Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Respiratory
Acute Pharyngitis
Acute Pharyngitis
·
Almost 100% given broad-spectrum antibiotics. Inappropriate in 90% of cases
·
Pathogens:
·
Viruses: Adenovirus, also rhinovirus,
coronaviruses, RSV, Parainfluenza virus, influenza, enteroviruses, EBV
·
Bacteria: S Pyogenes (GABHS = Group A
Beta-Haemolytic Strep) in about 20 – 30% of cases, predominantly in those over
4 years
·
Differentiating (at best 70% predictive accuracy):
·
Exudative tonsillitis: Adenovirus, GABHS, EBV
·
> 4 years, enlarged tender anterior cervical
lymph nodes and diffusely inflamed pharyngeal structures (+ exudates) suggests
S Pyogenes
· Diffuse, sandpaper-like red rash, accentuated in skin creases (Pastia lines) suggest Scarlet Fever.
·
Nasal discharge, cough, hoarseness, conjunctivitis
or diarrhoea +/- fever +/- tonsillar exudates suggests virus
·
Throat swabs: usually identify organism, but 10 –
50% are carriers
Treatment:
·
Aim: Prevent acute rheumatic fever, suppurative
complications (peri- or para tonsillar abscess) and hasten recovery
·
But
o
Only benzathine penicillin has been shown to reduce
RF – and this was in military personnel
o
No convincing data which shows antibiotics reduce
the risk of rare suppurative complications
o Antibiotics reduce symptoms by 8 hours only
o
Reinforces the notion that antibiotics are
effective and increases the likelihood of their future use for trivial
illnesses
·
If high risk for RF (eg Maori, PI, > 4 years of
age) take swabs or treat empirically. However, prescribing penicillin for sore
throat hasn‟t altered the rates of RF, and many children with RF haven‟t
consulted their doctor
·
S Pyogenes: penicillin, 500 – 1000 mg BID for 10
days (Allergy: erythromycin)
·
Clinical signs: fever,
respiratory distress, cervical lymphadenopathy, pharyngeal erythema, pharyngeal
exudates
Causal Organisms
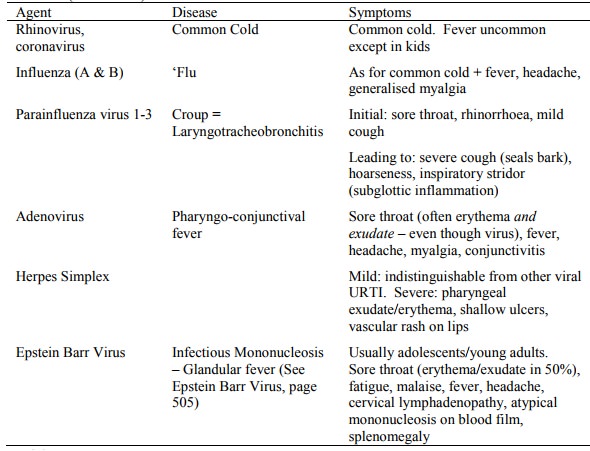
Bacterial Causes:
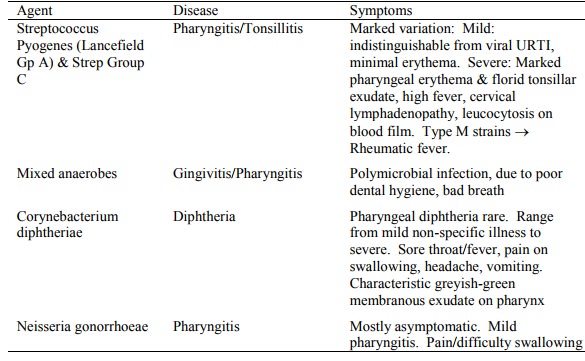
Fungal causes:

Diagnosis
·
Throat swabs:
o For routine bacterial culture: especially to confirm/exclude Strep
Pyogenes
o Low sensitivity (?30%) and specificity (?75%)
o 40 – 50% of people with sore throats have bacteria isolated
o Lots of variability: swab-taking technique, delays in transport, etc
o Worth it for $18?
·
Nasopharyngeal washings (kids):
Antigen detection by immunoflouresence for RSV, Influenza A & B,
Parainfluenza 1 – 3 and adenovirus
Related Topics