Matter Around Us | Term 1 Unit 3 | 7th Science - Questions Answers | 7th Science : Term 1 Unit 3 : Matter Around Us
Chapter: 7th Science : Term 1 Unit 3 : Matter Around Us
Questions Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the appropriate answer.
1. Which
of the following is an example of a metal?
a. Iron
b. Oxygen
c. Helium
d. Water
Answer : a. Iron
2.
Oxygen, hydrogen, and sulphur are examples of which of the following?
a. Metalsb.
b. Non-metals
c. Metalloidsd.
d. Inert gases
Answer : b. Non-metals
3.
Which of the following is a short and scientific way of representing one
molecule of an element or compound?
a. Mathematical formula
b. Chemical formula
c. Mathematical symbol
d. Chemical symbol
Answer : b. Chemical formula
4.
The metals which is a liquid at room temperature
a. Chlorine
b. Sulphur
c. Mercury
d. Silver
Answer : c. Mercury
5.
An element which is always lustrous, malleable and ductile
a. non-metal
b. metal
c. metalloid
d. gas
Answer : b. metal
II. Fill in the blanks.
1. The smallest particle of matter that can exist by itself atom.
2. A compound containing one atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen is Carbon-di-oxide.
3. Carbon is the only non-metal
conducts electricity.
4. Elements are made up of same kinds of atoms.
5. Symbol of some elements are
derived from Latin or Greek names of the elements.
6. There are 118 number of known elements.
7. Elements are the simplest form
of pure substances .
8. The first letter of an element always written in Capital letter
9. Molecule containing more than three atoms are known as Polyatomic.
10. Nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere.
III. Fill in the Blanks.
1. Mercury: liquid at room temperature Oxygen: gas (at room temperature)
2. Non metal conducting electricity: Carbon Metal conducting electricity Copper
3. Elements: combine to form compounds::
Compounds:
4. Atoms: fundamental particle of an
element:: Molecules :fundamental particles of a compound.
IV. True of False. If False, give the correct
statement.
1. Two different elements may have
similar atoms.
Two different element may
have different atoms.
2. Compounds and elements are pure
substance.
3. Atoms cannot exist alone; they
can only exist as groups called molecules.
Atom can exist alone; They
can also exist as groups called molecules.
4. NaCl represents one molecule of
sodium chloride.
5. Argon is mono atomic gas.
V. Answer in brief.
1.
Write the chemical formula and name the elements present in the following
compounds:
a.
Sodium chloride
b.
Potassium hydroxide
c.
Carbon-di-oxide
d.
Calcium oxide
e. Sulphur dioxide
a. Sodium chloride - NaCl : Sodium
& Chlorine
b. Potassium hydroxide - KOH : Pottassium, Oxygen & Hydrogen
c. Carbon-di-oxide - CO2
:
Carbon & Oxygen
e. Sulphur dioxide - CaO : Calcium & Oxygen
d. Calcium oxide - SO2 : Sulphur
& Oxygen
2.
Classify the following molecules as the molecules of element or compound
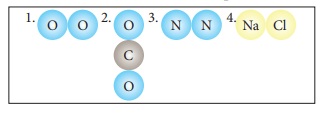

3.
What do you understand by chemical formula of a compound? What is its
significance?
A chemical formula is a symbolic representation of one molecule
of an element or a compound. It provides information about the elements present
in the molecule and the number of atoms of each element.
4.
Define the following terms with an example of each:
a.
Element
b.
Compound
c.
Metal
d.
Non-metal
e.
Metalloid
a) Element: Matter in its simplest form is called an element.
e.g: Hydrogen, Oxygen, Copper, lead, Iron
b) Compound : A compound is a pure substance that is formed when the atoms of
two or more element combine chemically in definite proportions. e.g: Water,
Sodium Chloride, Sugar.
c) Metal: Elements that are malleable (a material may be flattened into
thin sheets or various shapes) is called as metals. Metals are generally hard
and shiny elements. e.g: Copper, Lead, Iron, Zinc, Nickal
d) Non-metal : Non-metals are generally dull and soft. Non-metals are poor conductors
of heat and electricity. e.g: Oxygen, Hydrogen, Sulphur, Phosphorous, Bromine.
e) Metalloid : Metalloids exhibit the properties of both metals and non
metals. e.g: Silicon, Orsenic, Antimony, Boron.
