Chapter: Biology: Structural Organization and Acquaintance of Animals
Toad: Respiratory system
Respiratory system: Energy is necessary for different metabolic activities.Usable energy is
produced inside cells by oxidation-reduction of glucose with the help of
mitochondria. Water, C02, generally ATP (Adenosine Tri Phosphate) and heat are produced by this
process. Cells can not use heat energy, so it is lost. ATP instantly supplies energy
when it is needed. It should be kept in mind that in extensive heat, protoplasm
gets paralyzed. For these reasons the cellular respiration process takes place
step by step with the help of various type of enzymes. This process of energy
generation inside cells is known as internal or cellular respiration. For this
oxygen is essential. The process of collecting oxygen from the environment to
every cells of the body is known as external respiration. In this process body
receives oxygen enriched air and expels C02 from the body.
Cellular respiration process of metabolic activities of all organisms is
same, among these the main metabolic path is Kreb's Cycle. To live in different
habitats of environments, toads respire through different methods of external respiration.
To live in different environments, the toad respires in more than
Generally, the
process of external respiration in toad is of four types.
1.
Cutaneous respiration
2.
Bucco- pharyngeal respiration
3.
Pulmonary respiration
4.
Gill respiration
1. Cutaneous respiration : This type of respiration takes place through theskin. The skin of toad
is very thin and enriched with blood capillaries. The skin of toad contains a
large number of mucus glands. Mucus is discharged from these glands; as a
result the skin remains moist. For this reason, exchange of oxygen and carbon
dioxide take place through skin easily in the process diffusion. During
hibernation the toad respires by this process.
2. Bucco-pharyngeal respiration: The membrane of buccal cavity andpharynx of toad is very thin and there
are innumerable capillaries. When air enters the buccal cavity oxygen gets into
the blood of the capillaries by diffusion. This oxygenated blood flows to
different parts of the body through heart and at one stage takes part in the
oxidation of food inside the cell. The carbon dioxide produced as a result of
oxidation of food comes out through diffusion. The toad respires this way
generaly during rest.
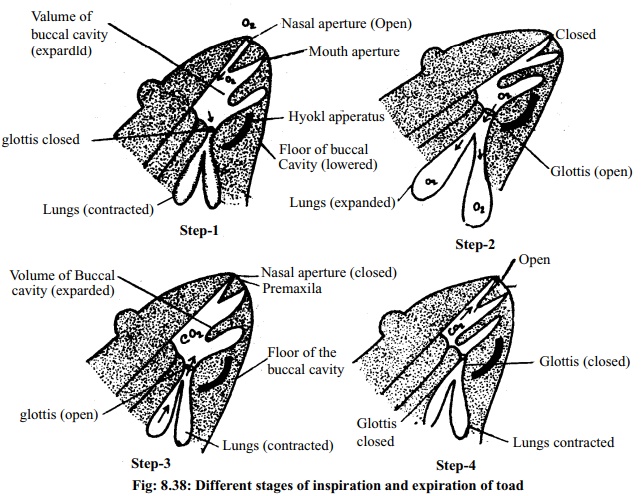
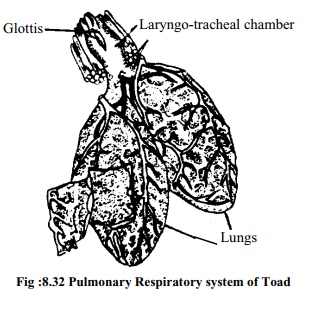
3. Pulmonary respiration: Lungs are the main
respiratory organs of toad. The toad has a pair of lungs. The lungs are pink
coloured hollow sacs. Each lung is formed of innumerable smaller chambers like
balloons. Each of this balloon like chambers is called air sac or alveolus. Its
wall is enriched with blood vessels. When the lungs expand the air sacs become,
filled with air. Exchange of oxygen andcarbon-dioxide taxes place through the
air sacs. The fine air tubes with which the air sacs remain connected are
called bronchioles. The two tubes which are formed one on each side by joining
all the bronchioles of each lung are called bronchus: Right and left bronchi
meet together and form a small trachea. Trachea and larynx or voice apparatus
together form the laryngo-tracheal chamber. The lungs of each side joining with
the larynx and glottis open through the nasal aperture. The adult and active
living toad respires through pulmonary respiration. The pulmonary respiration
is actually external respiration. External respiration is again divided into
two sub stages such as, Intake of air or
inspiration and Release of air or expiration.
