Light | Chapter 3 | 8th Science - Points to Remember, Glossary, Concept Map | 8th Science : Chapter 3 : Light
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 3 : Light
Points to Remember, Glossary, Concept Map
Points to Remember
• Mirror is an optical device with a
polished surface that reflects the light falling on it.
• Curved mirrors have surfaces that
are spherical, cylindrical, parabolic and ellipsoid.
• If the curved mirror is a part of
a sphere, then it is called a ‘spherical mirror’.
• A spherical mirror, in which the
reflection of light occurs at its concave surface, is called a concave mirror.
• A spherical mirror, in which the
reflection of light occurs at its convex surface, is called a convex mirror.
• The focal length of a spherical
mirror is half of its radius of curvature.
• Real images can be formed on a
screen, while virtual images cannot be formed on a screen.
• Concave mirrors form a real image
and it can be caught on a screen.
• Concave mirrors are used as
make-up mirrors.
• Convex mirrors are used in
vehicles as rearview mirrors.
• Based on the nature of the
surface, reflection can be classified into two types namely, regular reflection
and irregular reflection.
• The number of images formed by a
mirror depends on the angle of inclination of the mirrors.
GLOSSARY
1.
Center of Curvature The
center of the sphere from which the mirror is made.
2.
Dispersion of light Splitting
of white light into its seven constituent colours (wavelength).
3.
Focal length Distance
between the pole and the principal focus.
4.
Focus Point where the
reflected rays converge at or appear to diverge from a pointon the principal
axis.
5.
Kaleidoscope Device
which produces numerous and wonderful image patterns.
6.
Periscope Instrument used for
viewing objects, which are over and around another body.
7.
Pole Point on the mirror’s surface where
the principal axis meets the mirror.
8.
Principal Axis Line
joining the pole of the mirror and its center of curvature.
9.
Radius of Curvature Distance
between the center of the sphere and the vertex.
10.
Reflection Bouncing back of
the light rays as they fall on the smooth, shiny and polished surface.
11.
Refraction of light Bending
of light about the normal, at the point of incidence; as it passes from one
transparent medium to another.
12.
Refractive index Ratio
of the speed of light in the air to the speed of light in that particular
medium.
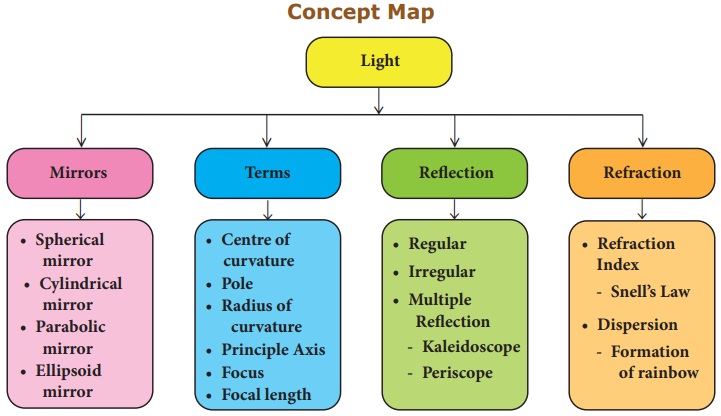
Concept Map
REFERENCE BOOKS
1. Frank New Certificate Physics
(2017). Frank Bros. & Co., Chennai.
2. Concise Physics (2017). Selena
Publishers, New Delhi.
3. Cambridge IGCSC Physics (2002) .
Hodder education, London.
4. Physics for Standard XI (2005). Tamil Nadu
Textbook Corporation, Chennai.
INTERNET RESOURCES
https://farside.ph.utexas.edu
https://britannica. com
https://studyread. Com
Related Topics