Book Back Important Questions Answers | Choose the Correct Answers | Short, brief Answers | Zoology - Molecular Genetics: Questions and Answers (Evaluation) | 12th Zoology : Chapter 5 : Molecular Genetics
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 5 : Molecular Genetics
Molecular Genetics: Questions and Answers (Evaluation)
Evaluation
1. Hershey and Chase experiment with bacteriophage showed that
a) Protein gets into the bacterial cells
b) DNA is the genetic material
c) DNA contains radioactive sulphur
d) Viruses undergo transformation
Answer: b) DNA is the
genetic material
2. DNA and RNA are similar with respect to
a) Thymine as a nitrogen base
b) A single-stranded helix shape
c) Nucleotide containing sugars, nitrogen bases and phosphates
d) The same sequence of nucleotides for the amino acid phenyl alanine
Answer: c) Nucleotide
containing sugars, nitrogen bases and phosphates
3. A mRNA molecule is produced by
a) Replication
b) Transcription
c) Duplication
d) Translation
Answer: b)
Transcription
4. The total number of nitrogenous bases in human genome is estimated to be about
a) 3.5 million
b) 35000
c) 35 million
d) 3.1 billion
d) 3.1 billion
5. E. coli cell grown on 15N medium are transferred to 14N medium and allowed to grow for two generations. DNA extracted from these cells is ultra centrifuged in a cesium chloride density gradient. What density distribution of DNA would you expect in this experiment?
(a) One high and one low density band.
(b) One intermediate density band.
(c) One high and one intermediate density band.
(d) One low and one intermediate density band.
Answer: d) One low
and one intermediate density band
6. What is the basis for the difference in the synthesis of the leading and lagging strand of DNA molecules?
(a) Origin of replication occurs only at the 5' end of the molecules.
(b) DNA ligase works only in the 3' → 5' direction.
(c) DNA polymerase can join new nucleotides only to the 3' end of the growing stand.
(d) Helicases and single-strand binding proteins that work at the 5' end.
Answer: c) DNA
polymerase can join new nucleotides only to the 3' end of the growing stand
7. Which of the following is the correct sequence of event with reference to the central dogma?
(a) Transcription, Translation, Replication
(b) Transcription, Replication, Translation
(c) Duplication, Translation, Transcription
(d) Replication, Transcription, Translation
Answer: d)
Replication, Transcription, Translation
8. Which of the following statements about DNA replication is not correct?
(a) Unwinding of DNA molecule occurs as hydrogen bonds break.
(b) Replication occurs as each base is paired with another exactly like it.
(c) Process is known as semi conservative replication because one old strand is conserved in the new molecule.
(d) Complementary base pairs are held together with hydrogen bonds.
Answer: b)
Replication occurs as each base is paired with another exactly like it
9. Which of the following statements is not true about DNA replication in eukaryotes?
(a) Replication begins at a single origin of replication.
(b) Replication is bidirectional from the origins.
(c) Replication occurs at about 1 million base pairs per minute.
(d) There are numerous different bacterial chromosomes, with replication ocurring in each at the same time.
Answer: d) These are
numerous different bacterial chromosomes, with replication occurring in each at
the same time.
10. The first codon to be deciphered was UUU which codes for Phenylalanine.
(a) AAA, proline
(b) GGG, alanine
(c) UUU, Phenylalanine
(d)TTT, arginine
11. Meselson and Stahl’s experiment proved
(a)Transduction
(b) Transformation
(c) DNA is the genetic material
(d) Semi-conservative nature of DNA replication
Answer: d) Semi-conservative nature of DNA replication
12. Ribosomes are composed of two subunits; the smaller subunit of a ribosome has a binding site for mRNA and the larger subunit has two binding sites for two tRNA. Ans (mRNA, tRNA)
13. An operon is a:
(a) Protein that suppresses gene expression
(b) Protein that accelerates gene expression
(c) Cluster of structural genes with related function
(d) Gene that switched other genes on or off
Answer: c) Cluster of
structural genes with related function
14. When lactose is present in the culture medium:
(a) Transcription of lac y, lac z, lac a genes occurs.
(b) Repressor is unable to bind to the operator.
(c) Repressor is able to bind to the operator.
(d) Both (a) and (b) are correct.
Answer: d) Both (a) and (b) are correct
15. Give reasons: Genetic code is ‘universal’.
• The genetic code is nearly universal.
• Almost all living
organisms use nucleic acids and the
particular triplet codon code for
the same amino acid in the synthesis of protein.
• Eg - In the mRNA UUU
codon codes for phenyl alanine in all
cells of all living organisms.