Inspiration: At this stage oxygen along with the air enters the lungs from
theenvironment. Inspiration occurs in two steps.
A. First step: At this time the nasal apertures remain open but the mouthaperture and
glottis remain closed. Simultaneously the lungs contract and the floor of the
buccal cavity are lowered. As a result, the volume of the buccal cavity
increases. The oxygenated air from outside enters the buccal cavity. At this
time exchange of oxygen and carbon-dioxide takes place in the blood of
capillaries situated in the walls of the buccal cavity and pharynx.
B. Second step: At this stage the nasal apertures are closed and the floor of thebuccal
cavity is raised. As a result, oxygenated air enters the alveoli of the lungs.
By the diffusion process oxygen from the cavities of the alveoli enters the
blood capillaries close to the walls of the alveoli. In a similar process
carbon-dioxide is released.
Expiration: At this stage from the alveoli carbon-dioxide comes out of thebody.
Expiration, occurs in two steps:
A. First step: At the first step of expiration the two lungs contract, externalnasal
apertures and mouth aperture remain closed and the floor of the buccal cavity
is lowered. As a result volume of the buccal cavity increases and
carbon-di-oxide mixed air returns to the buccal cavity.
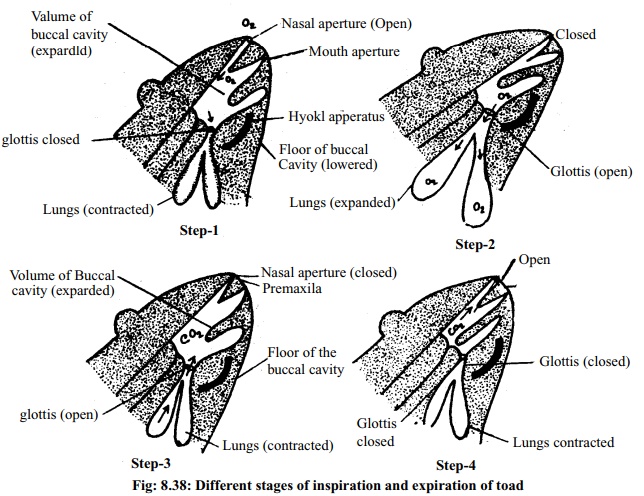
B. Second step: The floor of the buccal cavity is raised. The volume of buccalcavity
reduce. At this time the glottis remains closed and the nasal apertures remain
open. As a result through nasal apertures the carbon-dioxide enriched air comes
outside.
Internal respiration: We have learnt earlier that internal respiratior basicallycell
respiration. In this process exchange of oxygen and carbon-dioxide takes place
in the blood of capillaries. At the cellular level energy produced through
oxidation of glucose.
Transportation of oxygen: As a result of the entrance of air inside the lungsthe air of the lungs
gets oxygen. The moist vapor that remains in this reaches to the interior part
of the alveoli. Oxygen dissolves in watery drops a result the volume and
pressure of oxygen increase. At this time the volt and pressure of oxygen in
the blood of capillaries on the body walls of alvi remain less. As a result
oxygen enters the blood through diffusion process. this time oxygen combines
with the haemoglobin of blood, to form compound known as oxyhaemnglobin.
Haemoglobin + Oxygen →
Oxy-haemoglobin.
This oxygen enriched blood reaches the body cells through the heart. The
volume and pressure of oxygen remain less in the body cells, so breaking the
oxyhaemoglobin the oxygen separates and enters the cells. This oxygen oxidizes
the simple food (glucose) of the cells and produces energy.
Oxy-haemoglobin = Haemoglobin +
oxygen.
Related Topics