Chapter: Basic & Clinical Pharmacology : Agents Used in Cardiac Arrhythmias
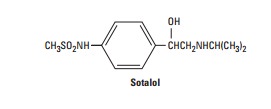
Sotalol
SOTALOL
Sotalol
has both ╬▓-adrenergic
receptor-blocking (class 2) and action potential-prolonging (class 3) actions.
The drug is formu-lated as a racemic mixture of D- and L-sotalol. All the ╬▓-adrenergicŌĆō blocking
activity resides in the L-isomer; the D- and L-isomers share action potential
prolonging actions. Beta-adrenergicŌĆō blocking action is not cardioselective and
is maximal at doses below those required for action potential prolongation.
Sotalol
is well absorbed orally with bioavailability of approxi-mately 100%. It is not
metabolized in the liver and is not bound to plasma proteins. Excretion is
predominantly by the kidneys in the unchanged form with a half-life of
approximately 12 hours. Because of its relatively simple pharmacokinetics,
solatol exhibits few direct drug interactions. Its most significant cardiac
adverse effect is an extension of its pharmacologic action: a dose-related
incidence of torsades de pointes that approaches 6% at the highest recommended
daily dose. Patients with overt heart failure may experience further depression
of left ventricular function during treatment with sotalol.
Sotalol
is approved for the treatment of life-threatening ven-tricular arrhythmias and
the maintenance of sinus rhythm in patients with atrial fibrillation. It is
also approved for treatment of supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias in
the pediatric age group. Sotalol decreases the threshold for cardiac
defibrillation.
Related Topics