Botany : Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance - Recombination | 12th Botany : Chapter 3 : Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 3 : Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
Recombination
Recombination
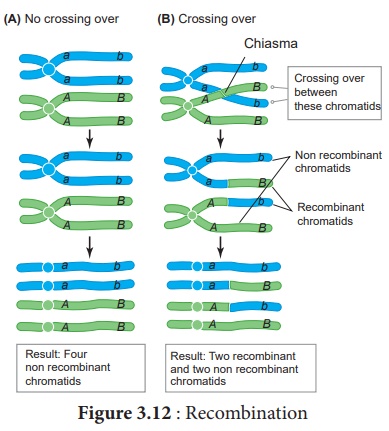
Crossing over results in
the formation of new combination of characters in an organism called recombinants.
In this, segments of DNA are broken and recombined to produce new combinations
of alleles. This process is called Recombination. (Figure 3.12)
The widely accepted
model of DNA recombination during crossing over is Holliday’s hybrid DNA
model. It was first proposed by Robin Holliday in 1964. It
involves several steps. (Figure 3.13)
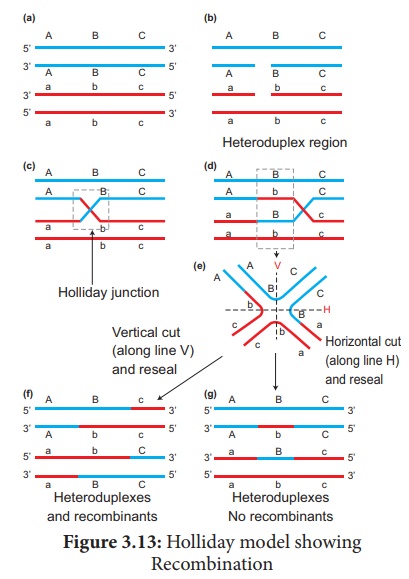
1. Homologous DNA molecules
are paired side by side with their duplicated copies of DNAs
2. One strand of both DNAs
cut in one place by the enzyme endonuclease.
3. The cut strands cross
and join the homologous strands forming the Holliday structure or
Holliday junction.
4. The Holliday junction
migrates away from the original site, a process called branch migration,
as a result heteroduplex region is formed.
5. DNA strands may cut
along through the vertical (V) line or horizontal (H) line.
6. The vertical cut will result
in hetero duplexes with recombinants.
7. The horizontal cut will
result in hetero duplex with non recombinants.
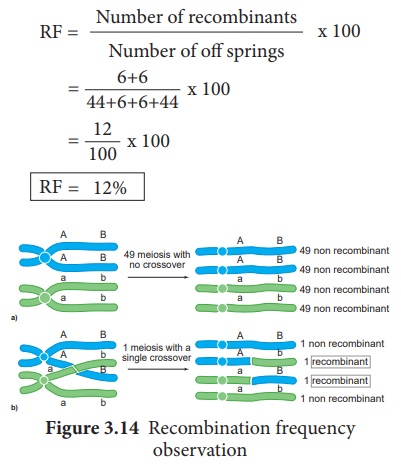
Calculation of
Recombination Frequency (RF)
The percentage of recombinant progeny in a cross is called recombination frequency. The recombination frequency (cross over frequency) (RF) is calculated by using the following formula. The data is obtained from alleles in coupling configuration (Figure 3.14)
Related Topics