Chapter: Medicine Study Notes : Haematology and Immunology
Microcytic Anaemia
Microcytic Anaemia
·
= MCV < 75 fl (normal is 76 –
98)
Causes
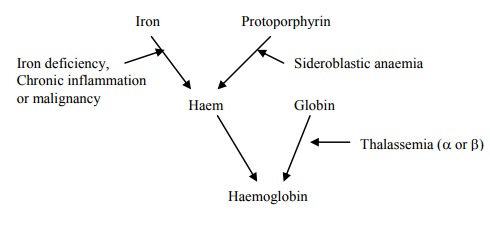
·
Iron deficiency anaemia
·
Thalassemia
· Chronic disease
·
Other Causes: Sideroblastic
anaemia, lead poisoning
Iron Deficiency Anaemia
·
Commonest cause of anaemia
·
15-25% of healthy pre-menopausal
women have low ferritin
·
2 mls of blood = 1 mg of
iron. Easy to get anaemia from a small
trickle bleed
·
Average menstrual loss = 60 ml
·
Iron absorption:
o Western diet contains 10 – 15 mg iron
o 5 – 10 % normally absorbed
o 20 – 30% absorbed in Fe deficiency and pregnancy
o Absorbed in duodenum, proximal jejunum
·
Iron transport and storage:
o Fe carried by Transferrin (MW 80,000): made in liver, T½ 8 – 10 days
o Ferritin: Water-soluble protein – MW 465,000. Stores iron in cells. Is
proportional to body iron stores
·
Clinical features of iron
deficiency:
o Anaemia
o Glossitis: swollen tongue, sore, lost papilla
o Koilonychia: spoon shaped nails
o Dietary cravings (pica): eating strange stuff – kids eat dirt, pregnant
women eat ice
o Blue sclera: highly specific
o Pharyngeal webs ® dysphagia
·
Diagnosis:
o Microcytic hypochromic anaemia: use MCV (not MCH – but highly
correlated)
o On film may see: target cells (haemoglobin in middle – non-specific),
pencil poikilocytes, platelets
o Lab findings: ¯serum ferritin (sufficient on it‟s own) – will also see ¯serum Fe
(but Serum Iron useless) and transferrin/ICP (Iron combining protein). Mean cell volume in normal
range may disguise a combination of small Fe deficient cells plus lots of large
reticulocytes
Related Topics