Solving the Problems | Botany Practicals - Chromosomal aberrations - Deletion, Duplication and Inversion | 12th Botany : Practicals
Chapter: 12th Botany : Practicals
Chromosomal aberrations - Deletion, Duplication and Inversion
Exercise : Chromosomal aberrations – Deletion,
Duplication and Inversion
Problem:
Given below is the
representation of a kind of chromosomal aberration such as deletion,
duplication and inversion. Identify and give reasons for identification. Also
mentions its significance.
Aim:
To understand the
abnormality in the chromosomal structure in an organism.
Principle:
To study about the
chromosomal aberration which can occur due to ionizing radiations or chemicals.
On the basis of breaks and reunions in the chromosomal segment different types
of aberrations can be recognized.
Requirements:
Copper wire, Alphabets
marked ( A to H ) yellow colour beads denotes gene, and red colour bead without
alphabet denote centromere. Using this materials make different kinds of
chromosomal segments with specific gene sequence, that can be given to the
students and asked to analyse the aberration involved in it.
Procedure:
·
Make a normal chromosome model using copper wire and yellow beads
and place it on the table. In the model chromosome with gene sequence A to H,
along with centromere ( red bead).
·
For Deletion - Give yellow colour beads without one or more marked
alphabets A to H (The lack of any one or more beads denotes deletion type of
chromosomal aberration).
·
For Duplication – Give yellow colour beads with addition of one or
more marked alphabets A to H (The repetition of one or more beads denotes
duplication type of chromosomal aberration).
·
For Inversion – Give yellow colour beads which marked alphabets
from A to H as in normal chromosome. (There is no addition or deletion of beads
(A to H) given, so the students can construct the inverted segment of the
chromosome using the given beads).
·
Based on the type of beads given the student has to identify and
construct the relevant chromosomal aberration.
A. Chromosomal Aberration – Deletion
Reasons:
·
The deletion of the chromosomal segement A and D. (Refer figure
17a)
·
When there is a loss of a segment of the genetic material in a
chromosome it is called deletion.
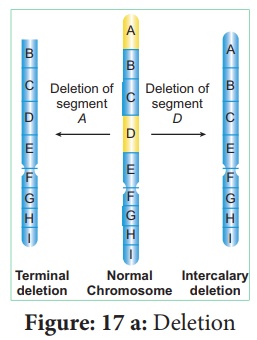
Significance:
Most of the deletions lead to death of an organism.
B. Chromosomal Aberration - Duplication
Reasons:
1. When a segment of a chromosome is present more
than once in a chromosome, then it is called duplication (Tandem duplication)
2. The order of the genes in a chromosome is A,
B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I. Due to aberration, the genes B and C are duplicated
and the sequence of genes becomes A, B, C, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and I. (Refer
figure 17b)
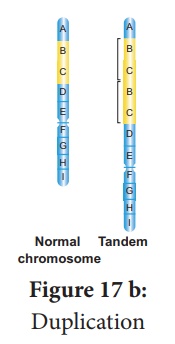
Significance:
Some duplications are
useful in the evolution of the organism.
C. Chromosomal Aberration – Inversion
Problem:
Given below is the
representation of a kind of chromosomal aberration. Identify it giving
reasons for your identification. Also mentions its significance.
Identification:
The given genetic
problem is identified as inversion type of chromosomal aberration.
Reasons:
·
When the order of genes in a chromosomal segment is reversed due
to rotation by an angle of 180°, it is called inversion.
·
The order of genes in a chromosome is A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H and
I. Due to aberration, the sequence of genes become A, D, C, B, E, F, G, H and I
(Refer figure 17c)
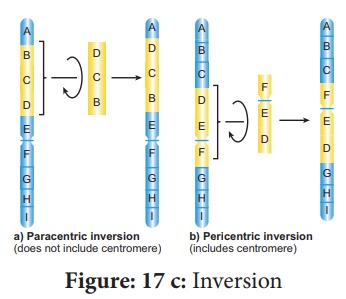
Significance:
Sometimes inversion is
responsible for evolution of the organism.
NOTE: Likewise the teacher
can give different types of chromosomal aberrations with various gene
sequence to students for practise. The external examiner can also use the same
technique by giving different gene sequence.
Related Topics