Light | Chapter 3 | 8th Science - Questions Answers | 8th Science : Chapter 3 : Light
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 3 : Light
Questions Answers
TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
I. Choose the best answer.
1.
Which of the following has curved reflecting surface?
a) plane mirrors
b) spherical mirrors
c) simple mirrors
d) None of the above
[Answer: (b) spherical mirrors]
2.
The spherical mirror with a reflecting surface curved inward is called
a) convex mirror
b) concave mirror
c) curved mirror
d) None of the above
[Answer: (b) concave mirror]
3.
The spherical mirror used as a rear view mirror in the vehicle is
a) concave mirror
b) convex mirror
c) plane mirror
d) None of the above
[Answer: (b) convex mirror]
4.
The imaginary line passing through the centre of curvature and pole of a
spherical mirror is called
a) centre of curvature
b) pole
c) principal axis
d) radius curvature
[Answer: (c) principal axis]
5.
The distance from the pole to the focus is called
a) pole length
b) focal length
c) principal axis
d) None of the above
[Answer: (b) focal length]
6.
If the image and object distance is same, then the object is placed at
a) infinity
b) at F
c) between f and P
d) at C
[Answer: (d) at C]
7.
If the focal length of a spherical mirror is 10 cm, what is the value of its
radius of curvature?
a) 10 cm
b) 5 cm
c) 20 cm
d) 15 cm
[Answer: (c) 20 cm]
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. The spherical mirror used in a
beauty parlour as make-up mirror is concave mirror.
2. Geometric centre of the spherical
mirror is pole.
3. Nature of the images formed by a
convex mirror is smaller, virtual and erect.
4. The mirror used by the
ophthalmologist to examine the eye is concave mirror.
5. If the angle of incidence is 45°,
then the angle of reflection is 45°.
6. If an object is placed between
two mirrors which are parallel to each other, the number of images formed is infinite.
III. Match the following.
1. Convex mirror - Radio telescopes
2. Parobolic mirror - Rear – view
mirror
3. Snell’s law - Kaleidoscope
4. Dispersion of light - sin i/sin r
=μ
5. Refractive index - Rainbow
[Ans : 1
- b, 2 - a, 3 - d, 4 – e 5-c]
1. Convex
mirror (b) rear - view mirror
2.
Parobolic mirror (a) Radio telescopes
3. Snell’s law (d) sini/sinr = μ
4. Dispersion of light (e) Rainbow
3. Refractive index
IV. Answer briefly.
1.
Define focal length.
Answer: The distance between the pole and the principal focus is called focal
length (f) of a spherical mirror.
2.
Give any two applications of a concave and convex mirror.
Answer:
Concave
mirrors :
(i) Concave mirrors are used while applying make-up or shaving,
as they provide a magnified image.
(ii) They are used in torches, search lights and head lights as
they direct the light to a long distance.
Convex
mirrors :
(i) Convex mirrors are used in vehicles as rear view mirrors
because they give an upright image and provide a wider field of view as they
are curved outwards.
(ii) They are found in the hallways of various buildings
including hospitals, hotels, schools and stores. They are usually mounted on a
wall or ceiling where hallways make sharp turns.
3.
State the laws of reflection.
Answer:
(i) The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the
point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are
always equal.
4.
Define the refractive index of a medium.
Answer: The amount of refraction of light in a medium is denoted by a
term known as refractive index of the medium, which is the ratio of the speed
of light in the air to the speed of light in that particular medium.
5.
State Snell’s law of refraction
Answer: Refraction of light rays, as they travel from one medium to
another medium, obeys two laws, which are known as Snell’s laws of refraction.
They are:
(i) The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal at the
point of intersection, all lie in the same plane.
