Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes - Types of Faults - Lithosphere | 11th Geography : Chapter 3 : Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes
Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 3 : Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes
Types of Faults - Lithosphere
Fault
A fault is a break in earth’s crust where blocks of
rock crust slide past each other.
Usually it occurs along plate boundaries, where the
forces of plate motion compress, pull or shear the crust that breaks the crust.
Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of
most earthquakes.
The fault
plane is the flat surface along which broken blocks of rock slide past one
another. A fault dip is an angle
between the fault plane and horizontal plane. Up thrown side represents the
uppermost block of a fault. Down thrown side represents the lowermost block of
a fault. Sometimes it becomes difficult to find out, which block has really
moved along the fault plane. Hanging wall is the upper wall of a fault. Foot
wall represents the lower wall of a fault.
A fault
scarp is the steep wall like slope caused by faulting of the crustal rocks.
Sometimes the fault scrap is so steep that it resembles a cliff.
Types of Faults
Based on how plates move about, the fault can be
divided into as follow:
a. Normal Fault
Vertical displacement of the crust is called a
normal fault. The normal fault is caused by tensional forces where plates
diverge. One block lies above the other (hanging wall). The other block lies
below the fault (footwall).
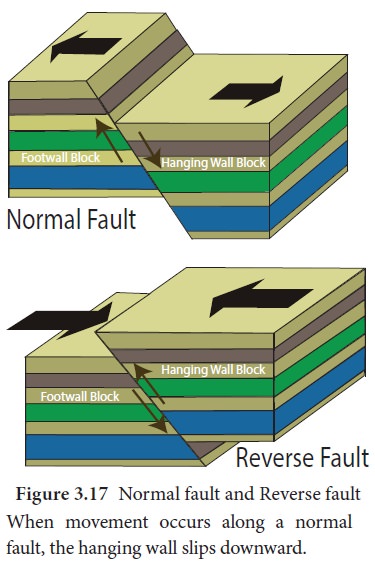
Figure
3.17 Normal fault and Reverse fault When movement occurs along a normal
fault, the hanging wall slips downward.
Landforms
made by Normal fault are:
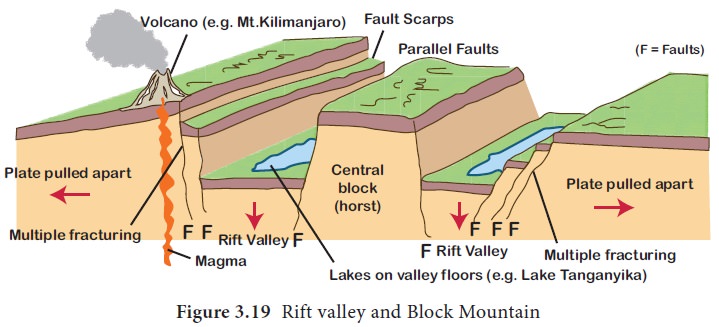
Rift Valley or Graben
When a narrow block of land drops or subsides
between two parallel normal faults, rift valley (Graben) is formed. Graben
originates from the German

A Rift Valley may
subsequently get filled by water and a river may flow through it. Normally, a
rift valley is long, narrow and very deep. For example,
·
Rhine
rift Valley is flanked by two Block Mountains namely the Vosges and the Black
Forest.
·
The
rift of River Narmada in India lies between the Vindhyas and Satpura block
mountains.
·
The
great rift valley of Africa.
The Great Rift Valley of Africa is the longest rift
valley in the world. It stretches for 6,400 km from Mozambique in the south to
Syria in the north. The depressions have become lakes. The lakes
Horst
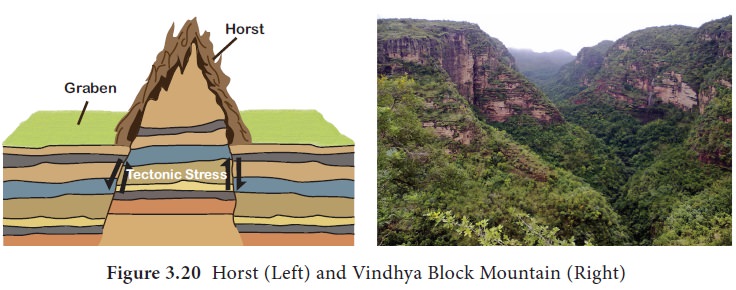
When a block of land between two faults is pushed
up, block mountain or horst is formed. In this case, the central block is not
only up thrown but the side blocks are also relatively downthrown so that the
whole central mass appears like a dome.
In India, specifically the mountain ranges of
Vindhya and Satpura found in the central western part of the India are block
mountains.
b. Reverse Fault
A reverse fault is a horizontal displacement of the crust. It is formed where two fractured blocks move towards each other. It is caused by compressional forces along convergent plate boundaries. One side of the fault lies at an angle above the other.
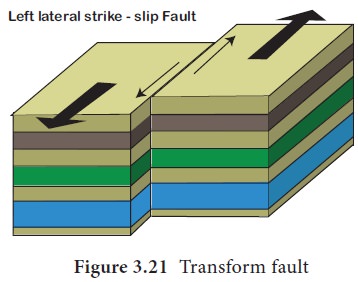
c. Shear Fault / Transform Fault/ Strike – Slip Fault
It is created by shearing along transform
boundaries. Rocks on either side of fault slip past each other sideways with
little up or down motion. It mostly occurs in the ocean basin and connects
offsets in the mid ocean ridge.
Related Topics