5.
Write the symbols for the following elements and classify them as solid, liquid
and gas Aluminum, carbon, chlorine, mercury, hydrogen and helium
Elements Symbol Classify
Aluminum Al Solid
Carbon C Solid
Chlorine Cl Gas
Mercury Hg Liquid
Hydrogen H Gas
Helium He Gas
6. Classify the following as metals, non-metals and metalloids
Sodium,
Bismuth, Silver, Nitrogen, Silicon, carbon, chlorine, Iron, copper
Elements - Classify
Sodium - metal
Bismuth - metal
Silver - metal
Nitrogen - non-metal
Silicon - metalloid
Carbon - non-metal
Chlorine -
non-metal
Iron -
metal
copper - metal
7.
Classify the following as elements and compounds
Water,
common salt, sugar, carbon dioxide, iodine and lithium
water - compound
commson salt - compound
sugar - compound
carbon dioxide - compound
iodine - element
lithium - element
8.
Write the chemical formula for the following elements
a.
Hydrogenb.
b.
Nitrogen
c.
Ozoned.
d.
Sulphur
a) Hydrogen - H2
b) Nitrogen - N2
c) Ozone - O3
d) Sulphur – S8
9.
What are elements? What are they made of? Give two examples.
A molecule of an element consists of a fixed number of one types
of atom chemically combined. E.g: oxygen, hydrogen, carbon.
10.
Define molecule.
A molecule is made up of two or more atoms chemically combined.
11.
What are compounds? Give two examples.
A compound is a pure substance that is formed when the atoms of
two or more elements combine chemically in definite proportions. e.g: ammonia,
hydrogen chloride, calcium oxide.
12.
Give an example for the elements derived from their Latin names.
Gold - Au, Copper - Cu
13.
What is atomicity of elements?
Atomicity of an element implies that the total number of atoms present
in one molecule of that element.
e.g : Hydrogen - 2 (diatomic), Sodium - 1 (monoatomic)
14.
Calculate the atomicity of H2SO4.
Molecule of sulphuric acid (H2SO4)
contains two atoms of hydrogen, one atom of Sulphur and four atoms of oxygen,
Hence the atomicity is 2 + 1 + 4 = 7.
VI. Answer in detail.
1. Differentiate
metals and non metals.
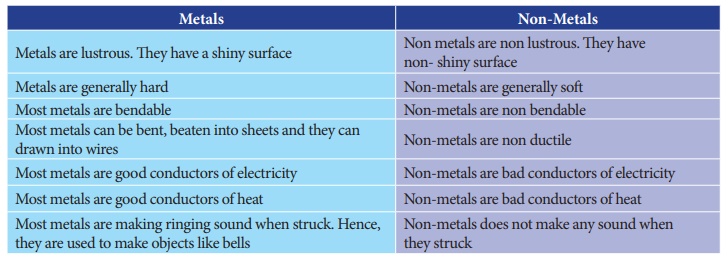
Metals
1. Metals are lustrous. They have a shiny surface.
2. Metals are generally hard.
3. Most metals can be bent, beaten into sheets and they can
drawn into wires
4. Most metals are good conductors of electricity
5. Most metals are good conductors of heat.
6. Most metals are making ringing sound when struck. Hence, they
are used to make objects like bells
e.g: Copper, Silver, Gold, Iron, Nichal
Non-Metals
1. Non metals are non lustrous. They have non-shiny surface.
2. Non-metals are generally soft.
3. Non-metals are non ductile
4. Non-metals are bad conductors of electricity
5. Non-metals are bad conductors of heat.
6. Non-metals does not make any sound when they struck.
e.g: Hydrogen, Oxygen, Chlorine, Bromine, Sulphur.
2.
Explain the characteristics of compounds
❖ A compound
if formed only when the constituent elements combine in a fixed proportion.
❖ The
properties of a compound are different from those of its constituent elements.
❖ A compound
cannot be broken down by physical methods. This is because a compound is made
up of different elements that are chemically combined. Sodium chloride cannot
be separated by physical methods such as filtration.
❖ A compound
can be separated into its constituent elements by chemical methods only.
3.
Describe the different ways in which we can write the symbols of elements. Give
appropriate examples.
