cool. Thus forest areas have lower range of temperature throughout the
year in contrast to non-forested areas.
Related Topics