Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Musculoskeletal Care Modalities
Nursing Process: Preoperative Care of the Patient Undergoing Orthopedic Surgery
NURSING PROCESS: PREOPERATIVE
CARE OF THE PATIENT UNDERGOING ORTHOPEDIC SURGERY
Assessment
Assessment of the
patient is focused on hydration status, current medication history, and
possible infection. Adequate hydration is an important goal for orthopedic
patients. Immobilization and bed rest contribute to DVT, to urinary stasis and
associated blad-der infections, and to kidney stone formation. Adequate
hydra-tion decreases blood viscosity and venous stasis and ensures adequate
urine flow. To determine preoperative hydration status, the nurse assesses the
skin and mucous membranes, vital signs, urinary output, and laboratory values.
The medication history provides information for perioperative management. The patient with chronic illness (eg, rheumatoid arthritis, chronic pulmonary disease, multiple sclerosis, allergies) frequently has received corticosteroid medications to control symptoms.
The corticosteroid should be administered preoperatively, intraoperatively, and postoperatively as
prescribed to pre-vent the occurrence of adrenal insufficiency from suppressed
adrenal function. The patient’s use of other medications, such as
anticoagulants, cardiovascular agents, or insulin, needs to be doc-umented and
discussed with the surgeon and anesthesiologist to ensure adequate management.
The nurse asks the patient specifically about the
occurrence of colds, dental problems, urinary tract infections, and other
infec-tions within the 2 weeks before surgery. Osteomyelitis could de-velop
through hematologous spread. Permanent disability can result if infection occurs
within a bone or joint. Preexisting infec-tions must be resolved before
elective orthopedic surgery is per-formed.
Other areas of preoperative assessment are similar to
those for any patient undergoing surgery. Intramuscular medications are
injected into an uninvolved area, because tissue absorption is bet-ter in
nontraumatized tissues.
Nursing Diagnosis
Based on the nursing assessment data, the patient’s major
preop-erative nursing diagnoses related to orthopedic status may include the
following:
·
Acute pain related to
fracture, orthopedic problem, swelling, or inflammation
·
Risk for peripheral
neurovascular dysfunction related to swelling, constricting devices, or
impaired venous return
·
Risk for ineffective
therapeutic regimen management re-lated to insufficient knowledge or lack of
available support and resources
·
Impaired physical mobility
related to pain, swelling, and possible presence of an immobilization device
·
Risk for situational low
self-esteem: disturbed body image and/or functional impairment related to
impact of musculo-skeletal disorder
Planning and Goals
The major goals for the patient before orthopedic surgery
may in-clude relief of pain, adequate neurovascular function, health
pro-motion, improved mobility, and positive self-esteem.
Nursing Interventions
RELIEVING PAIN
Physical, pharmacologic,
and psychological strategies to control pain are useful in the preoperative
period. Specific strategies are tailored to the individual patient. Discomfort
is decreased with immobilization of a fractured bone or an injured, inflamed
joint. Elevation of an edematous extremity promotes venous return and reduces
associated discomfort. Ice, if prescribed, relieves swelling and directly
reduces discomfort by diminishing nerve stimulation. Analgesics are frequently
prescribed to control the acute pain of musculoskeletal injury and associated
muscle spasm. During the immediate preoperative period, the nurse needs to
discuss and coordinate the administration of analgesic medications with the
anesthesiologist and surgeon. Alternative methods of pain control (eg,
distraction, focusing, guided im-agery, quiet environment, backrubs) may be
used to decrease pain perception.
MAINTAINING ADEQUATE NEUROVASCULAR FUNCTION
Trauma,
edema, or immobilization devices may interrupt tissue perfusion. The nurse must
frequently assess neurovascular status (ie, color, temperature, capillary
refill, pulses, edema, pain, sensation, motion) of the extremity and document
the findings. If circulation is compromised, the nurse institutes measures to
re-store adequate circulation. These include promptly notifying the physician,
elevating the extremity, and releasing constricting wraps or casts as
prescribed.
PROMOTING HEALTH
The nurse assists the patient in activities that promote
health dur-ing the perioperative period. The nurse assesses nutritional status
and hydration. The preoperative fasting regimen is usually toler-ated well. If
the patient has diabetes, is elderly and frail, or is the victim of multiple
trauma, special fluid and nutritional provisions may be necessary.
The nurse monitors fluid
intake, urinary output, urinalysis findings, and complaints of burning on
urination. At times, patients may limit their fluid intake to minimize the use
of a bed-pan. A small fracture pan may be more comfortable for the pa-tient to
use. An indwelling catheter should be used only when absolutely necessary to
minimize the risk of urinary tract infec-tion. Urinary tract infection must be
addressed before surgery.
