Chapter: Medical Physiology: Pregnancy and Lactation
Milk Composition and the Metabolic Drain on the Mother Caused by Lactation
Milk Composition and the Metabolic Drain on the Mother Caused by Lactation
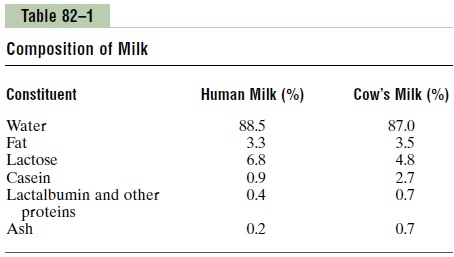
Table 82–1 lists the contents of human milk and cow’s milk. The concentration of lactose in human milk is about 50 per cent greater than in cow’s milk, but the concentration of protein in cow’s milk is ordinarily two or more times greater than in human milk. Finally, only one third as much ash, which contains calcium and other minerals, is found in human milk compared with cow’s milk.
At the height of lactation in the human mother, 1.5 liters of milk may be formed each day (and even more if the mother has twins). With this degree of lactation, great quantities of metabolic substrates are drained from the mother. For instance, about 50 grams of fat enter the milk each day, and about 100 grams of lactose, which must be derived by conversion from the mother’s glucose. Also, 2 to 3 grams of calcium phos-phate may be lost each day; unless the mother is drink-ing large quantities of milk and has an adequate intake of vitamin D, the output of calcium and phosphate by the lactating mammae will often be much greater than the intake of these substances. To supply the needed calcium and phosphate, the parathyroid glands enlarge greatly, and the bones become progressively decalci-fied. The mother’s bone decalcification is usually not a big problem during pregnancy, but it can become more important during lactation.
Antibodies and Other Anti-infectious Agents in Milk. Not onlydoes milk provide the newborn baby with needed nutrients, but it also provides important protection against infection. For instance, multiple types of anti-bodies and other anti-infectious agents are secreted inmilk along with the nutrients. Also, several different types of white blood cells are secreted, including both neutrophils andmacrophages, some of which are especially lethal to bacteria that could cause deadly infections in newborn babies. Particularly important are antibodies and macrophages that destroy Escherichia coli bacteria, which often cause lethal diar-rhea in newborns.
When cow’s milk is used to supply nutrition for the baby in place of mother’s milk, the protective agents in it are usually of little value because they are normally destroyed within minutes in the internal environment of the human being.
Related Topics