Zoology - Molecular Genetics: Summary | 12th Zoology : Chapter 5 : Molecular Genetics
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 5 : Molecular Genetics
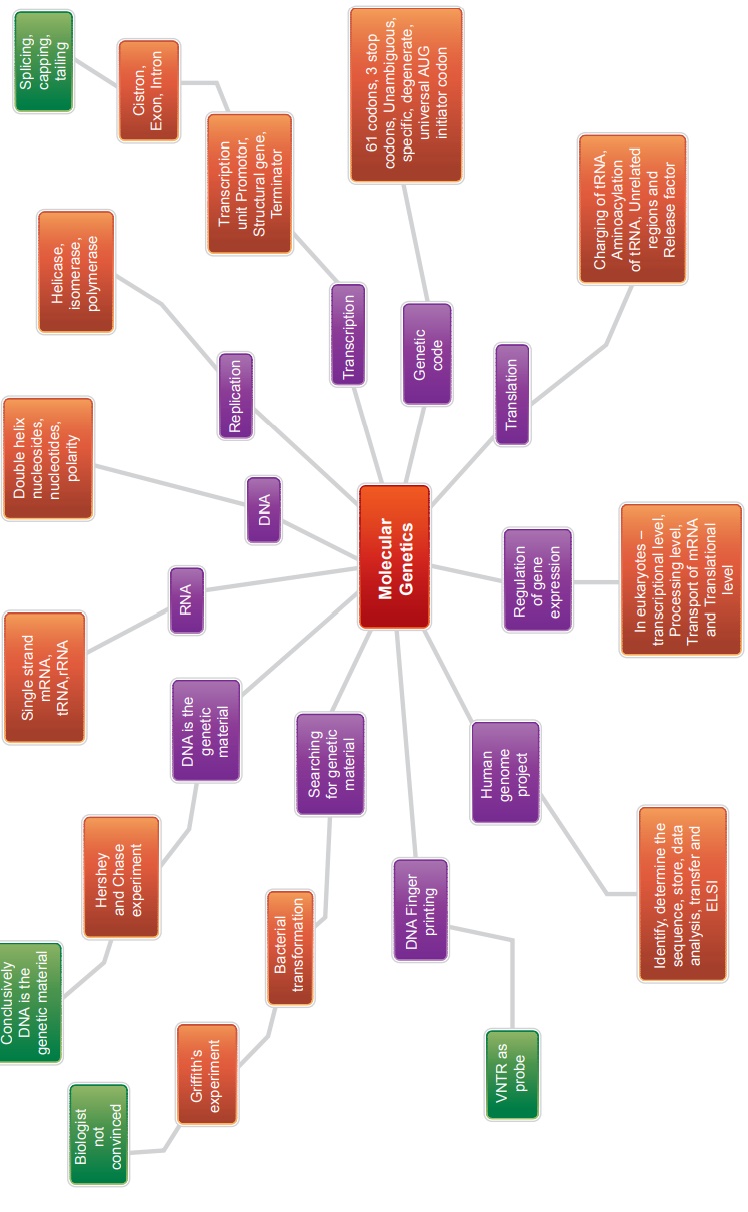
Molecular Genetics: Summary
Summary
In the twentieth
century, one of the landmark discovery in biology was the identification of
DNA, as genetic material of living organisms. Gene may be defined as a segment
of DNA which is responsible for inheritance and expression of a particular
character.
In 1953, James Watson
and Francis Crick proposed DNA structure based on X-ray crystallographic
studies provided by Maurice Wilkins and Rosalind Franklin. Nucleotides are the
structural units of nucleic acids. Each nucleotide has three components, i)
pentose sugar ii) nitrogenous base and iii) phosphate. DNA and RNA are
polynucleotides. DNA has double stranded helical structure while RNA is a
single stranded structure. DNA acts as genetic material of almost all the
living organism except few viruses.
The non genetic RNAs are
of three types; m-RNA, r-RNA and t-RNA. They help in protein synthesis. DNA has
capacity of replication, while the three types of RNA are transcribed on DNA.
Meselson and Stahl (1958) proved experimentally the semi-conservative nature of
DNA replication using heavy isotope of nitrogen N15 in E.coli.
In 1958 Crick proposed
that DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide (protein)
through mRNA, and proposed the central dogma of protein synthesis which
involves transcription and translation. The process of copying genetic
information from one strand of DNA into RNA is termed transcription. The DNA
transcribed RNA molecules serve as a template for the synthesis of polypeptides
by a process termed translation. Each amino acid in a polypeptide chain is
represented by a sequence of three nucleotides in the RNA known as the genetic
code. RNA transfers genetic message from nucleus to the cytoplasm. DNA is
always present in the nucleus and synthesis is also confined to the nucleus
Jacob and Monod proposed
the classical model of Lac operon to explain gene expression and regulation in
E. coli. In lac operon a polycistronic structural gene is regulated by a common
promoter and regulator. It is an example of negative control of transcription
initiation.
Human genome project, a mega project was aimed to sequence every gene in the human genome. Polymerase chain reaction is an in vitro method of synthesis of nucleic acids wherein, a specific DNA segment is amplified rapidly without concomitant replication of the rest of the DNA molecule. DNA fingerprinting is a technique to identify variations in individuals of a population at the DNA level. It has immense applications in the field of forensic analysis, pedigree analysis, anthropological studies, and conservation of wild life.
Related Topics