(ii) The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence (i) to the
sine of the angle of refraction (r) is equal to the refractive index of the
medium, which is a constant,
(sin i/ sin r) = μ
V. Answer in detail.
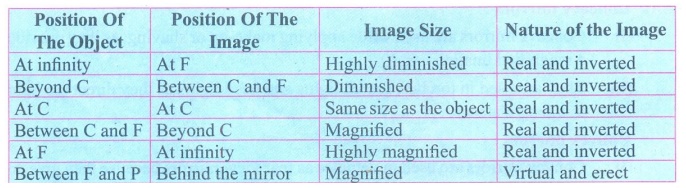
1. Explain the images formed by a
concave mirror.
Answer:
2.
What is reflection? Write a short note on regular and irregular reflection.
Answer: A ray of light, falling on a body having a shiny polished and
smooth surface alone is bounced back. This bouncing back of the light rays as
they fall on the smooth, shiny and polished surface is called reflection.
Regular
reflection :
(i) When a beam of light (collection of parallel rays) falls on
a smooth surface, it gets reflected.
(ii) After reflection, the reflected rays will be parallel to
each other. Here, the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection of each
ray will be equal.
(iii) Hence, the law of reflection is obeyed in this case and
thus a clear image is formed. This reflection is called ‘regular reflection’ or
‘specular reflection’.
Irregular
reflection :
(i) In the case of a body having a rough or irregular surface,
each region of the surface is inclined at different angles.
(ii) When light falls on such a surface, the light rays are
reflected at different angles.
(iii) In this case, the angle of incidence and the angle of
reflection of each ray are not equal.
(iv) Hence, the law of reflection is not obeyed in this case and
thus the image is not clear. Such a reflection is called ‘irregular reflection’
or ‘diffused reflection’.
3.
Explain the working of a periscope.
Answer:
Periscope
: .
(i) It is an instrument used for viewing bodies or ships, which
are over and around another body or a submarine.
(ii) It is based on the principle of the law of reflection of
light.
(iii) It consists of a long outer case and inside this case
mirrors or prisms are kept at each end, inclined at an angle of 45°.
(iv) Light coming from the distant body, falls on the mirror at
the top end of the periscope and gets reflected vertically downward.
(v) This light is reflected again by the second mirror kept at
the bottom, so as to travel horizontally and reach the eye of the observer.
(vi) In some complex periscopes, optic fibre is used instead of
mirrors for obtaining a higher resolution.
(vii) The distance between the mirrors also varies depending on
the purpose of using the periscope.
4.
What is dispersion? Explain in detail.
Answer:
(i) Splitting of white light into its seven constituent colours
(wavelength), on passing through a transparent medium is known as dispersion of light.
(ii) Dispersion occurs because, light of different colours
present in white light have different wavelength and they travel at different
speeds in a medium.
(iii) Refraction of a light ray in a medium depends on its
speed.
(iv) As each coloured light has a different speed, the
constituent coloured lights are refracted at different extents, inside the
prism. Moreover, refraction of a light
ray is inversely proportional to its wavelength.
VI. Numerical problems.
1. The
radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 25 cm. Find its focal length.
Answer:
Given : Radius of curvature = 25 cm
To find : f = ?
Solution
: f = R/2 = 25/2
f = 12.5 cm
2.
If two plane mirrors are inclined to each other at an angle of 45°, find the
number of images formed.
Answer:
Given : Angle of inclination = 45o
To find : Number of images formed = [ 360o / angle ] − 1
Solution
:
= [ 360o / 45o
] −1
= 8 – 1 = 7 images
3.
Speed of light in air is 3 × 108 m s–1 and the refractive
index of a medium is 1. 5. Find the speed of light in the medium.
Answer:
Given : Speed of light in air c = 3 × 108 ms-1
Refractive index of a medium μ = 1.5
To find : Speed of light in medium v
= ?
Formula : μ= c/v
Solution : 1.5 = [ 3 × 108 ] / v
V = [3×108] / 1.5
v = 2 × 108 ms-1
Speed of light in medium v = 2 × 108 ms-1
Related Topics