• Exceptions to genetic code
1. Prokaryotes
2. Mitochondrial / Chloroplast genomes
• However have more similarities than differences.
16. Name the parts marked ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the given transcription unit:
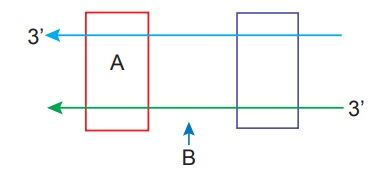
A - Promoter
B - Coding strand.
17. Differentiate - Leading stand and lagging strand
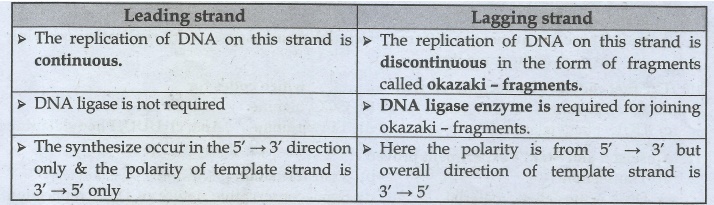
Leading strand
• The replication of DNA
on this strand is continuous.
• DNA ligase is not
required
• The synthesize occur
in the 5' → 3' direction only & the polarity of template strand is 3' → 5' only
Lagging strand
• The replication of DNA
on this strand is discontinuous in the form of fragments called okazaki
- fragments.
• DNA ligase enzyme is required for
joining okazaki - fragments.
• Here the polarity is
from 5' → 3' but overall direction of template strand is 3' → 5'
18. Differentiate - Template strand and coding strand.

Template strand
• It act as a template
for synthesis of mRNA.
• It has a sequence
complementary to the mRNA.
• It runs in 3' → 5'
direction or polarity.
Coding strand
• It does not act as
template.
• It has a sequence
similar to the mRNA.
• It runs from 5' → 3'
direction or polarity
19. Mention any two ways in which single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs) identified in human genome can bring revolutionary change in biological and medical science.
• Scientists have
identified 1.4 million locations in Human Genome, where SNP occur.
• This findings will
bring in biological & medical science revolutionary changes.
• It helps to
understand, predict certain diseases (Sickle cell anaemia, B thalassemia,
Cystic fibrosis etc)
• It also helps to
predict an individuals response to certain drugs, susceptibility to
environmental factors such as toxins etc.
20. State any three goals of the human genome project.
• The main goals of HGP.
• Identifying all the genes (approximately 30,000) of human DNA.
• Determining the sequence of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that
make up the human DNA.
• To store these informations in data bases & improve Tools for
data analysis.
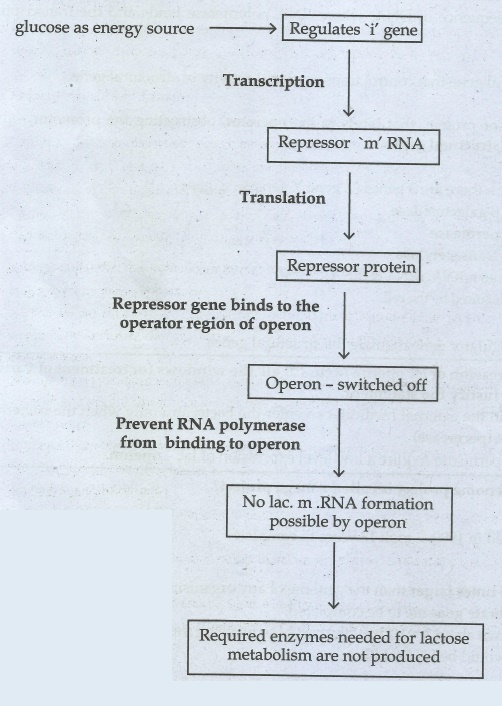
21. In E.coli, three enzymes β- galactosidase, permease and transacetylase are produced in the presence of lactose. Explain why the enzymes are not synthesized in the absence of lactose.
In the Absence of lactose,
22. Distinguish between structural gene, regulatory gene and operator gene.
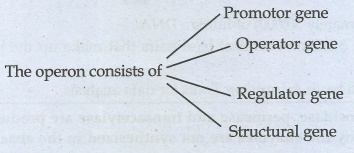
Promotor gene
• All other genes -
under the control of promoter.
• They are signal
sequence of DNA, where RNA polymerase binds and the transcription begins.
Operator gene
Adjacent to structural
gene that control transcriptional activity of structural gene.
Regulator gene
Codes for a repressor
protein, that binds to the operator,
obstructing the promotor - thus transcription of the structural genes.