Coughing, deep
breathing, and use of the incentive spirometer are practiced preoperatively for
improved respiratory function during the postoperative period. Preoperative
teaching facilitates postoperative compliance. Smoking should be stopped during
the preoperative period to facilitate optimal respiratory function.
The nurse provides skin
care, paying special attention to pres-sure points. It is important to
institute the use of pressure-reducing surfaces (i.e., special mattresses)
before surgery for patients at high risk for skin breakdown.
To minimize the risk for
infection, the nurse meticulously and gently cleans the skin with soap and
water on the day before surgery. If the surgery is elective, the orthopedic
surgeon may instruct the pa-tient to use a germicidal soap for several days
before hospitalization.
The nurse discusses with
the patient and the family the need for assistance with ADLs and the
therapeutic regimen during convalescence so that adequate support is available
when the pa-tient is discharged. Modification of the home environment may be
necessary to accommodate the altered mobility of the patient after surgery.
Referral to the social worker and the case manager may be needed to ensure a
smooth transition to home care.
IMPROVING MOBILITY
Preoperatively, the
patient’s mobility may be impaired by pain, swelling, and immobilizing devices
(eg, splints, casts, traction). The nurse should elevate and adequately support
edematous ex-tremities with pillows. It is important to control pain before an
in-jured part is moved by administering medication in time for it to take
effect and by supporting the injured part when it is moved. The nurse
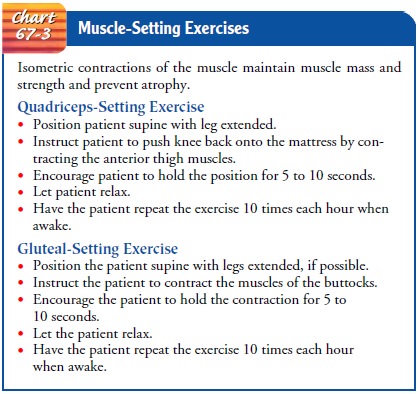
encourages movement within the limits of therapeutic immobility. The patient
should perform active range-of-motion exercises of uninvolved joints, and,
unless contraindicated, the nurse teaches gluteal-setting and
quadriceps-setting isometric exercises to maintain the muscles needed for
ambulation (see Chart 67-3). The patient who will be using assistive devices
post-operatively may exercise to strengthen the upper extremities and
shoulders. If the use of assistive devices (eg, crutches, walker, wheelchair)
is anticipated, the nurse encourages the patient to practice with them
preoperatively to facilitate their safe use and to promote earlier independent
mobility.
HELPING THE PATIENT MAINTAIN SELF-ESTEEM
Preoperatively,
orthopedic patients may need assistance in accept-ing changes in body image,
diminished self-esteem, or inability toperform their roles and
responsibilities. The degree of assistance re-quired in this area varies
greatly, depending on the events preceding hospitalization, the surgery and
rehabilitation planned, and the tem-porary or permanent nature of the problems.
The nurse promotes a trusting relationship for patients to express concerns and
anxieties and helps them examine their feelings about changes in self-concept.
The nurse clarifies any misconceptions patients may have and helps them work
through modifications needed to adapt to alterations in physical capacity and
to reestablish positive self-esteem.
Evaluation
EXPECTED PATIENT OUTCOMES
Expected patient outcomes may include:
1) Reports
relief of pain
a) Uses
multiple approaches to reduce pain
b) States
that medication is effective in relieving pain
c) Moves
with increasing comfort
2) Exhibits
adequate neurovascular function
a) Exhibits
normal skin color
b) Has
warm skin
c) Has
normal capillary refill response
d) Reports
normal sensation and demonstrates joint motion
e) Demonstrates
reduced swelling
3) Promotes
health
a) Eats
balanced diet appropriate to meet nutritional needs
b) Maintains
adequate hydration
c) Abstains
from smoking
d) Practices
respiratory exercises
e) Repositions
self to relieve skin pressure
f) Engages
in strengthening and preventive exercises
g) Plans
for assistance during convalescence at home
4) Maximizes
mobility within the therapeutic limits
a) Requests
assistance when moving
b) Elevates
edematous extremity after transfer
c) Uses
immobilizing devices and assistive devices as pre-scribed
5) Expresses
positive self-esteem
a) Acknowledges
temporary or permanent changes in body image
b) Discusses
role performance changes
c) Participates
in decisions about care
Related Topics