Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: DNA Synthesis in Vivo and in Vitro
Reverse Transcriptase PCR
REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE PCR
Reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) uses the enzyme reverse
transcriptase to make a cDNA copy of mRNA from an organism, and then uses PCR
to amplify the cDNA (Fig. 4.26). The advantage of this technique is evident when
trying to use PCR to amplify a gene from eukaryotic DNA. Eukaryotes have
introns, some extremely long, which interrupt the coding segments. After
transcription, the primary RNA transcript is processed to remove all the
introns, hence becoming mRNA. Using mRNA as the source of the target DNA relies
on the cell removing the introns. In practice, RT-PCR has two steps. First,
reverse transcriptase recognizes the 3′ end of primers containing repeated
thymines and synthesizes a DNA strand that is complementary to the mRNA.
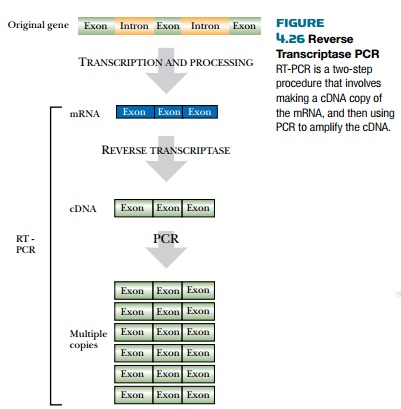
(The thymines base-pair with
the poly(A) tail of mRNA.) Then the RNA strand is replaced with another DNA
strand, leaving a double-stranded DNA (i.e., the cDNA).
Next, the cDNA is amplified
using a normal PCR reaction containing appropriate primers (one usually
recognizes the poly(A) tail), Taq polymerase, and nucleotides.
Related Topics