Light | Chapter 3 | 8th Science - Terms related to Spherical Mirrors | 8th Science : Chapter 3 : Light
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 3 : Light
Terms related to Spherical Mirrors
Terms related to
Spherical Mirrors
In
order to understand the image formation in spherical mirrors, we need to know
about some of the terms related to them.
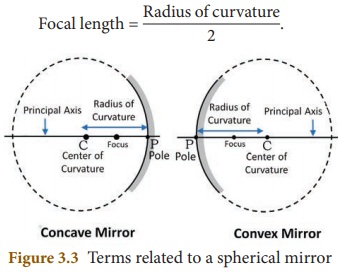
Center of Curvature
It
is the center of the sphere from which the mirror is made. It is denoted by the
letter C in the ray diagrams. (A ray diagram represents the formation of an
image by the spherical mirror. You will study about them in the higher
classes).
Pole
It
is the geometric centre of the spherical mirror. It is denoted by the letter P.
Radius of Curvature
It
is the distance between the center of the sphere and the vertex. It is shown by
the letter R in ray diagrams (The
vertex is the point on the mirror’s surface where the principal axis meets the
mirror. It is also called as ‘pole’).
Principal Axis
The
line joining the pole of the mirror and its center of curvature is called
principal axis.
Focus
When
a beam of light is incident on a spherical mirror, the reflected rays converge
(concave mirror) at or appear to diverge from (convex mirror) a point on the
principal axis. This point is called the ‘focus’ or ‘principal focus’. It is
also known as the focal point. It is denoted by the letter F in ray diagrams.
Focal length
The
distance between the pole and the principal focus is called focal length (f) of
a spherical mirror.
There
is a relation between the focal length of a spherical mirror and its radius of
curvature. The focal length is half of the radius of curvature.
Focal
length = Radius of curvature / 2.
Problem 1
The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. Find its
focal length.
Solution
Radius of curvature =
20 cm
Focal length (f) =
Radius of curvature / 2
= R/2 = 20/2 = 10 cm
Problem 2
Focal length of a spherical mirror is 7 cm. What is its radius
of curvature?
Solution
Radius of curvature (R) = 2 × Focal length
= 2 × 7 = 14 cm

Related Topics