papaya, Sphaerocarpos, maize - Botany : Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance - Sex determination in plants | 12th Botany : Chapter 3 : Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 3 : Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
Sex determination in plants
Sex
determination in plants
About 94% of all
flowering plants have only one type of individual, which produces flowers with
male organs (the stamens) and female organs (the carpels). Such plants are
termed as sexually monomorphic. Some 6% of flowering plants which have
two separate sexes are called dimorphic. Male plants produce flowers
with stamens and female plants produce flowers with carpels only.
Researchers are interested to study the mechanism of sex determination in
plants.C.E. Allen (1917) discovered sex determination in plants. Sex
determination is a complex process determined by genes, the environment and
hormones.
Sex determination in Silene
latifolia (Melandrium album) is of controlled by three distinct
regions in a sex chromosome.
1. Y chromosome determines
maleness
2. X specifies femaleness
3. X and Y show different
segments (I II III IV and V)
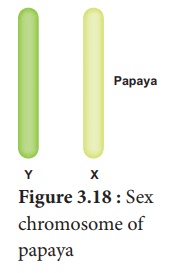
1. Sex determination in papaya
Recently researchers in
Hawaii discovered sex chromosomes in Papaya Papaya (Carica papaya, 2n=36). Papaya
has 17 pairs of autosomes and one pair of sex chromosomes. Male Y X papaya
plants have XY Figure 3.18 : Sex and female plants have chromosome of XX.
Unlike human sex papaya chromosomes, papaya sex chromosomes look like autosomes
and it is evolved from autosome. The sex chromosomes are functionally distinct
because the Y chromosome carries the genes for male organ development and X
bears the female organ developmental genes (Figure 3.18).
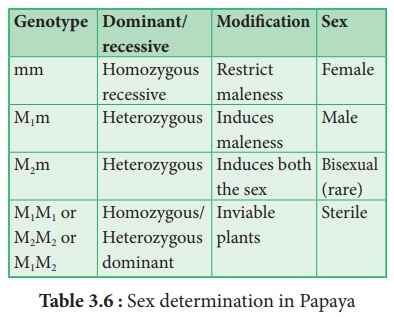
In papaya sex
determination is controlled by three alleles. They are m, M1 and M2
of a single gene.
2. Sex Determination in Sphaerocarpos
Sex determination was
first described in the bryophyte Sphaerocarpos donnellii which
has heteromorphic chromosomes. The gametophyte is haploid and heteromorphic.
The male gametophyte as well as the female gametophyte is an haploid organism

with 8 chromosome (n=8).
The diploid sporophyte is always heterogametic. Seven autosomes are similar in
both male and female gametophyte. But the eighth chromosome of female is X
which is larger than the seven autosomes. The eighth chromosome of male is Y
which is comparatively smaller than autosomes. The sporophyte containing XY
combination produces two types of meiospores, that is some with X and others
with Y chromosomes. The meiospores with X chromosomes produce female
gametophyte and those with Y chromosome produces male gametophyte.
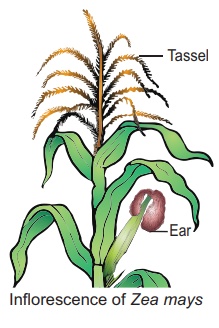
3. Sex determination in maize
Zea mays (maize) is an
example for monoecious, which means male and female flowers are present on the
same plant. There Tassel are two types of inflorescence.
The terminal
inflorescence which bears staminate florets develops from Ear shoot apical
meristem called tassel. The lateral inflorescence
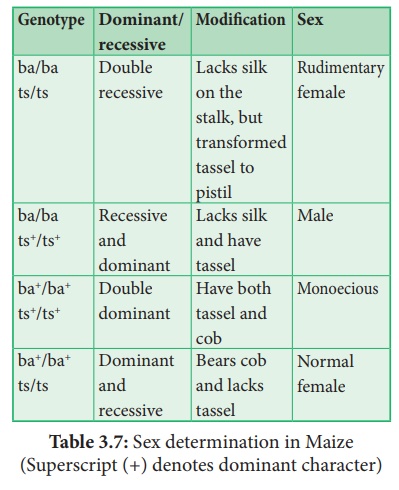
Unisexuality in maize
occurs through the selective abortion of stamens in ear florets and pistils in
tassel florets. A substitution of two single gene pairs 'ba' for barren
plant and 'ts' for tassel seed makes the difference between monoecious
and dioecious (rare) maize plants. The allele for barren plant (ba) when
homozygous makes the stalk staminate by eliminating silk and ears. The allele
for tassel seed (ts) transforms tassel into a pistillate structure that produce
no pollen. The table-3.7 is the resultant sex expression based on the
combination of these alleles. Most of these mutations are shown to be defects
in gibberellin biosynthesis. Gibberellins play an important role in the
suppression of stamens in florets on the ears.
Related Topics