Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Respiratory
Respiratory Exam
Respiratory Exam
· For Chest X-ray, see Chest X-ray Topic
Inspection, Palpation and Percussion *
·
Inspection:
o Count respiratory rate (at rest should be < 14 per minute)
o Chronic airways disease ® barrel (expended chest) ® can‟t find apex beat
o Look for use of accessory muscles. Are intercostals depressed (ie being
used a lot)? Look for paradoxical breathing of the abdomen
o Cyanosis (eg tongue)
·
Ask patient to cough. Listen for wheeze, gurgling, etc
·
Inspect sputum
·
Listen for stridor or hoarseness
(laryngitis, cancer affecting left recurrent nerve or larynx)
·
Hands:
o Clubbing (and maybe Hypertrophic Pulmonary Osteoarthropathy – „swollen‟ metacarpals and elsewhere, eg in lung cancers).
o Staining from cigarettes
o Wasting (Pancoast tumour)
o Pulse rate: tachycardia
o Flapping tremour: late and unreliable sign of severe CO2
retention
·
The face:
o Eyes for Horner‟s syndrome (constricted pupil, partial ptosis)
o Tenderness over sinuses ® sinusitis
o Nose: check for polyps (associated with asthma), deviated septum (nasal
obstruction), etc
o Throat for URTI
o Check lymph nodes
·
Trachea:
o Check for displacement
o Tracheal Tug: trachea moves inferiorly with inspiration, due to over
expansion of the lung in airflow obstruction
·
Chest:
o Inspect:
§ Shape and symmetry, including funnel chest (= pectus excavatum or sunken
sternum), kyphosis (forward curvature) and scoliosis (lateral bowing)
§ Scars, signs of radiotherapy
§ Subcutaneous emphysema – crackling under the skin due to air from
pneumothorax
§ Prominent veins in SVC obstruction
§ Movement when breathing in and out – better from behind. Look for
uni-lateral or bi-lateral reduction in movement
o Palpation:
§ Check expansion: the affected side dose NOT expand – regardless of
pathology
§ Apex beat: if not found then ® ?hyper-expanded. Maybe displaced
by pathology (pneumothorax, fibrosis, etc)
§ Vocal fremitus: Feel with hand while patient says 99, each side font and
back
§ Compress sternum to spine ® pain if fracture or bone tumour
o Percussion:
§ Ask patient to move elbows forward to move scapula off the lungs
§ Around lung and also directly on the clavicle
§ Normal lung is resonant, pneumothorax is hyper-resonant, liver is dull,
consolidation is dull, effusion is stony dull
·
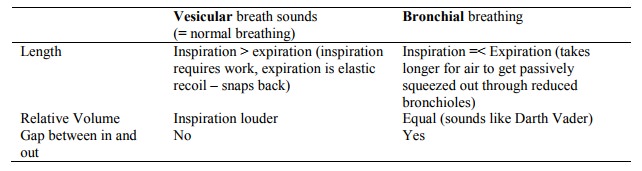
Chest Sounds
·
When auscultating, ask patient to
breath through mouth – not to take deep breaths
·
Crackle:
o = Crepitations
o Coarse or fine (like hair rubbing)
o Short, discontinuous, non-musical sounds heard mostly during inspiration
o Fine (high pitched) are from distal air-spaces, coarse (low pitched) are
proximal air spaces
o Produced when there is fluid inside a bronchus with collapse of the
distal airways and alveoli
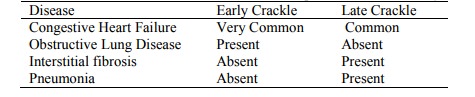
o Wheeze= Rhonchi, rhonchus, rale
o Continuous musical sounds heard mostly during expiration
o Produced by airflow through narrowed bronchi
o Narrowing may be due to swelling, secretions, spasm, tumour, or a
foreign body
·
Pleural Rub
o Grating sound like Velcro ripping or walking on snow on inspiration
and expiration
o Produced by motion of roughened or thickened pleura
o Caused by inflammatory or neoplastic cells or fibrin deposits
·
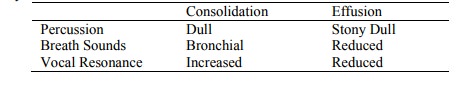
Differentiating Consolidation
from Pleural Effusion
o Consolidation = exudate into alveoli.
Signs are:
§ Expansion: reduced on affected side
§ Vocal resonance and tactile fremitus (patient says „99‟ and listen with
stethoscope/feel with hand): on affected side
§ Percussion: dull but not stony dull
§ Breath Sounds: increased volume
and bronchial not vesicular (ie will hear coarse breath sounds like over the
trachea)
§ Additional Sounds: inspiratory crackles (as pneumonia resolves)
§ Vocal Resonance: increased
§ Plural Rub: may be present
o Effusion = fluid in pleural space (but not blood – that‟s haemothorax,
and not pus – that‟s empyema). Signs of effusion are:
§ Displaced trachea if massive effusion
§ Expansion: reduced on affected side
§ Percussion: stony dullness over effusion
§ Breath Sounds: reduced or
absent
§ Vocal Resonance: reduced
o The key differences are therefore:
·
Common presentations:
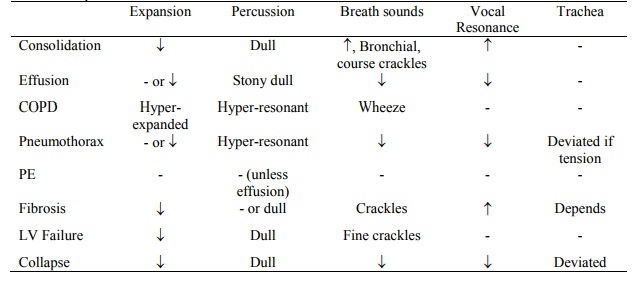
Other systems *
·
Check JVP for right heart failure
·
Listen to P2 of second
heart sound, at 2nd intercostal space on the left. If louder ®
?pulmonary hypertension
·
Check liver for tumour 2nd to lung cancer, and for „ptosis‟
– displaced downwards in emphysema
·
Pemberton‟s sign: SVC obstruction
– hold arms over head ® facial plethora, inspiratory stridor and JVP
·
Feet: check for oedema (pulmonary
hypertension) and DVT
Related Topics