Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Haematology and Immunology
Polycythaemia Vera - Myeloproliferative Disorders (MPD)
Polycythaemia Vera
· = Erythrocytosis
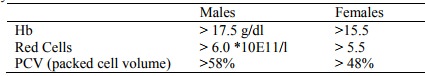
· Investigation: total red cell volume by 51Cr. Also erythropoietin assay
· Classification (given Raised PCV):
o RCM (Red cell mass) = Absolute
o Normal RCM = apparent
Primary Proliferative Polycythaemia
· Clonal stem cell disorder
· Predominant age 55 – 60 years
· Diagnosis:
o RCM > 36 ml/kg (i.e. absolute polycythaemia)
o No secondary cause: e.g. O2 saturation > 92% (e.g. CORD)
· Effects:
o Vascular complications: TIA, cerebral thrombosis, microvascular (e.g. toes), headaches, DVTs (but usually arterial problems due to viscosity e.g. stroke)
o Haemorrhage
o Pruritis
o Gout
o Splenomegaly (also liver)
· Lab findings:
o Hb & PCV
o WBC in 2/3
o Serum B12
o Low erythropoietin
o Platelets 400 – 800 in 50%
o Hypercellular marrow: little fat, in megakaryocytes
o „Hot‟ looking bone scan: lots of activity
o Tear drop red cells
· Treatment:
o Venesection: take off a unit of blood every 3 or 4 months (if old do it slow)
o If platelets as well (Þ clotting risk) then radioactive P32 (risk of leukaemia 10 years on), Busulphan & allopurinol (® ¯gout). Also hydroxyurea
· Course:
o 20% progress to myelofibrosis
o AML transition
o ?Splenectomy if massive
o Median survival = 8 – 15 years
Secondary Causes of Polycythaemia
· Hypoxia: normal erythropoietin. High altitude, lung disease, cyanotic CHD, smoking
· Inappropriate erythropoietin: renal tumours, renal ischaemia (ascultate for renal bruits), fibroids, hepatoma
· Miscellaneous: e.g. drugs like androgens for breast cancer
Apparent Polycythaemia
· Packed cell volume (=PCV = Haematocrit) but normal RCM (ie RBCs a greater proportion of a unit of blood, but normal volume of RBCs in the body):
o Diuretics
o Alcohol
o Hypertension
o Early primary polycythaemia
· High altitude: initially ¯plasma volume then absolute polycythaemia (and O2 curve shifts left)
Related Topics