Chapter: 11th 12th std standard Political Science History goverment rule laws life Higher secondary school College Notes
Political Science : State and Government
State and Government:
Government is often used with the 'state' as synonym.
But both the government and the state are two different entities. There are differences between the state and the government.
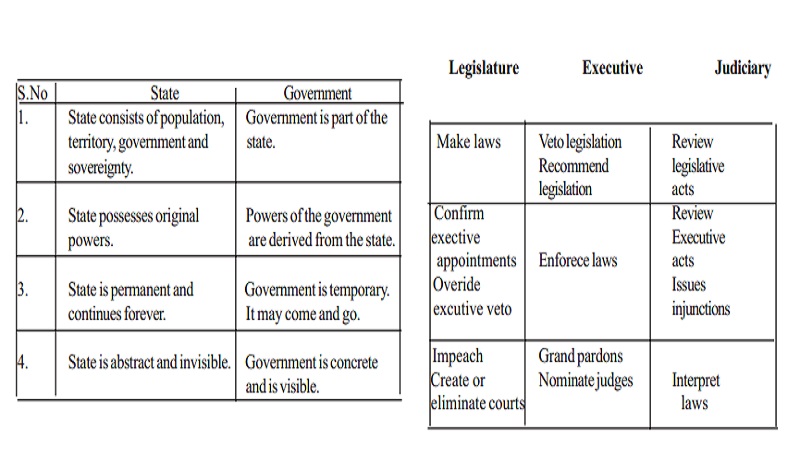
State
1. State consists of population, territory, government and sovereignty.
2. State possesses original powers.
3. State is permanent and continues forever.
4. State is abstract and invisible.
Government
1. Government is part of the state.
2. Powers of the government are derived from the state.
3. Government is temporary. It may come and go.
4. Government is concrete and is visible.
Branches of government
Legislature : Make laws
Executive : Veto legislation Recommend legislation
Judiciary : Review legislative acts
Legislature : Confirm exective appointments Overide excutive veto
Executive : Enforece laws
Judiciary : Review Executive acts Issues injunctions
Legislature : Impeach Create or eliminate courts
Executive : Grand pardons Nominate judges
Judiciary : Interpret laws
Executive:
It is one of the three branches of government as given
above.
State functions through the executive, the namely the government. It is the duty of the executive or enforce the laws passed by the legislature.
The executive who exercise real power is the real executive. The executive who has nominal power is the normal executive.
The President of India is the nominal executive. The union council of ministers led by the Prime Minister of India is the real executive.
Parliamentary executive is chosen from the legislature and is responsible to the legislature. The executive in India is parliamentary in its character.
Powers and functions of executive are :
1. Enforcing law
2. Maintaining peace and order.
3. Repelling aggression.
4. Building friendly relations with other states
5. When necessary to wage war to protect the country.
6. Making appointments to higher posts.
7. Raising money and spending them.
8. Convening the sessions of the legislature and conducting business.
9. Issues ordinances whenever the legislature is to in session.
10. Implement schemes and projects to improve he social and economic conditions of the people.
11. Power to grant pardon, reprieve or remission of punishment.
Legislature :
The legislature is the law making branch. The legislature has an important role in the amendment of the constitution. The legislature is a deliberative body where matters of social, economic and political concerns are discussed, debated and decided.
The British parliament is said to be 'the mother of parliaments'. It is the oldest legislature in the world.
According to Prof. Laski, law- making is not the only function of the legislature but its real function is to watch the process of administration to safeguard the liberties of private citizens. The legislature of the union is called the parliament in India. It consists of two chambers.
The House of the People or the Lok Sabha as the Lower House.
The Council of State or the Rajya Sabha as the Upper House
The functions of legislature are
a) Enact laws
b) Oversee administration
c) Pass the budget
d) Hear public grieveances.
e) Discuss subjects like
1) Development plans
2) National policies
3) International relations.
Judiciary:
Judiciary is the third important organ of the government machinery. Its main function is to interrupter laws and administer justice.
Lord Bryce has said that there is to better test of excellence of government than the efficiency of its judicial system.The welfare of citizens depends to a larger extent upon the judiciary.
Judiciary is one of the pillars of democracy. Its interpretation ensures justice, equality and liberty to all its citizens. An independent and impartial judiciary is an essential feature of a democratic setup.
The Supreme Court of India consists of a Chief Justice and other judges. The Supreme Court has its permanent seat in Delhi.
According to Justice Hughes, 'we are under a constitution, but the constitution is what the judges say it is'.
Functions of Judiciary:
1. Administration of justice.
2. To determine what is law and what is the cope and meaning of it.
3. To give advisory opinion on matters referred to it.
Related Topics