Experiments | Botany Practicals - Water holding capacity of garden soil and roadside soil | 12th Botany : Practicals
Chapter: 12th Botany : Practicals
Water holding capacity of garden soil and roadside soil
Experiments
Exercise : Water holding capacity of garden soil and
roadside soil
The maximum amount of
water retained by soil per unit of its dry weight after the gravitational flow
has ceased is called water holding capacity or field capacity of the soil. The
water holding capacity varies in different type of soils and depends upon the
types of soil particles and porocity of the soil. Sandy soils have poor water
holding capacity then the loam and clay soils.
Aim:
To study the water
holding capacity of garden soil and roadside soil.
Requirements:
Garden soil, roadside
soil, measuring cylinders, funnels, filter papers, beakers, balance, etc.
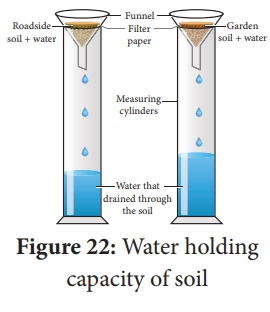
Procedure:
Take two funnels and
line them with filter paper. Lable them A and B. Place them on measuring
cylinders. Take 100 gm dried sample each of the garden soil and roadside soil.
Put the garden soil in funnel A and roadside soil in funnel B. Pour 100 ml of
water in each funnel. Record the volume of filtered out water in the measuring
cylinder when the dripping of water stops from the funnel.
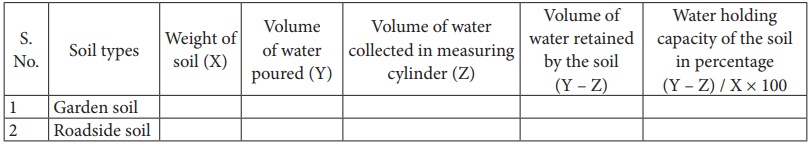
Observation:
Record the observation
in the table as follows:
Inference:
Garden soil has a high
water holding capacity than the roadside soil, because roadside soil has larger
quantities of sand and silt.
Precautions:
·
Weighing of soil samples should be done accurately.
·
Pour water slowly and gently on the soil in the funnel
·
Record the volume of collected water in the measuring cylinders
carefully.
Related Topics