Geography - Rock Types | 11th Geography : Chapter 3 : Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes
Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 3 : Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes
Rock Types
Rocks
Rock is the solid mineral material forming the
surface of the earth. Petrology is the science of rocks. The age of the rock is
determined based on Carbon-14 dating.
Rock
Types
Based on their origin, the rocks are classified as
follows:
1. Igneous Rocks
Igneous rocks are formed out of magma and lava and
they are known as primary rocks. If the magma cools slowly at great depths,
mineral grains increase in their size. Sudden cooling (at the surface) results
in small and smooth grains. The igneous rocks are the oldest of all the rocks.
Granite, pegmatite, basalt, etc are some of the examples of igneous rocks.
There are two types of igneous rocks: intrusive rocks (Granite) and extrusive
rocks (Basalt-Deccan Traps).
Granite is less dense and is lighter in colour than
basalt rocks.
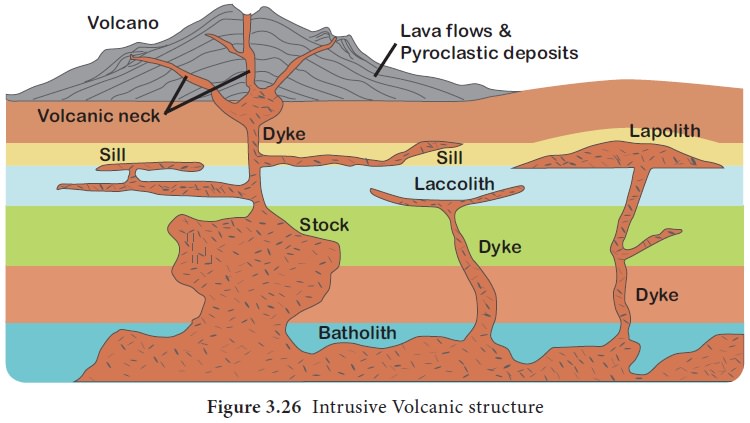
Intrusive Igneous rocks
Intrusive Igneous rocks are formed when magma rises
and cools within the crust. The intrusive activity of volcanoes gives rise to
various forms. We see them one by one as follow.
1. Batholiths
Batholiths are large rock masses formed due to
cooling and solidification of hot magma inside the earth. It is granitic in
origin.
2. Laccoliths
Laccoliths are large dome-shaped intrusive rock
connected by a pipe-like conduit from below. These are basically intrusive
counterparts of an exposed domelike batholiths. The Karnataka plateau is
spotted with dome hills of granite rocks. Most of these, now exfoliated, are
examples of laccoliths.
3. Lapoliths
When the magma moves upwards, a saucer shape,
concave shaped body called Lapolith is formed.
4. Sill
Sill is a solidified sheet-like horizontal lava
layer inside the earth. The near horizontal bodies of the intrusive igneous
rocks are called sill or sheet, depending on the thickness of the material. The
thinner ones are called sheets while the thick horizontal deposits are called
sills.
5. Dyke
When the magma makes its way through cracks and the
fissures developed in the land, it solidifies almost perpendicular to the
ground. It gets cooled in the same position to develop a wall-like structure.
Such structures are called dikes.
These are the most commonly found intrusive forms
in the western Maharashtra area. These are considered the feeders for the
eruptions that led to the development of the Deccan traps.
2. Sedimentary Rocks
Sedimentary rocks are also called as detrital rocks. They are formed as a result of denudation. These deposits through compaction turn into sedimentary rocks.
They occupy
only 5 percent of the earth. They are layered or stratified of varying
thickness. Example: sandstone, shale etc. Ice deposited sedimentary rocks is
called Till. Wind-deposited sediments are called Loess.
1.
Depending
upon the mode of formation, sedimentary rocks are classified into Mechanically
formed sedimentary rocks: sandstone, conglomerate, limestone, shale, loess,
etc.
2.
Organically
formed sedimentary rocks: geyserites, chalk, limestone, coal etc.
3.
Chemically
formed: halite, potash, etc.
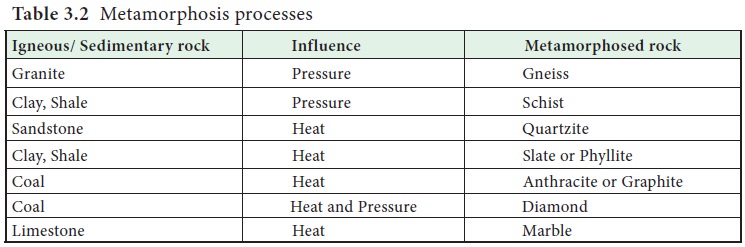
3. Metamorphic Rocks
The word metamorphic means ‘change of form’. The
metamorphic rocks form under the action of pressure, volume and temperature
(PVT) change.
Metamorphism is a process by which the already
consolidated rocks undergo recrystallisation and reorganization of materials
within original rocks. Gneiss, slate, schist, diamond, marble, quartzite etc.
are some examples of metamorphic rocks. The igneous and metamorphic rocks
together account for 95 percent of the earth.
Related Topics