A symbol is an abbreviation or short representation of a chemical
element. These symbols are allocated by the International Union of Pure and
Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
Dalton was the first scientist to use the symbols for elements
in a very specific sense. When he used a symbol for an element he also meant a
definite quantity of that element, that is, one atom of that element. Berzelius
suggested that the symbols of elements be made from one or two letters of the
name of the element.
Symbols for some elements as proposed by Dalton.
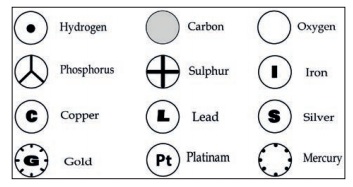
The following rules are followed while assigning symbol to an
elements:
Chemical symbols usually consist of one or two letters.
The symbols of most elements correspond to the first letter (which is capitalized) of their English name. For example, the symbol for oxygen is "O" and that for hydrogen is "H".
Element Symbol
Hydrogen H
Fluorine F
Oxygen 0
Carbon C
Phosphorus P
Sulphur S
Potassium K
Uranium U
When there is more than one element that begins with the same
letter, their symbols take two letters. The first letter is capitalised while the
second letter has a lower case. For example, the names of both hydrogen
and helium begin with H. So, hydrogen is represented by the symbol H and Helium
by He. Similarly, the symbol for carbon is C while the symbols for calcium,
chlorine and chromium are Ca, Cl and Cr, respectively.
Elements represented by symbols of two letters.
Element Symbol
Aluminium Al
Argon Ar
Arsenic As
Barium Ba
Nickel Ni
Bromine Br
Chromium Cr
Cobalt Co
Helium He
Magnesium Mg
Calcium Ca
Chlorine Cl
The symbols for some elements are derived from their Latin
names. For example, the symbol for gold is Au after its Latin name Aurum.
Similarly, the symbols for copper is Cu after its Latin name Cuprum.
Element - Latin name :
Symbol
Copper - Cuprum : Cu
Lead - Plumbum : Pb
Potassium - Kalium : K
Iron - Ferrum : Fe
Mercury - Hydrargyrum
: Hg
Sodium - Natrium : Hg
4.
Differentiate between elements and compounds.
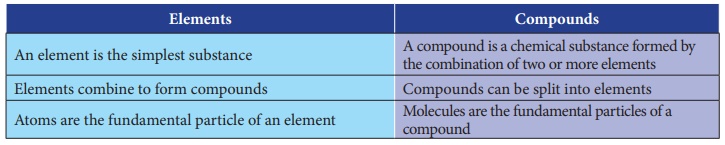
Elements
An element is the simplest substance.
Elements combine to form compounds.
Atoms are the fundamental partcicle of an element.
Compounds
A compound is a chemical substance formed by the combination of
two or more elements.
Compounds can be split into elements.
Molecules are the fundamental particles of a compound.
5.
Write any five characteristics of compound.
❖ A compound
if formed only when the constituent elements combine in a fixed proportion.
❖ The
properties of a compound are different from those of its constituent elements.
❖ A compound
cannot be broken down by physical methods. This is because a compound is made
up of different elements that are chemically combined. Sodium chloride cannot
be separated by physical methods such as filtration.
❖ A compound
can be separated into its constituent elements by chemical methods only.
❖ "Molecules
are the fundamental particles of a compound."
6.
List comparative properties of metals and non-metals. Give three examples of
each.

Metals
1 .Metals are lustrous.They have a shiny surface.
2. Metals are generally hard.
3. Most metals can be bent, beaten into sheets and they can
drawn into wires
4. Most metals are good conductors of electricity
5. Most metals are good conductors of heat.
6. Most metals are making ringing sound when struck. Hence, they
are used to make objects like bells.
e.g: Copper, Silver, Gold, Iron, Nichal
Non-Metals
1 .Non metals are non lustrous. They have non-shiny surface.
2 .Non-metals are generally soft.
3. Non-metals are non ductile
4. Non-metals are bad conductors of electricity
5 .Non-metals are bad conductors of heat.
6 .Non-metals does not make any sound when they struck.
e.g: Hydrogen, Oxygen, Chlorine, Bromine, Sulphur.
7.
Write down the properties of metalloids.
Metalloids exhibit the properties of both metals and non-metals:
1) Look shiny as metals.
2) Brittle as non-metals.
3) Conduct heat and electricity letter than non-metals but not
as well as metals.
4) They are solids at room temperature as metals.
5) Their hardness is less than that of metals but more than that
of non-metals.
