Chapter: Biology: Structural Organization and Acquaintance of Animals
External morphology of Toad
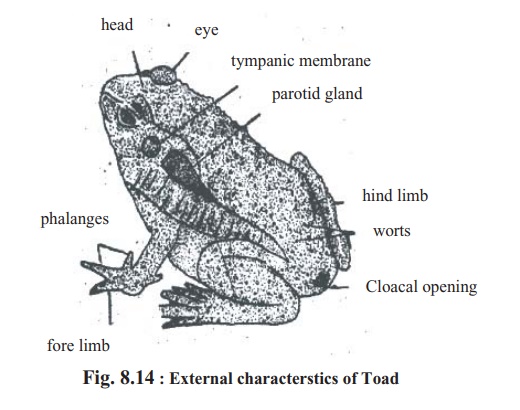
External morphology of Toad :
Toad is an ugly animal. Its skin is grey coloured with warts. Toad is 10-13 cm long and 7 cm wide. Its body can be divided longitudinally into two similar parts. So they are bilaterally symmetrical.
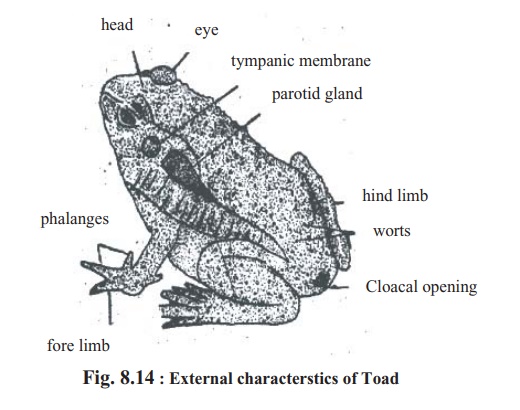
The body of toad can be divided into two regions head and trunk. It has no neck. A fully-grown toad has no tail and the fingers of the feet are clawless.
Head : The front portion of the head of toad is blunt and the posterior portionwide. At the front end of the head there is a wide mouth situated transversely. There are two jaws above and below the mouth aperture. There are no teeth in the jaw. At the upper side of the mouth towards the front end of the head there are two apertures provided with thin valves. These apertures are the nasal apertures. Two round eyes are situated at the posterior part of the nasal apertures. In the eye of toad there are three eyelids, upper eyelid, lower eyelid and a transparent thin membrane. This thin membrane is called nictitating membrane. There are no hairs in the eyelids of toad, nictitating membrane protects the eye from dust and keeps it moist.
At the back of each eye there is situated a round, smooth membrane they are tympanum. At the back of the ears there are two glands on the two sides. These are called parotid glands. From these glands toxic juices are secreted. Toad utilizes this secretion for self-defense. At the junction of head and trunk of male toad, that is, on the ventral side of the mouth cavity, there is a blackish sac. It is called vocal sac. Vocal sac takes part in the production of sound.
Trunk : The trunk of the toad is small and the thorax and abdomen cannot bemarked separately. The trunk is wider and bulkier than the head. They have a pair of legs in front and a pair at the back of the trunk. Front pair of legs is called forelimbs and the posterior pair is called hind limbs. As the base of the fingers of their legs is partly joined together by a thin membrane, they are called webbed feet. In the forelimb of toad there are four and in the hind limb there are five clawless fingers.
During the breeding season at the lower side of the forelimb of the male toad a kind of pad is seen. It is called nuptial pad. At the end of the posterior there is an aperture. This aperture is known as cloacal aperture, through which faeces, urine and reproductive cells are discharged outside. Observing the external characteristics, it is possible to separate the female toads from the male ones. During the breeding season these differences are more obvious.

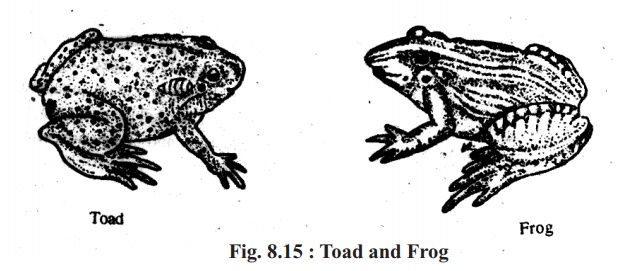
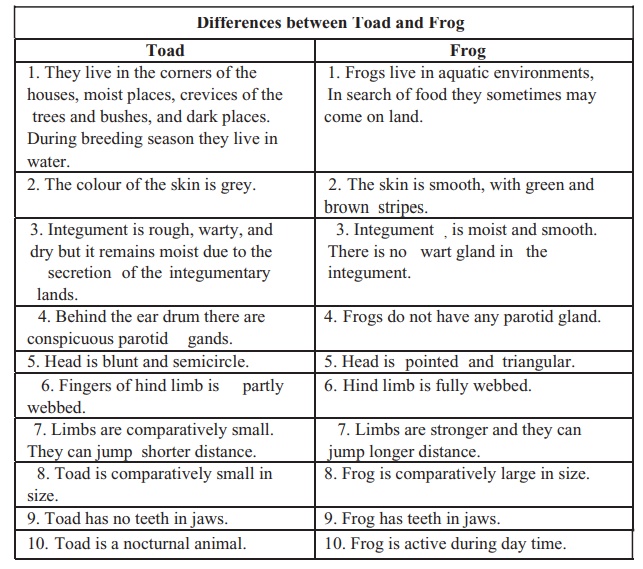
In our country mainly two types of toad are available; One is the toad and the other is frog. They both feed on insects, worms and other small living creatures, Many of the insects, worms and the living creatures harm the crops. Toads eat them to benefit men. The differences between these two types of toads are given in the following table.
Related Topics