Presentation, Uses, Limitations - Organisational Chart | 12th Office Management and Secretaryship : Chapter 3 : Organising Function
Chapter: 12th Office Management and Secretaryship : Chapter 3 : Organising Function
Organisational Chart
Organisational Chart
Organisation
chart is the vital tool for providing information about organisational
relationships. Such a chart is a diagrammatical form which shows the major
functions and their respective relationships.
Organisation
charts can be divided into:
1. Master
Charts: The master chart shows the entire formal organisation structure.
2. Supplementary
Charts: The supplementary chart shows details of relationships, authority and
the duties within the prescribed area of a department or major component of the
organisation.
Presentation of Organisation Chart
There are
three ways in which organisation chart can be prepared
1. Vertical or
top - down chart
2. Horizontal
or left to right chart
3. Circular
Chart
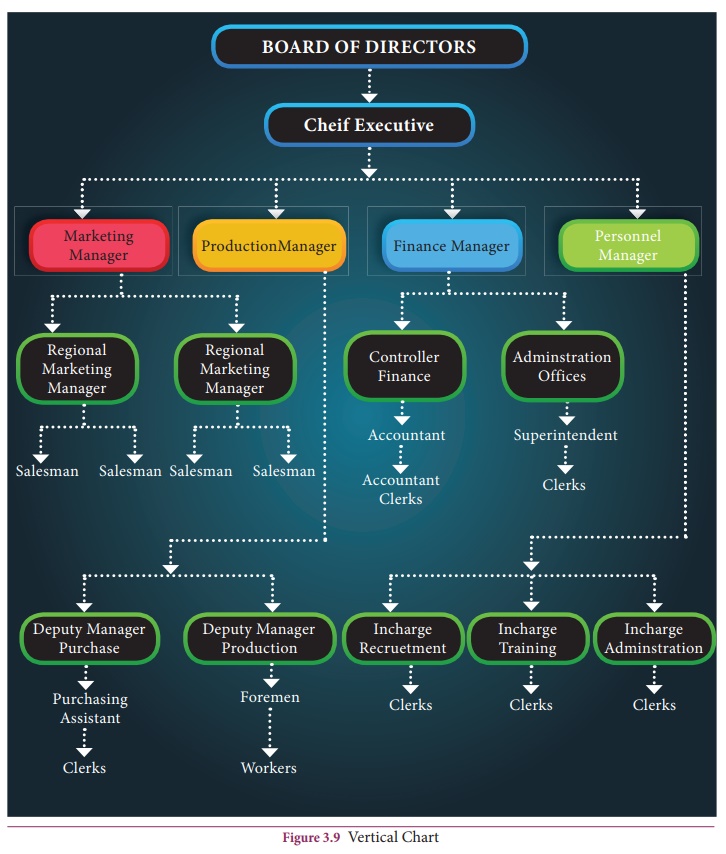
Vertical or top-down chart
In top down
chart, highest position is shown at the top level followed by other positions
in the hierarchy or management levels. Positions shown in the same horizontal
level in the chart can usually be considered to have the same relative
importance in the organisation.
