Chapter: Medical Physiology: Pregnancy and Lactation
Ejection (or ŌĆ£Let-DownŌĆØ) Process in Milk Secretion-Function of Oxytocin
Ejection (or ŌĆ£Let-DownŌĆØ) Process in Milk Secretion-Function of Oxytocin
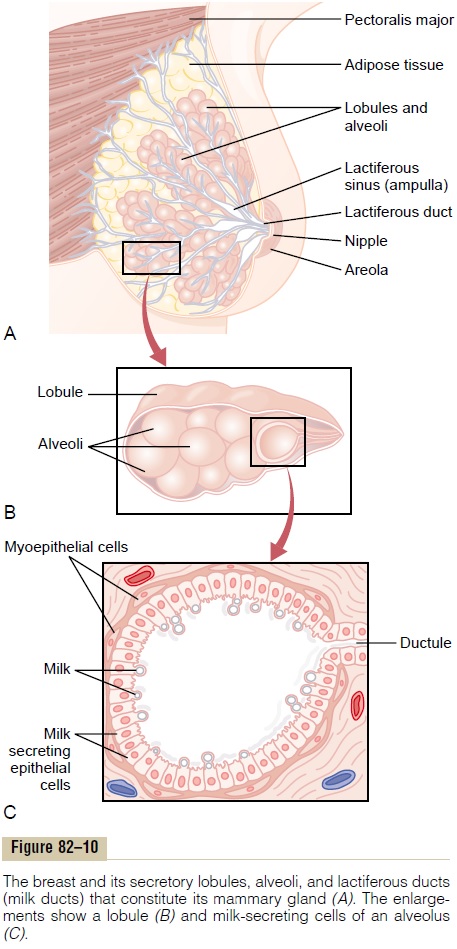
Milk is secreted continuously into the alveoli of the breasts, but milk does not flow easily from the alveoli into the ductal system and, therefore, does not contin-ually leak from the breast nipples. Instead, the milk must be ejected from the alveoli into the ducts before the baby can obtain it. This is caused by a combined neurogenic and hormonal reflex that involves the posterior pituitary hormoneoxytocin, as follows.
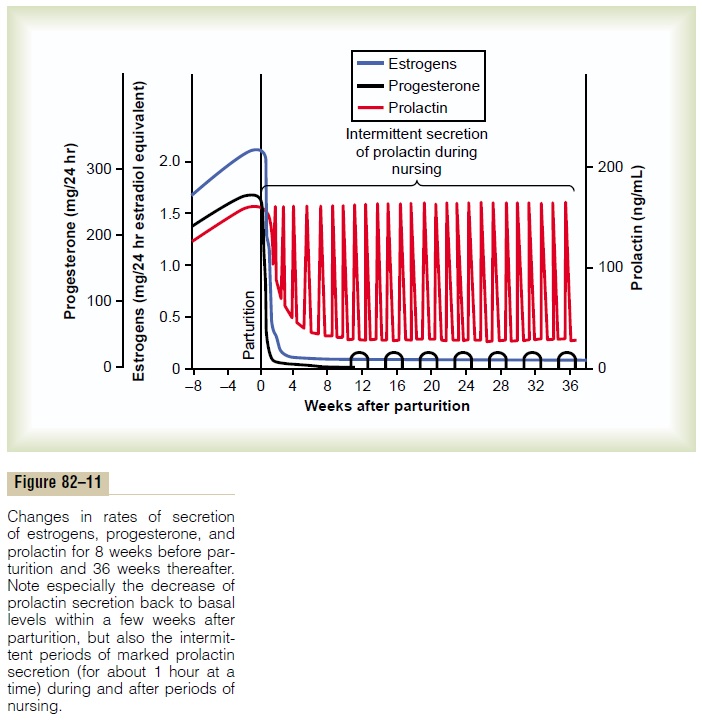
When the baby suckles, it receives virtually no milk for the first half minute or so. Sensory impulses must first be transmitted through somatic nerves from the nipples to the motherŌĆÖs spinal cord and then to her hypothalamus, where they cause nerve signals that promote oxytocin secretion at the same time that they cause prolactin secretion.The oxytocin is carried in the blood to the breasts, where it causes myoepithelial cells (which surround the outer walls of the alveoli) to con-tract, thereby expressing the milk from the alveoli into the ducts at a pressure of +10 to 20 mm Hg. Then the babyŌĆÖs suckling becomes effective in removing the milk. Thus, within 30 seconds to 1 minute after a baby begins to suckle, milk begins to flow. This process is called milk ejection or milk let-down.
Suckling on one breast causes milk flow not only in that breast but also in the opposite breast. It is espe-cially interesting that fondling of the baby by the mother or hearing the baby crying often gives enough of an emotional signal to the hypothalamus to cause milk ejection.
Inhibition of Milk Ejection. A particular problem innursing a baby comes from the fact that many psy-chogenic factors or even generalized sympathetic nervous system stimulation throughout the motherŌĆÖs
body can inhibit oxytocin secretion and consequently depress milk ejection. For this reason, many mothers must have an undisturbed puerperium if they are to be successful in nursing their babies.
Related Topics