Chapter: Essential Clinical Immunology: Immunological Aspects of Immunodeficiency Diseases
Major Categories of Combined Immunodeficiency
Major Categories of Combined Immunodeficiency
SEVERE COMBINED IMMUNODEFICIENCY
SCID comprises a group of inherited diseases characterized by a severe defi-cit in T-cell development and function with variable defects in B-cell and natural killer or NK cell development. SCID leads to death within the first two years of life, unless patients are rescued by hemato-poietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). These are rare disorders with an estimated frequency between 1 in 50,000 and 1 in 100,000 live births.
Classification of SCID
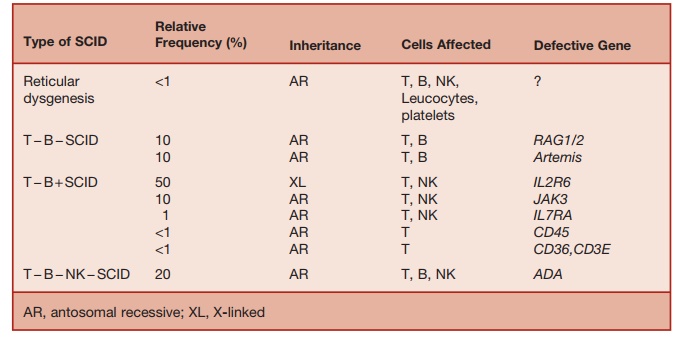
The classification of SCID, based on immunological and genetic criteria, is sum-marized in Table 5.6.
Table 5.6 Classification of SCID
SCID: Clinical Features
These patients typically present in the first year of life with failure to thrive and recurrent infections caused by bacterial, viral, and fungal pathogens. Infections typically affect the respiratory and gas-trointestinal systems. The infections may be caused by common pathogens (adenovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza virus), as well as by opportunistic organisms of low-grade virulence (Candida, Pneumocystis carinii, cytomegalovirus). Live vaccines such as BCG can lead to disseminated life-threat-ening infections. The persistent infections developing in SCID patients rapidly lead to malnutrition, growth impairment, and early death. Because of the patient’s inability to reject allogeneic cells, graft-versus-host disease (GvHD) can be caused by transplacentally acquired maternal lymphocytes or by allogeneic cells following blood transfusion. GvHD manifests as skin rashes or hepatospleno-megaly and lymphadenopathy.
The absence of tonsils or other lymphatic tissue may be evident and radiographic studies may reveal thymic-hypoplasia. Lymphopenia (absolute lymphocyte count < 3 Ă— 109/L in the first year of life) is a char-acteristic feature seen in over 80 percent of patients with SCID. (Therefore, SCID needs to be excluded in any infant with unexplained lymphopenia.)
Related Topics