Chapter: Mechanical : Robotics : Fundamentals of Robot
Robotics Co-ordinate System
Co-ordinate System
A coordinate system defines a plane or space by axes
from a fixed point called the origin. Robot targets and positions are located
by measurements along the axes of coordinate systems. A robot uses several
coordinate systems, each suitable for specific types of jogging or programming.
The Robots are mostly divided into
four major configurations based on their appearances, sizes, etc. such as:
·Cylindrical
Configuration,
·Polar
Configuration,
·Jointed
Arm Configuration, and
·Cartesian
Co-ordinate Configuration.
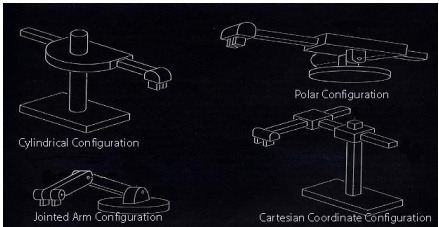
Cylindrical
Configuration:
This kind of robots incorporates a
slide in the horizontal position and a column in the vertical position. It also
includes a robot arm at the end of the slide. Here, the slide is capable of
moving in up & down motion with the help of the column. In addition, it can
reach the work space in a rotary movement as like a cylinder.
Example:
GMF Model M1A Robot.
Advantages:
·
Increased rigidity, and
· Capacity of carrying high payloads. Disadvantages:
·
Floor space required is
more, and
·
Less work volume.
Polar Configuration:
The polar configuration robots will possess an arm, which can
move up and down. It comprises of a rotational base along with a pivot. It has
one linear & two rotary joints that allows the robot to operate in a
spherical work volume. It is also stated as Spherical Coordinate Robots.
Example:
Unimate 2000 Series Robot.
Advantages:Long reach capability in the horizontal position.
Disadvantages:
·Vertical reach is low.
Jointed Arm
Configuration:
The arm in these configuration robots
looks almost like a human arm. It gets three rotary joints and three wrist
axes, which form into six degrees of freedoms. As a result, it has the capability
to be controlled at any adjustments in the work space. These types of robots
are used for performing several operations like spray painting, spot
welding, arc welding, and more.
Example:
Cincinnati Milacron T3 776 Robot
Advantages:
·
Increased flexibility,
·
Huge work volume, and
· Quick operation. Disadvantages:
·
Very expensive,
·
Difficult operating
procedures, and
·
Plenty of components.
Cartesian Co-ordinate
configuration:
These robots are also called as XYZ
robots, because it is equipped with three rotary joints for assembling XYZ
axes. The robots will process in a rectangular work space by means of this
three joints movement. It is capable of carrying high payloads with the help of
its rigid structure. It is mainly integrated in some functions like pick and
place, material handling, loading and unloading, and so on. Additionally, this
configuration adds a name of Gantry Robot.
Example:
IBM 7565 Robot.
Advantages:
·
Highly accurate &
speed,
·
Fewer cost,
·
Simple operating
procedures, and
·
High payloads.
Disadvantages:
·
Less work envelope, and
·
Reduced flexibility.
Work Envelop
It is the shape created when a manipulator
reaches forward, backward, up and down.
These
distances are determined by the length of a robot's arm
and the design of its axes. Each axis contributes its own range of motion.
A robot can only
perform within the confines of this work envelope.
Still, many of the robots
are designed with considerable flexibility. Some have the ability to reach
behind themselves. Gantry robots defy traditional constraints of work
envelopes. They move along track systems to create large work spaces.
Technical Features of
an Industrial Robot
The technical features of an industrial robot
determine its efficiency and effectiveness at performing a given task. The
following are some of the most important among these technical features.
Related Topics