Structural gene
• It is polycistronic -
there are 3 genes (Z gene Y gene & 'a' gene)
• Z gene codes for β galactosidase
• Y gene codes for permease
• A gene codes for transacetylase
• It get transcribed
into mRNA, rRNA & tRNA encodes proteins required by the cell
Conclusion
The promoter &
Regulator gene regulate the structural genes.
23. A low level of expression of lac operon occurs at all the windows for treatment of various genetic disorders. Justify the statement.
• Lactose present in the
external medium can enter the bacterium only when the bacterium contain the
enzyme (permease)
• So, formation of permease
require a low level expression of lac -
operon.
24. Why the human genome project is called a mega project?
Time
HGP – was launched in
1990 & took 13 years to complete.
Size
• HG – is about 25
times larger than the genome of any organism sequenced.
• It is the 1st
vertebrate genome to be completed.
• HG – is said to have
about 3 × 109 bp – the
cost of sequencing this in US $ per bp – is 3 dollors & the total cost
would be US $ 9 billion.
Data Storage & Retrieval
• The data need atleast
3300 books (1000 letters & 1000 pages in each book) to store the complete
information of DNA sequence from a single human cell.
• We need high speed
computing devices for storage, retrieval & analysis.
Bio informatics
A new area in biology
encompasses the application of computing science & technology to analyse
and manage the biological data.
25. From their examination of the structure of DNA, What did Watson and Crick infer about the probable mechanism of DNA replication, coding capability and mutation?
Watson & Crick, from their examination of the structure of DNA (DNA -
model) - inferred that DNA replication was semi
conservative replication.
• The two polynucleotide
strands of DNA - unwind and start separating at one end breaking the covalent
hydrogen bond.
• The separated single
strand act as template for the
synthesis of a new strand.
• Daughter double helix
|→ One polynucleotide strand (parental)
|→ another polynucleotide strand (newly synthesised)
• The two strands are complementary to each other.
26. Why tRNA is called an adapter molecule?
• Francis Crick - postulated this term.
• tRNA, - molecule of a cell acts as a vehicle that reads the
specific codes of mRNA molecules & intum picks up the specific amino acid, according to the specific code - (from the
amino acids scattered in the cytoplasm)
• Hence t-RNA is also
known as Adapter molecule.
27. What are the three structural differences between RNA and DNA?
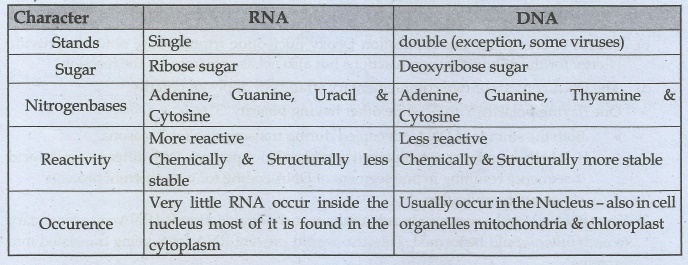
RNA:
Stands: Single
Sugar: Ribose sugar
Nitrogenbases: Adenine, Guanine, Uracil & Cytosine
Reactivity: More reactive Chemically & Structurally less stable
Occurence: Very little RNA occur inside the nucleus most of it is
found in the cytoplasm
DNA
Stands: double (exception, some viruses)
Sugar: Deoxyribose sugar
Nitrogenbases: Adenine, Guanine, Thyamine & Cytosine
Reactivity: Less reactive Chemically & Structurally more stable
Occurence: Usually occur in the Nucleus - also in cell organelles
mitochondria & chloroplast
28. Name the anticodon required to recognize the following codons: AAU, CGA, UAU, and GCA.
Codons 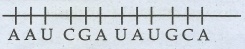
Anti codon UUA GCU AUA CGU
29. a) Identify the figure given below
b) Redraw the structure as a replicating fork and label the parts
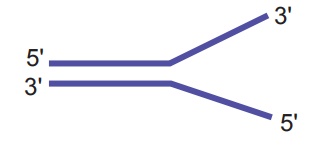
c) Write the source of energy for this replication and name the enzyme involved in this process.
d) Mention the differences in the synthesis of protein, based on the polarity of the two template strands.
a) Mechanism of
Replication, showing a Replication fork
b) 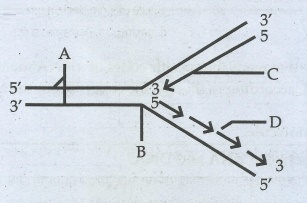
Answer: A - Template
Stands
B - Replication Fork
C - Leading strand
D - Lagging Strand
c) Source of energy
for this replication Deoxy nucleotide triphosphate not only provide
energy for the polymerization reactions but also act as substrate for
the reaction.
d) The DNA consists of
two complementary strands of opposite polarity.