VII. Rewrite the sentence in correct form
1. Elements
contains two or more kinds of atoms and compounds contains only one kinds of
atoms.
Elements contains only one kinds of atoms and compounds contains
two or more kinds of atoms.
VIII. Higher Order Thinking questions
1.
Lists the metals, non-metals and metalloids which you used in your house,
schools. Compare their properties.
2.
Aakash noticed that the metal latch on gate was difficult to open during hot
sunny days. However, this same latch was not difficult to open at night. Aakash
observed that the latch and the gate are exposed to the sun during the day.
a.
Formulate a hypothesis based on the information provided.
b.
Briefly state how you would test the hypothesis stated in (a).
a. Formulate a
hypothesis based on the information provided.
During hot sunny days the gate and the latch are exposed to the
sunlight. Due to the absorption of heat from the sun the gate and the latch
expand. This makes no space between the latch and gate. Therefore it was
difficult to open during hot sunny days. Absorbed heat is released at night.
This regains the space between the latch and gate due to the contraction of
them. So it was not difficult to open at night.
b. Briefly state
how you would test the hypothesis stated in (a). Experiment to test the above
observation
Take an iron rod and measure the length. Now keep the rod over
the stove and heat it. Again measure the length using a wooden scale without
touching. You can observe the increase in the length of the rod.
Now take the hot rod using a tongs and cool it under a water
tap. Again measure its length. Now you can observe that the rod regains its
original length. (Caution: Don't touch the hot rod)
3.
What changes take place in the movement and arrangement of particles during
heating process?
i) Size and number of particles and mass of the matter do not
change upon heating.
ii) Particles of matter gain energy, vibrate vigorously and
overcome the strong forces of attractin between one another.
iii) Then, particles move slightly further apart and break free
from one another and move randanly.
iv) This results changes in its state. For Example, When solid
ice is heated 0°c, it melts to become liquid water. In the same way, liquid
water is heated to 100°c, it boils to become steam. Temperature at which solid
changes into its liquid state is called Melting
Point. Temperature at which liquid changes into its gaseous state is called
boiling Point.
v) Density of gas decreases due to its expansion upon heating.
4.
In the diagram below, the circle, square and triangle represent the atoms of
different elements.
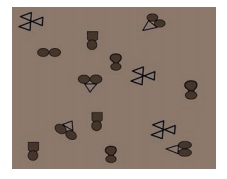
5.
In the diagram above, identify all combinations that represent
a.
A molecule of a compound
b.
A molecule of an element consisting of two atoms
c.
A molecule of an element consisting of three atoms
Answer: d) molecules of a mixture.
IX. Assertion-reason questions
Directions: Please refer to the
following instructions:
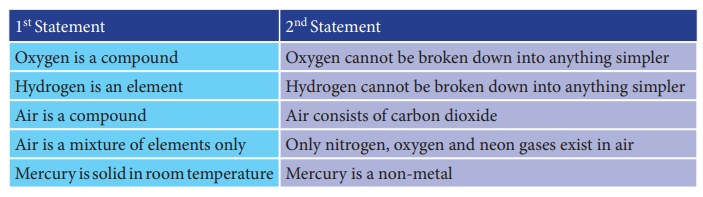
1. Assertion : Oxygen
is a compound.
Reason : Oxygen cannot be broken down into anything simpler.
2. Assertion :
Hydrogen is an element.
Reason : Hydrogen cannot be broken down into anything simpler.
3. Assertion : Air is
a compound.
Reason : Air consists of carbon dioxide.
4. Assertion : Air is
a mixture of elements only.
Reason : Only nitrogen, oxygen and neon gases exist in air.
5. Assertion :
Mercury is solid in room temperature.
Reason : Mercury is a non-metal.
A. Both statements are true and the 2nd statement is a
correct explanation of the 1st statement.
B. Both statements are true but the 2nd statement is NOT a
correct explanation of the 1st statement.
C. The 1st statement is false while the 2nd statement is
true.
D. Both statements are false.
Answer:
1. C. The 1st statement is false while the 2nd statement is
true.
2. A. Both statements are true and the 2nd statement is a
correct explanation of the 1st statement.
3. D. Both statements are false.
4. A. Both statements are true and the 2nd statement is a
correct explanation of the 1st statement.
5. D. Both statements are false.
Related Topics