Neutropenia is defined as a decrease in the blood neutrophil count below 1.5 Ă— 109/ L. In some racial groups (e.g., Africans), the normal neutrophil count is somewhat lower (up to 1.2 Ă— 109/L).
Neutropenia
Neutropenia is defined as a decrease in the blood neutrophil count below 1.5 Ă— 109/ L. In some racial groups (e.g., Africans), the normal neutrophil count is somewhat lower (up to 1.2 Ă— 109/L). While mild neu-tropnia may be asymptomatic, severe neu-tropenia (counts < 0.5 Ă— 109/L) is invariably associated with the risk of life-threatening microbal sepsis caused by a broad range of endogenous Gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus) and Gram-negative bacteria (E. coli, Pseudomonas spp., Klebsiella spp.) as well as fungi (Candida). Neutrophils are particu-larly important for maintaining the integ-rity of mucous membranes. Hence, oral ulceration and perianal inflammation can be features of severe neutropenia. Causes of neutropenia are summarized in Table 5.7.
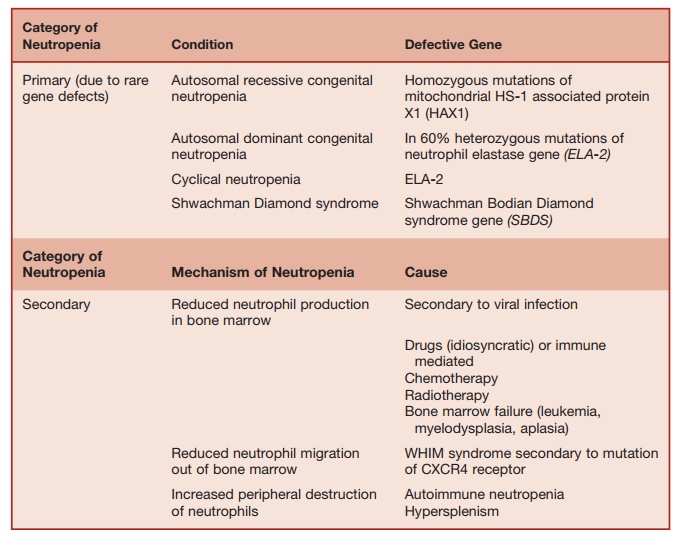
Table 5.7 Causes of Neutropenia
Study Material, Lecturing Notes, Assignment, Reference, Wiki description explanation, brief detail
Essential Clinical Immunology: Immunological Aspects of Immunodeficiency Diseases : Neutropenia - Phagocyte Deficiencies |