One having polarity 5'
to 3' while other having polarity 3' to 5'.
• Both the strands of
DNA not copied during transcription for 2 reasons.
1) If both strands act
as template it would code for proteins with different amino acid sequence
resulting in one segment of DNA coding for two different proteins - create
complication.
2) If two RNA molecules
were produced simultaneously, double stranded RNA complementary to each other
would be formed. This also would prevent RNA from being translated into
proteins.
30. If the coding sequence in a transcription unit is written as follows:
5' TGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGCATGC 3'
Write down the sequence of mRNA.
Answer:

31. How is the two stage process of protein synthesis advantageous?
Yes, The synthesis of
proteins takes place in two steps
|→ Transcription &
|→ Translation
• Francis Crick - proposed the Central
dogma in molecular biology
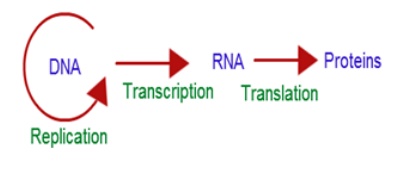
I - stage - Transcription
The information
encoded in DNA should be transcribed into mRNA
II - stage - Translation
The encodes
information in mRNA heads out of the cells nucleus and into the cytoplasm &
The Translation machinery work here, with rRNA, mRNA, tRNA & various
enzymes so, the two stage - process is essential & it is advantageous too.
32.Why did Hershey and Chase use radioactively labelled phosphorous and sulphur only? Would they have got the same result if they use radiolabelled carbon and nitrogen?
I. - Radio actively labelled carbon
If Hershey & Chase
would have used radio labelled carbon - it would be found in all components of
bacteria.
• Carbon is found in all organic molecules
II. - Radio actively labelled Nitrogen
If they had used radio
actively labelled Nitrogen, they would have seen that all the cells would be
labelled in the nucleolus, in the
membrane and through out the cell, also the multiplied numerous components of phage,
would be also labelled -
• Nitrogen is found in proteins & DNA, so Hershey & Chase
wisely used radio actively labelled phosphorus
(component of nucleic acids) and sulphur
(component of proteins) in their experiment.
33. Explain the formation of a nucleosome.
I. • Chromosome
is made up of chromatin.
• Chromatin is formed of a series
of repeated units called Nucleosomes.
Kornberg's model for
the nucleosome
• In this 2 molecules of
four histone proteins H2 A, H2 B, H3 & H4 are organised to form a unit of 8
molecules called Histone octomer.
• The negatively
charged DNA is wrapped around the positively charged histone octomer
to form a structure called nucleosome.
• A typical nucleosome
contain 200 bp of DNA helix.
• DNA connecting two
adjacent nucleosome are called linker DNA, (H1) exposed to
enzymes
II. • The DNA makes two
complete turns around the histone octomer, and sealed off by an H1
molecule.
• Chromatin lacking H1-,
nucleosomes are thread like stained bodies present in Nucleus (look like beads
on a string - (under EM)
• H1 of one nucleosome can
interact with H1 of another - resulting in further folding of the Chromatin
fibre.
• The Chromatin is packed to form a solenoid
structure of 30 nm diameter (having six nucleosome per turn)
• Stabilized by
interaction between different H1 molecules.
• DNA - is a solenoid
& packed about 40 folds.
• This further
supercoils & forms chromatin fibre.
• Chromatin fibre → Further coils &
condenses to form chromatids.
• Chromatids → Further condenses
at metaphase stage of cell division to form chromosomes.
III. NHC - Proteins
• The Non histone
chromosomal proteins are required for a higher level packaging.
Euchromatin - regions of
chromatin loosely packed and transcriptionally active.
Hetero chromatin - regions of
chromatin densely packed (Stained darkly), and
transcriptionally in active.
34. It is established that RNA is the first genetic material. Justify giving reasons.
Amount: A typical cell contains, about ten times as
much as RNA as DNA
Various roles : Through various researchers the essential life processes
such as metabolism, translator splicing
etc.
Evidences : • Frankel - Conrat &
Singer (1957)
Said RNA - the genetic
material in TMV - and separated it from the protein of TMV virus.
• Leslie Orgel, Francis Brick & Carl Woese, these three
Molecular biologists
(1980s) - proposed RNA world - as
the first stage in evolution of life - when RNA catalysed all molecules
necessary for survival &
replication.
• Walter Gilbert (1986) - First used the term RNA World
• RNA has ability act as
|→ Genetic material
|→ Catalyst
• Catalytic RNA - is ribozyme
• RNA, being a catalyst was reactive & hence unstable
• DNA has evolved from RNA - with chemical modifications.
Related Topics