Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: DNA Synthesis in Vivo and in Vitro
Comparing Replication in Gene Creatures, Prokaryotes, and Eukaryotes
COMPARING
REPLICATION IN GENE CREATURES, PROKARYOTES, AND EUKARYOTES
Although the basic mechanism
for replication is the same for most organisms, the timing, direction, and
sites for initiation and termination are variable. The major differences in
replication occur mainly because of the special challenges posed by circular
and linear genomes. Normal DNA replication occurs bidirectionally in
prokaryotes and eukaryotes, whether the genome is linear or circular. Two
replication forks travel in opposite directions, unwinding the DNA helix as
they go. In bacteria such as E. coli, there is only one origin, oriC, and
replication occurs in both directions around the circular chromosome until it
meets at the other side, the terminus, terC. Halfway through this process, the
chromosome looks like the Greek letter θ; therefore, this process is often
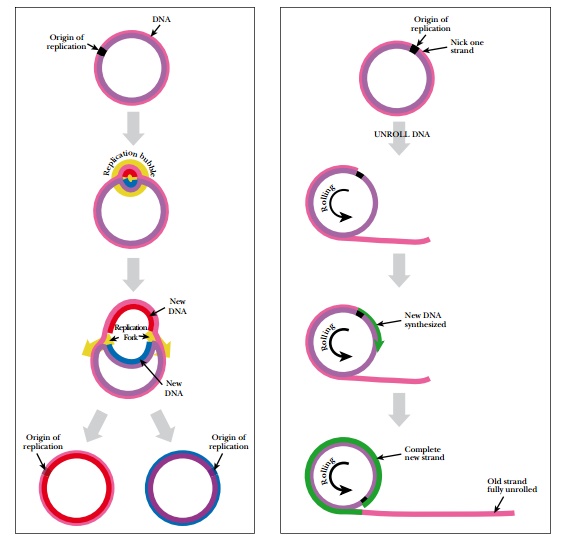
called theta-replication (Fig. 4.7). The single circular chromosome then
becomes two. Theta replication is also used by many plasmids, such as the F
plasmid of E. coli, when growing and dividing asexually (as opposed to
transferring its genome to another cell via conjugation).
Some plasmids and many viruses replicate their genomes by a process called rolling circle replication ( Fig. 4.8 ). At the origin of replication, one strand of the DNA is nicked and unrolled. The intact strand thus rolls relative to its partner (hence “rolling circle”). DNA is synthesized from the origin using the circular strand as a template. As DNA polymerase circles the template strand, the new strand of DNA is base-paired to the circular template. Meanwhile the other parental strand is dangling free. This dangling strand is removed, ligated to form another circle, and finally a second strand is synthesized. This results in two rings of plasmid or viral DNA, each with one strand from the original molecule and one newly synthesized strand.
Some viral genomes use rolling circle replication, but continue to make more and more copies of the original circular template. They continue rolling around the circle, synthesizing more and more copies that are all dangling as a long single strand. The long strand of new DNA may be made double-stranded or left single-stranded (depending on the type of virus). Finally the dangling strand is chopped into genome-sized units and packaged into viral particles. Some viruses circularize these copies before packaging; others simply leave the genomes linear.
Long linear DNA molecules such as human chromosomes pose several problems for replication. The ends pose a particularly difficult problem because the RNA primer is synthesized at the very end of the chromosome. When the RNA primer is removed by an exonuclease (MF1), there is no upstream 3′-OH for addition of new nucleotides to fill the gap. (In eukaryotes, there is no equivalent to the dual-function DNA polymerase I. A separate exonuclease (MF1), there is
no upstream 3′-OH for addition of new nucleotides to fill the gap. (In
eukaryotes, there is no equivalent to the dual-function DNA polymerase I. A
separate

exonuclease, MF1, removes the
RNA primers, and DNA polymerase δ fills in the gaps.) Over successive rounds of
replication, the ends of linear chromosomes get shorter and shorter. Special
structures called telomeres are
found at the tips of each linear chromosome and prevent chromosome shortening
from affecting important genes. Telomeres have multiple tandem repeats of a
short sequence (TTAGGG in humans). The enzyme telomerase can regenerate the telomere by using an RNA template to
synthesize new repeats. This only happens in some cells; in others, the
telomeres shorten every time the cell replicates its DNA. One theory regards
telomere shortening as a molecular clock, aging the cell, and eventually
triggering suicide.
The length of linear
chromosomes also poses a problem. The time it takes to synthesize an entire
human chromosome would be too long if replication began at only one origin. To
solve this issue, there are multiple origins, each initiating new strands in both
directions. These are elongated until they meet the new strands from the other
direction.
The cellular structure of eukaryotes also poses some problems for replication. (In bacteria, the chromosome simply replicates, the two copies move to each end of the cell, and a new wall forms in the middle. There are no nuclear membranes or organelles to divide; there is just one chromosome plus, perhaps, some plasmids.) In eukaryotes, the cell has a specific cell cycle, with four different phases and replication occurs at specific points (Fig. 4.9). During G1, the cell rests for a period before DNA synthesis begins. This period varies, lasting about 25 minutes for yeast. The next phase is S or synthesis, during which the entire genome is replicated. This is usually the longest phase, lasting about 40 minutes in yeast. The third phase is G2 and is another resting phase before the cell undergoes mitosis, in the M phase. During mitosis, cells divide their walls and membranes into two separate cells, partitioning the new chromosomes and other cellular components into each half. The signal that triggers cell division depends on many factors, including environment, size, and age. Most of these are still not understood.
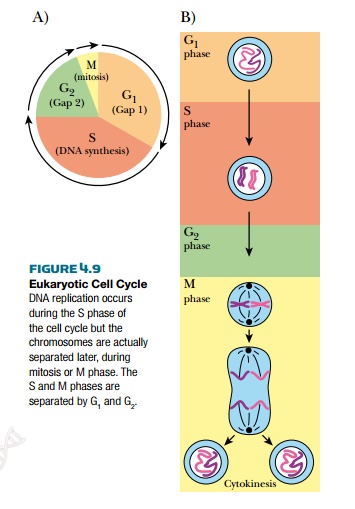
Eukaryotic mitosis is a
dynamic process with much movement and repositioning of cellular components.
First, the nuclear membrane must be dissolved before the chromosomes can
separate. After replication, the two sets of chromosomes are partitioned to
separate sides of the cell. The chromosomes attach to long fibers making up the
spindle via special sequences called
centromeres. They slide along the
spindle fibers until they reach separate ends of the cell. A new cell membrane
separating the two halves is then synthesized. Other cellular components
including mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, and so forth are
split between the two daughter cells. Finally, a new nuclear membrane must be
assembled around the chromosomes of each new daughter cell. The dynamics of
this process are still being investigated, and new proteins and molecules are
still being discovered that mediate different parts of mitosis in eukaryotic
cells.
Related Topics