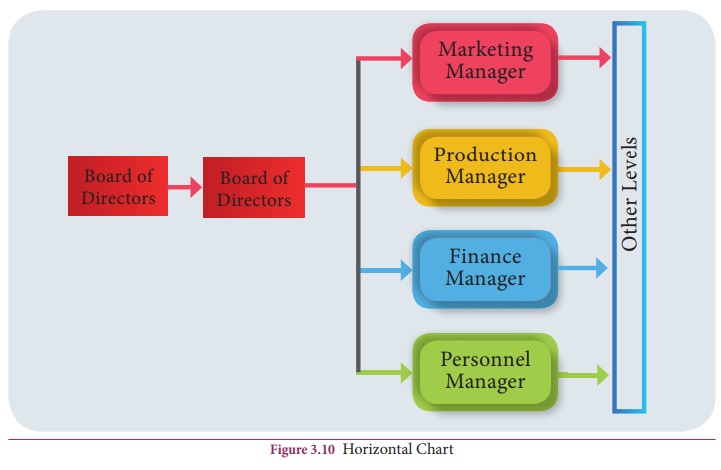
Horizontal or left to right chart
An
organisation chart can be drawn to show the highest to the lowest level reading
from left to right. In the left to right chart, organisational levels are
represented by vertical columns, the flow of authority from higher to lower
levels being represented by movement from left to right
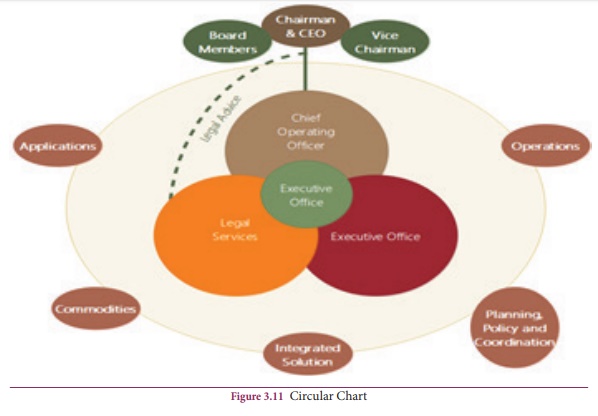
Circular Chart
The various
positions or functions of an organisation can be shown in circular form. In
this arrangement, centre of circle represents the position of supreme
authority. Functions and positions making up the organisation structure are
clustered around this centre in such a way that the closer the position of
function to the centre, the more important is the function. Positions of
relative equal importance are located at the same distance from the centre,
that is, on the same concentric circle. Lines joining the different blocks of
functions or positions indicate the channels of formal authority, the same as
in other arrangements.
Uses of Organisation Chart
Management Tool: Charts serve as tools by providing
the broad picture of authority and responsibility relationships. Thus, they
provide clarity in interactional pattern of the organisation.
Avoidance of Overlapping and Duplication: Charts are prepared after careful analysis of jobs and position requirements in the organisation. Primarily it ensures that all activities are covered properly by various positions and there is no duplication of activities. If there is any corrective action can be taken.
Secondly, it will bring out the
organisational weakness (very easily), if any. If anything is hampering,
measures can be taken to overcome that.
Solution of Organisational
Conflicts:
Many conflicts
of jurisdictional and procedural nature take place in the organisation either
because of misunderstanding or because of lack of authority and responsibility.
Such conflicts can be avoided with the help of organisation chart if it is
prepared carefully.
Training Guides: Organisational chart can be
used as an integral part of training. It prescribes what one is expected to do
in the organisation. It can also act as the information centre. It is also
helpful in pinpointing the type of training that a person should receive in
order to perform his task properly in the organisation.
References for Outsiders: With clarity of
authority and responsibility organisational chart serve as reference for
outsiders in dealing with the organisation. Outsiders who are strangers to the
organisation may know very easily with whom they have to interact for a
particular work.
Limitations of Organisational Chart
Organisational
charts have their own limitations and have to be used with certain precaution
1. Rigidity: Organisational
chart provides rigidity in the
organisational functioning. Since charts are in written forms frequent changes
that take place in an organisation can be reflected in the chart immediately
and it becomes outdated.
2. Partial View: Organisational chart represents only limited view of
the total organisation and its functioning. They show only official
relationship and procedures. Besides formal relationship certain informal
relationship also exists in an organisation which is not reflected in the
chart.
3. Inappropriate Description: Organisation
chart particularly provides description of authority. The exact quantum of
authority and responsibility is not shown by the chart. It merely depicts the
reporting relationships, who should report to whom. The organisation may equate
a personnel officer with production manager in terms of reporting relationships
but both may differ considerably in terms of salary, perquisites and authority.
4. Psychological Problems: Organisational
chart may create psychological problems among individuals in the organisation.
A chart puts people in superior or subordinate positions more prominently.
Therefore a feeling of superiority or inferiority may develop which may work
against the team spirit
Related Topics