Measuring, Causes, Effects, Distribution - Earthquake | 11th Geography : Chapter 3 : Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes
Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 3 : Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes
Earthquake
Earthquake
Earthquake is a sudden shaking of the earth’s
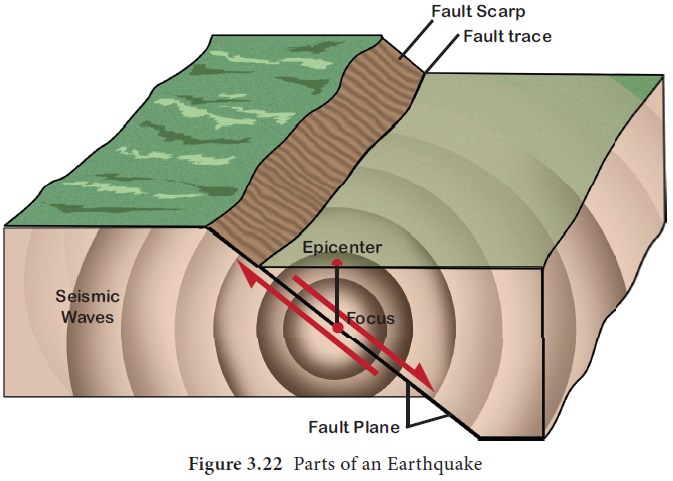
surface. Focus is the location
inside the earth where the earthquake originates. Epicenter is the point on the earth's surface vertically above the
focus of an earthquake. Earthquake results from the sudden release of pressure
which has slowly built up within the earth’s crust. Energy is released in the
form of shockwaves known as seismic waves. The seismic waves can broadly be
classified into two types namely Body waves and surface waves.
1. Body Waves are the waves that travel through the interior of the earth. They are further divided into the following.
a. P or Primary or Compressional
waves are the fastest seismic waves
(6 km/ sec. in the upper crust). They cause the matter to oscillate forward and
backward, parallel to the motion of the seismic wave front. P waves push
(compress) and pull (dilate) the rock that they pass through. They pass through
all medium.
b. S or Secondary or Shear waves are slower than the primary waves
(3.5 km/sec. in the upper crust). They cause matter to oscillate side to side,
perpendicular to the motion of the wave front. S waves shear the rock that they
pass through. They pass through only solid medium.
II. Surface Waves are the waves that travel
along the earth's surface. They are slower than body waves. They cause damage
during earthquakes.
Love waves shake the ground side to side
like S wave.
Rayleigh waves displace the ground like
rolling ocean waves. The ground rolls forward and up and then down and
backwards. This is similar to a p wave but with the extra up-down motion.
Measuring the earthquake
It is estimated that about 100,000 earthquakes
occur but all cannot be felt. A few earthquakes may be severe causing huge
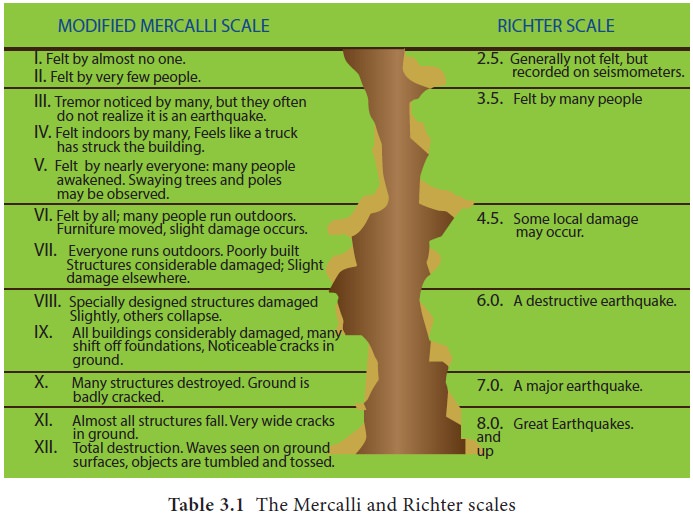
damage to property. Earthquake magnitude is measured on the Richter scale
(named after the seismologist who devised it), which rates them on a scale of 1
to 10. Earthquake intensity is measured on the modified Mercalli scale, which
ranges from 1 to 12, depending upon the intensity. The seismograph is an instrument
used to detect and record seismic waves created by the earthquakes.
Description of effects of earthquake in Richter scale
Causes of Earthquakes
There are many factors controlling the occurrence
of the earthquake. Some of the major factors include:
1.
Plate
Tectonic Movements
2.
Volcanic
Eruptions.
3.
Construction
of large dams results in earthquake. Example. Koyna dam, Maharashtra.
4.
Other
Reasons: The nuclear explosions also release massive energy to cause tremors in
the earth crust. When underground cave collapses, earthquake may occur.
Effects of the Earthquakes
1.
Damage
to buildings, roads, rails, factories, dams, bridges etc.
2.
Landslides
caused by earthquakes damage infrastructure.
3.
Fires
in the forest and urban areas.
4.
Flash
floods.
5.
Tsunami
- The high amplitude oceanic waves caused by submarine earthquake (measuring
more than 7 on Richter scale). The seismic waves travel through seawater
generates high sea waves. They cause severe loss of life and property. For
instance, on 26th December 2004, a tsunami originating from a magnitude 8.9
earthquake in northern Sumatra killed over 1,50,000 people in countries
surrounding the Indian Ocean.
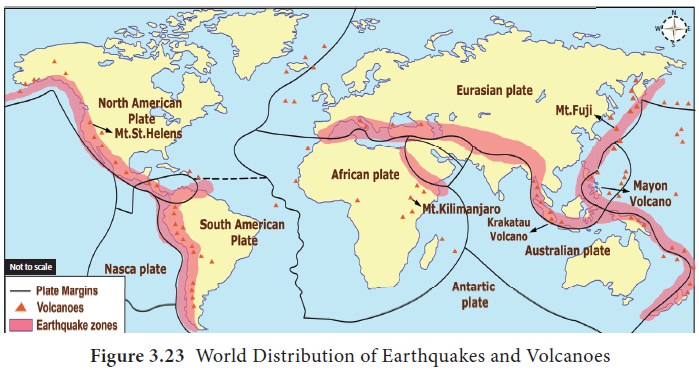
Distribution of earthquakes
1. Circum-Pacific region: This region includes all the coastal areas around the Pacific Ocean. It extends through the coasts of Alaska, Aleutian Islands, Japan, Philippines, New Zealand, west coast of North and South America. This zone accounts for 68% of all earthquakes on the surface of the earth.
2. Mediterranean-Himalayan region: This region
extends from Alps mountain to the Himalayan Mountains and Tibet to China. About
31% of world's earthquakes occur in this region.
3. Other Areas: These include Northern Africa and
Rift Valley areas of the Red Sea and the Dead Sea.
Related Topics