Causes, Types, Effects, Distribution - Volcano | 11th Geography : Chapter 3 : Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes
Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 3 : Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes
Volcano
Volcano
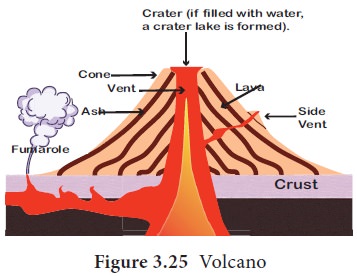
A volcano is an opening in the earth's crust
through which magma, gases and ash are released to the earth's surface. The
molten rock material found in the interior of the earth is called magma. It can
be noted that when magma reaches the earth’s surface, it is known as lava
(Figure. 3.25). Vent is an opening or mouth of a volcano. Fumaroles are the
gushing fumes through the gap in the volcano. Crater is a saucer shaped
depression in the mouth of a volcano. When the crater is widened, it is called
as Earthquake,Iran-Iraq border, 2017 Caldera. Volcanic ash consists of
fragments of pulverized rock, minerals and volcanic glass, created during
volcanic eruptions. Volcano generally erupts either through the vent (E.g. Mt.
Fujiyama, Japan) or fissure (The Deccan Plateau, India).
Pumice is a volcanic rock produced when lava with a very high content of water and gases is discharged from a volcano.
Causes of Volcanic Eruptions
The following are the causes of volcanic eruptions:
Weak
Zones in the Earth Crust: The parts of the earth where two tectonic
plates collide against or drift apart from each other are considered very weak.
Volcanoes may erupt in such zones, for example, African and Eurasian plates.
Magma
Saturated with Gases: The magma, in the interior of the earth,
is often found saturated with gases like carbon dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide.
These gases together with water vapour make the magma highly explosive. Magma is
forced out as lava on the surface of the earth due to the pressure exerted by
these gases.
Types of Volcanoes
Based on the frequency
of eruption, there are three types of volcanoes:
1. Active
Volcanoes: Volcanoes which erupt frequently are called active
volcanoes. Generally, their vent remains open. Mount Etna of Italy, Cotopaxi in
Ecuador are some examples.
2. Dormant
Volcanoes: These volcanoes may not have erupted in the recent
past but there is a possibility of eruption at any time. In other words, they
may lie dormant awaiting active eruption anytime. Sometimes gases and steam
come out of them. They cause great destruction to life and property once they
become active again. Mt. Vesuvius of Italy and Mt. Fujiyama of Japan are
examples.
3. Extinct
Volcanoes: These volcanoes have exhausted their energy and have
not erupted during the known geological period. The vent of these volcanoes
remains closed with solidified lava. The formations such as craters may be
filled with water and crater lakes may be formed. The slopes of these landforms
may be covered with vegetation. Popa in Myanmar and Mt. Kenya in eastern Africa
are the examples of extinct volcano.
On the basis
of nature of eruption and form developed
on the surface, they are classified
into following types:
1. Shield
Volcanoes: These are made up of basalt, a type of lava that is very
fluid when erupted. They become explosive when water gets into the vent. They
develop into a cinder cone. Hawaiian volcano is an example of this category.
2. Composite
cone volcanoes: They are also called 'strato volcanoes'. They are cone-shaped volcanoes
composed of layers of lava, ash and rock debris. Mount Vesuvius and Mount St.
Helens are examples of composite volcanoes.
3. Cinder
Cone Volcano : It forms when magma is thrown out to the surface,
cooled in to ash and cinders and settled around the mouth of volcano. It is
less dangerous than other volcanoes.
4. Lava
Dome: Unlike composite and shield volcanoes, lava domes are of
significantly smaller structure. They are formed when the lava is too viscous
to flow to a great distance. As the lava dome slowly grows, the outer surface
cools and hardens as the lava continues to pile within. Eventually, the
internal pressure can shatter the outer surface, causing loose fragments to
spill down its sides.
Fact File
The greatest volcanic explosion known to humans is perhaps Mt. Krakatau in August 1883.
Krakatau is a small volcanic island in the Sunda Straits, between Java and Sumatra.
The explosion could be heard in Australia, almost 4,000 km away.
The vibration set up enormous waves over 30 m high which drowned 36,000 people in the coastal districts of Indonesia.
Effects of Volcanic Activities
Destructive effects of volcano
Showers of cinders and bombs can cause damage to
life and properties. Sometimes ash can precipitate under the influence of rain
and completely cover large areas.
The volcanic gases pose potential hazard to people,
animals; agriculture, while sulfur dioxide gas can lead to acid rain and air
pollution.
Positive Effects of Volcanoes
Volcanism creates new landforms. Volcanic rocks
yield very fertile soil upon weathering and decomposition.
The Kimberlite rock of South Africa, the source of
diamonds, is the pipe of an ancient volcano.
In the vicinity of active volcanoes, waters in the
depth are heated from contact with hot magma giving rise to springs and
geysers. The Puga valley in Ladakh region and Manikaran (Himachal Pradesh) are
promising spots in India for the generation of geothermal electricity.
Distribution of Volcanoes across the World
Most known volcanic activity and the earthquakes
occur along converging plate margins and mid-oceanic ridges. The major regions
of volcanic distributions are as follows.
1. Pacific Ring of Fire
Circum-Pacific region, popularly termed the
‘Pacific Ring of Fire’, has the greatest concentration of active volcanoes.
Volcanic belt and earthquake belt closely overlap along the ‘Pacific Ring of
Fire’. It is estimated to include two-thirds of the world’s volcanoes.
2. Mid Atlantic Region
The Mid Atlantic Region coasts has comparatively
fewer active volcanoes but many dormant or extinct volcanoes, example. St.
Helena, Cape Verde Islands and the Canary Islands. But the volcanoes of Iceland
and the Azores are active.
3. The Great Rift valley of Africa
In Africa some volcanoes are found along the East
African Rift Valley. Kilimanjaro and Mt. Kenya are extinct volcanoes. The only
active volcano in West Africa is Mt. Cameroon.
4. Mediterranean Region
Volcanoes of the Mediterranean region are mainly
associated with the Alpine folds. Example, Mt. Vesuvius, Mt. Stromboli (known
as the Light House of the Mediterranean Sea).
5. Other Regions
Elsewhere in the interiors of continents of Asia,
North America and Europe active volcanoes are rare. There are no volcanoes in
Australia.
Volcanoes in India
There are no volcanoes in the Himalayan region of
India. However, Barren Island, lying 135 km north-east of Port Blair became
active in 1991 and 1995.
However, the other volcanic island in Indian
Territory is Narcondam (Andaman and Nicobar Islands) It is probably extinct.
Its crater wall has been completely destroyed.
Related Topics