Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: Senses
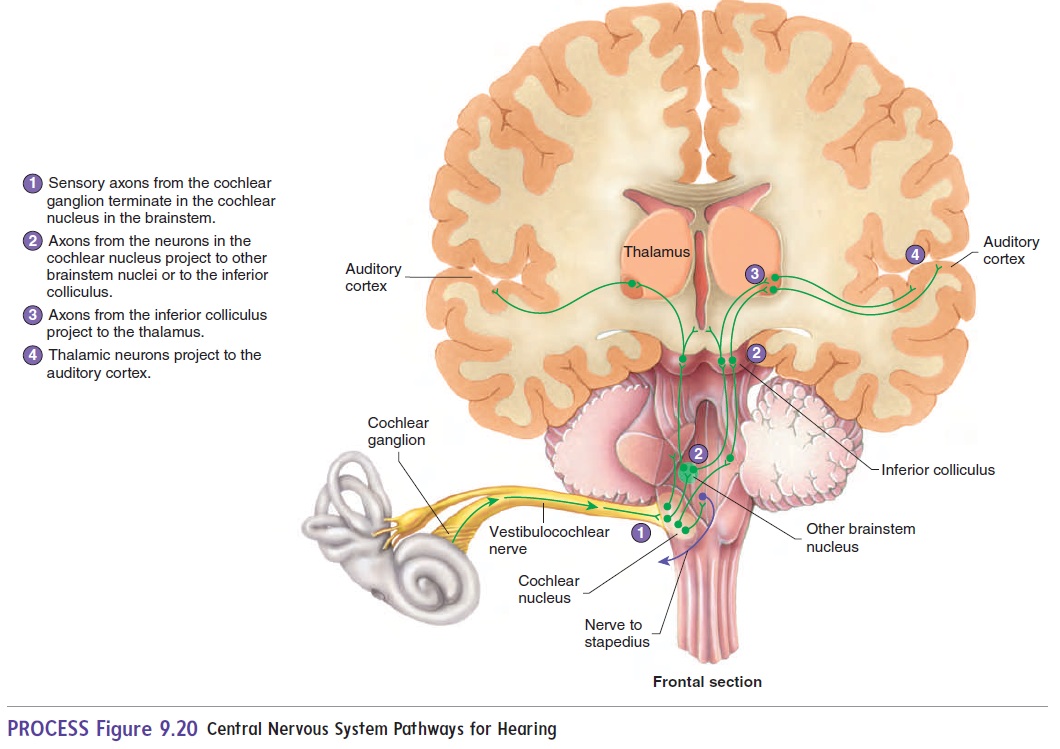
Neuronal Pathways for Hearing
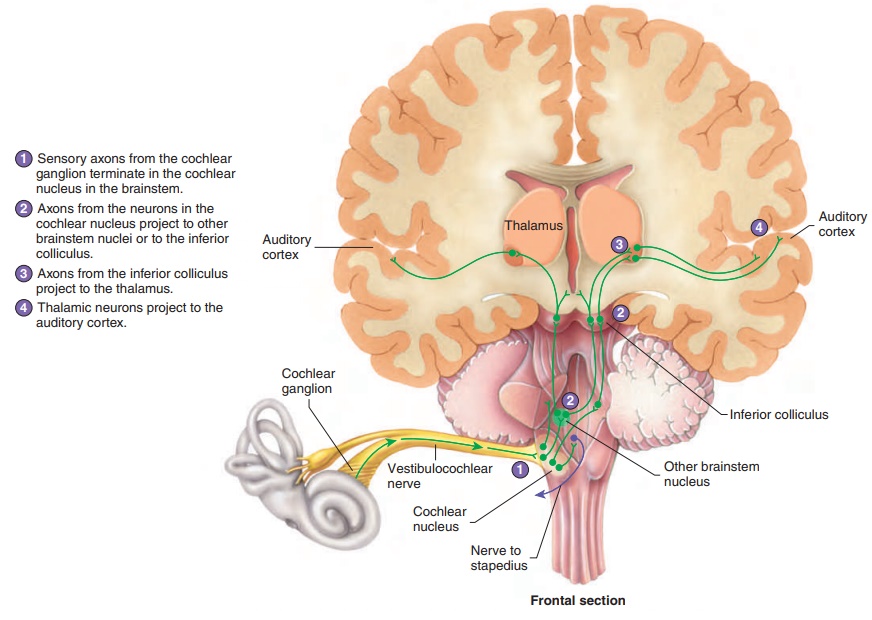
Neuronal Pathways for Hearing
The senses of hearing and balance are both transmitted by the vestib-ulocochlear nerve (VIII). This nerve functions as two separate nerves, carrying information from two separate but closely related structures. The cochlear nerve is the portion of the vestibulocochlear nerve involved in hearing; the vestibular nerve is involved in balance. The cochlear nerve sends axons to thecochlear nucleus in the brainstem. Neurons in the cochlear nucleus project to other areas of the brain-stem and to the inferior colliculus in the midbrain. Neurons from the inferior colliculus also project to the superior colliculus, where reflexes that turn the head and eyes in response to loud sounds are initiated. From the inferior colliculus, fibers project to the thalamus and from there to the auditory cortex of the cerebrum (figure 9.20).
Related Topics