Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes - Plate boundaries | 11th Geography : Chapter 3 : Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes
Chapter: 11th Geography : Chapter 3 : Lithosphere: Endogenic Processes
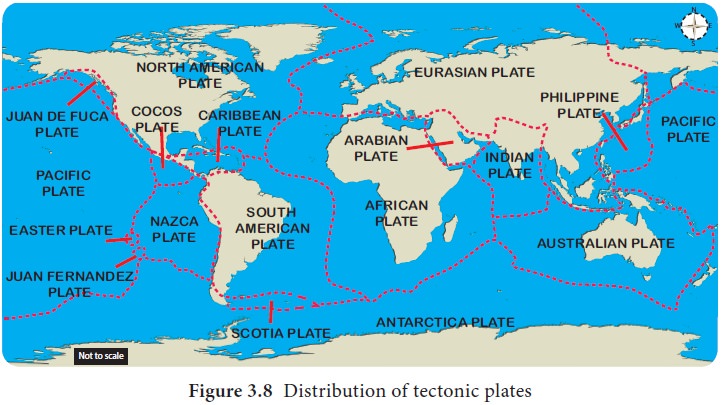
Plate boundaries
Plate
boundaries
Plate boundaries are the zones where two or more
plates move about. Plate tectonics describes the distribution and motion of the
plates. The earth's surface is composed of rigid lithospheric slabs technically
called “plates”. The word
Lithospheric plates are sometimes called as crustal
plates or tectonic plates. Earth's lithosphere is divided into a series of
major and minor mobile plates. Eurasian plate, Indo-Australian plate, North
American plate, South American plate, Pacific plate, African plate and
Antarctic plate are the major plates. Arabian plate, Caribbean plate, Cocas
plate and Scotia plate are the examples of minor plates. Plates move at the
rate of 2 to 3 centimeters per year.
Plates are composed of the continental or oceanic
landmass. The subduction of the oceanic plates results in the occurrence of
earthquakes and volcanoes adjacent to trenches.
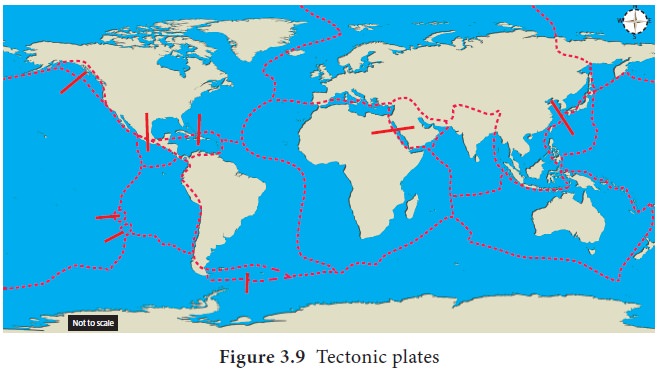
Plate margins mark the occurrence of the most
significant landforms, including volcanoes, fold mountains, island arcs and
deep-sea trenches. There are three principal types of plate boundaries. They
are divergent, convergent, and transform boundaries.
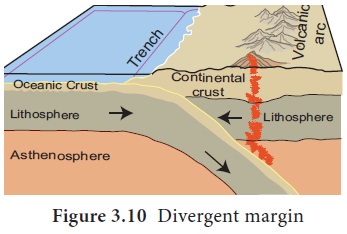
Divergent plate boundaries
Divergent plate boundary is the margin where two
plates move apart. For instance, the African plate and South American plate
move apart and form a divergent plate boundary. Narrow oceans represent young
divergent boundaries and wide oceans are indications of old ocean basins. Ocean
ridges are the boundaries between plates of the lithosphere.
A fissure is created when oceanic lithosphere
separates along the oceanic plate boundary. The gap is filled by magma that
rises from the asthenosphere. The magma cools and solidifies to create a new
oceanic crust. Hence, the divergent plate boundary is termed as the
constructive plate boundary. It is also called as accreting plate margin.
Let us see what happens in the divergent plate boundary.
Firstly, submarine mountain ridge is formed through the fissures in the oceanic
crust when the plates move apart.
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is an ideal example of a
submarine mountain ridge in the Atlantic Ocean. It is the longest mountain
ridge in the world.
It extends for about 16,000 km, in a 'S' shaped path, between Iceland in the north and Bouvet Island in the south. It is about 80 to 120 km wide. It reaches above the sea level in some places thus forming the islands such as the Azores, Ascension, St. Helena and Tristan da Cunha.
Secondly, rift valley is formed when two plates
move apart. If a divergent boundary runs through the continent, the continent
splits apart and rift valley is formed. The African Rift Valley of East Africa
is an example.
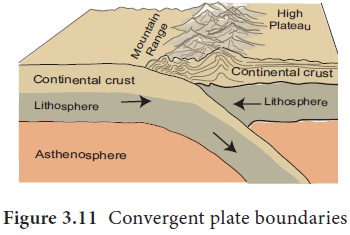
Convergent plate boundary
Convergent plate boundary is the margin where two
plates collide with one another. For instance, the South American plate and
Nazca plate collide with each other. There are two kinds of surface features
associated with the convergent margin. The first is the ocean trench that forms
a line between the two colliding plates.
A trench is a narrow and deep depression of the
ocean floor. It is formed when the oceanic plate slides down underneath
continental plate as the oceanic plate is denser than the continental plate.
For instance, Mariana Trench in the Pacific Ocean, is the deepest trench in the
world. It is formed when the Pacific plate sinks down the Eurasian plate. It is
about 10,994 metres (10.99 km) deep. Mariana Trench stretches for more than
2,540 km with a width of 69 km.
You could take Mount Everest and sink it in the
Mariana Trench, the deepest point in the ocean, and still you have a km of
depth to reach the surface of the ocean.
When a continental plate and an oceanic plate
collide with each other, denser oceanic plate sinks below the lighter
continental plate, subduction zone is formed.
A subduction zone is a boundary where one plate
sinks under the other plate. It was first identified by Kiyoo Wadati and
Benioff.
Secondly fold mountain is formed when two plates
collide each other. For instance, the Himalayas were formed when the Indian
plate collided with the Eurasian plate. The zone marking the boundary of the
two colliding plates is known as suture line.
As the crust
is less dense than the mantle, the newly formed magma will tend to rise to the
Earth’s surface, where it may form volcanoes. The area in the subduction zone
where most earthquakes occur is known as the Benioff zone.
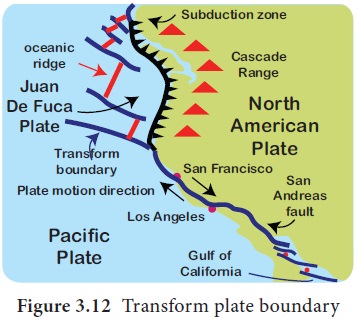
Transform plate boundaries
Transform plate boundary is the margin where two
plates move side by side. The lithosphere is neither destroyed nor created by
the transform plate boundary. Hence it is called as the Conservative or passive
plate boundary. The San Andreas Fault, California, is a transform boundary that
separates the North American plate and Pacific Plates.
Related Topics