Light | Chapter 3 | 8th Science - Student Activities | 8th Science : Chapter 3 : Light
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 3 : Light
Student Activities
Activity 1
Take a curved silver spoon and see the image formed by it. Now, turn it and find the image formed. Do you find any difference? Find out the reason.

Answer:
Reason :
(i) The curved surface of the spoon acts as a reflecting surface. But this reflecting surface is not flat like that of a plane mirror. Thus the spoon behaves as a curved mirror.
(ii) The inner side of the spoon is referred to as the concave side whereas the back (outer) bulging side is referred to as the convex side.
(iii) You will observe that the image is (inside bowl) always real, inverted and formed on the same side of the object.
(iv) In outside bowl the image is diminished erect and virtual.
Activity 2
List out various convex and concave mirrors used in daily life.
Answer:
Concave mirrors :
(i) It is used as torch to reflect the light.
(ii) It is used in the aircraft landing at the airports to guide the aeroplanes.
(iii) In shaving mirrors to get an enlarged and erect image of face.
(iv) In front light of cars.
(v) In marine lighthouses to guide the ships and
(vi) In the solar ovens for cooking food, heating water, recharging power back ups or melting metals.
(vii) In satellite dishes, telescopes, Dentist and ENT Doctors to obtain a larger image.
(viii) In electron microscopes and magnifying glasses.
(ix) In visual bomb detectors,
(x) In flash light mirror of camera.
Convex mirrors :
(i) Used as side - view mirror of a car as it forms an erect and smaller image.
(ii) Suitable for convenient shop and big supermarket any other comer where need anti - thief.
(iii) In the turning off the road and parking.
(iv) In making lenses of sunglasses.
(v) In securities and used in telescopes.
(vi) Used as street light reflectors because they can spread the light over a bigger area.
(vii) Used as ceiling dome mirrors.
Activity 3
Take a plane mirror and focus the light coming from the Sun on a wall. Can you see a bright spot on the wall? How does it occur? It is because the light rays falling on the mirror are bounced onto the wall. Can you produce the same bright spot with the help of any other object having a rough surface?
Answer: (i) All the objects cannot produce the same effect as produced by the plane mirror.
(ii) A ray of light, falling on a body having a shiny, polished and smooth surface alone is bounced back.
Activity 4
Take two plane mirrors and keep them perpendicular to each other. Place an object between them. You can see the images of the object. How many images do you see in the mirrors? You can see three images. How is it possible to have three images with two mirrors?
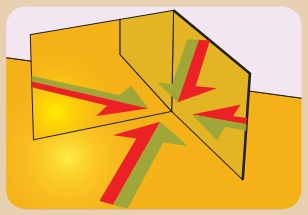
Answer:
Aim : To understand the concept multiple reflection.
Materials required : Two plane mirrors, an object.
Procedure :
(i) Take two plane mirrors and keep them perpendicular to each other.
(ii) Place an object between them.
Observation : We can see three images of the object.
Inference :
(i) When a body kept in between two plane mirrors, which were inclined to each other. You could see many images. This is because, the image formed by one mirror acts as an object for the other mirror.
(ii) The image formed by the first mirror acts as an object for the second mirror and the image formed by the second mirror acts as an object for the first mirror.
(iii) Thus we have three images of a single body. This is known as multiple reflection.
Activity 5
Take three equal sized plane mirror strips and arrange them in such a way that they form an equilateral triangle. Cover the sides of the mirrors with a chart paper. In the same manner cover the bottom of the mirrors also. Put some coloured things such as pieces of bangles and beads inside it. Now, cover the top portion with the chart paper and make a hole in it to see. You can wrap the entire piece with coloured papers to make it attractive. Now, rotate it and see through its opening. You can see the beautiful patterns.
Caution: Be careful while handling the glass pieces. Do this under the supervision of your teacher.
Answer:
Aim : To construct kaleidoscope and to produce numerous patterns of images.
Materials required : Three equal sized plane mirrors, chart paper, pieces of bangles and beads, coloured papers.
Procedure :
(i) Take three equal sized plane mirror strips and arrange them in such a way that they form an equilateral triangle.
(ii) Cover the sides of the mirrors with a chart paper.
(iii) With the help of a chart paper cover the bottom of the mirrors also.
(iv) Put some coloured things such as pieces of bangles and beads inside it.
(v) Now, cover the top portion with the chart paper and make a hole in it to see.
(vi) You can wrap the entire piece with coloured papers to make it attractive.
(vii) Now, rotate it and see through its opening. You can see the beautiful patterns.
Observation : We can see the beautiful image patterns.
Inference : Kaleidoscope is a device, which functions on the principle of multiple reflection of light to produce numerous patterns of images.
Activity 6
Take a glass beaker, fill it with water and place a pencil in it. Now, look at the pencil through the beaker. Does it appear straight? No. It will appear to be bent at the surface of the water. Why?

Answer:
Aim : To understand refraction of light.
Materials required : Glass beaker, water, pencil.
Procedure :
(i) Take a glass beaker.
(ii) Fill it with water
(iii) Place a pencil in it.
(iv) Now look at the pencil through the glass beaker.
(v) Does it appear straight?
Observation : It will appear to be bent at the surface of the water.
Inference :
The light rays actually travel from the water (a denser medium) into the air (a rarer medium).
(ii) When a light ray travels from a denser medium to a rarer medium, it is deviated from its straight line path.
(iii) So, the pencil appears to be bent when you see it through the glass of water.
(iv) Thus; the bending of light rays when it travels from one medium to another medium is called refraction.
Activity 7
Place a prism on a table and keep a white screen near it. Now, with the help of a torch, allow white light to pass through the prism. What do you see? You can observe that white light splits into seven colored light rays namely, violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red (VIBGYOR) on the screen. Now, place another prism in its inverted position, between the first prism and the screen. Now, what do you observe on the screen? You can observe that white light is coming out of the second prism.

Answer:
Aim : To understand about dispersion of light.
Materials required : Prism - 2, white screen, torch light.
Procedure :
(i) Place a prism on a table and keep a white screen near it.
(ii) Now with the help of a torch, allow white light to pass through the prism. What do you see?
(Hi) Now, place another prism in its inverted position, between the first prism and the screen. What do you observe on the screen?
Observation I : We can observe that white light splits into seven coloured light rays namely, violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red (VIBGYOR) on the screen.
Observation II : (After placing second prism)
(i) We can observe that white light is coming out of the second prism.
(ii) The first prism splits the white light into seven coloured light rays and the second prism recombines them into white light again.
Inference : It is clear that white light consists of seven colours.
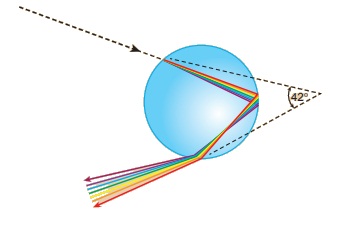
Conclusion : Splitting of white light into its seven constituent colour, on passing through a transparent medium is known as dispersion of light.
The formation of rainbow is an example of dispersion of white light. This can be seen on the opposite side of the Sun. After rainfalllarge number of droplets still remain suspended in the air. When white light passes through them, it is split into seven colours. Dispersion of white light from a large number of droplets eventually forms a rainbow.
Related Topics