Real Numbers | Maths - Points to Remember | 9th Maths : UNIT 2 : Real Numbers
Chapter: 9th Maths : UNIT 2 : Real Numbers
Points to Remember
Maths: Real Numbers
Points to Remember
•
When the decimal expansion of p/q , q≠0 terminates that is, comes to an end,
the decimal is called a terminating decimal.
•
In the decimal expansion of p/q , q≠0
when the remainder is not zero, we have a repeating (recurring) block of digits
in the quotient. In this case, the decimal expansion is called non-terminating and
recurring.
•
If a rational number p/q , q≠0 can be
expressed in the form 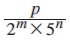 , where p ∈ Z and m, n ∈ W, then the rational number will have a terminating decimals.
Otherwise, the rational number will have a non-terminating repeating (recurring)
decimal.
, where p ∈ Z and m, n ∈ W, then the rational number will have a terminating decimals.
Otherwise, the rational number will have a non-terminating repeating (recurring)
decimal.
• A
rational number can be expressed either a terminating or a non- terminating recurring
decimal.
• An
irrational number is a non-terminating and non-recurring decimal, i.e. it cannot
be written in form p/q , where p and q are both integers and q ≠ 0.
• The
union of all rational numbers and all irrational numbers is called the set of real
numbers.
• Every
real number is either a rational number or an irratonal number.
• If
a real number is not rational number, then it must be an irrational number.
• If ‘a’
is a positive rational number, ‘n’ is a positive integer and if n√a
is an irrational number, then n√a
is called as a surd.
• If ‘m’, ‘n’ are positive integers and a, b are positive rational numbers, then
(i)
( n√a)n = a =
n√an (ii) n√a
× n√b = n√ab (iii) m√n√a = mn√a =
n√m√a (iv) n√a / n√a = n√[a/b]
•
The process of multiplying a surd by another surd to get a rational number is called
Rationalisation.
• Expressing
a number N in the form of N = a ×10n
where, 1 ≤ a < 10 and ‘n’ is an integer is called as Scientific Notation.
Related Topics